Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) presents the greatest number of identified therapeutic targets, some of which have therapeutic utility. Currently, detecting EGFR, BRAF, KRAS and MET mutations, ALK, ROS1, NTRK and RET translocations, and PD-L1 expression in these patients is considered essential. The use of next-generation sequencing facilitates precise molecular diagnosis and allows the detection of other emerging mutations, such as the HER2 mutation and predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy responses. In this consensus, a group of experts in the diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC selected by the Spanish Society of Pathology and the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology have evaluated currently available information and propose a series of recommendations to optimize the detection and use of biomarkers in daily clinical practice.
Keywords: ALK, Biomarkers, BRAF, EGFR, Non-small cell lung cancer, PD-L1, ROS1
Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a group of tumours with the greatest number of identified therapeutic targets, some of which have clinical utility from the earliest stages. Undoubtedly, providing the correct molecular diagnosis is required to offer the best therapeutic option to each patient, which should be applied as widely as possible. Fortunately, in recent years, important advances in both molecular diagnostic techniques and personalized therapies have been achieved. This document aims to offer new recommendations for the detection of predictive biomarkers of NSCLC and will be an update to those already published in 2012, 2015 and 2020 as a result of this consensus between the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology (SEOM) and the Spanish Society of Pathology (SEAP) [1].
Requirements for the analysis of an optimal biological sample
Several types of samples can be useful for the study of biomarkers, such as biopsies, surgical specimens and/or cytology, as long as they contain a sufficient number of tumour cells and have been correctly processed [2, 3]. The decision about which one to consider will depend on the experience and technologies available at each laboratory. In general, using the most recent sample is recommended, especially in previously treated patients [4].
The sample should be stored in 10% buffered neutral formalin for 6–48 h depending on its size (6–12 h for small samples and 24–48 h for surgical resections), and a minimum of 50–100 cells that are viable for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) studies should be present. The use of alternative fixatives, such as mercury-based or alcohol-based fixatives, should be avoided. For cytological samples, the cell block is processed exactly like a biopsy. Smears are fixed in 96% alcohol and should be stained with Papanicolaou. From these materials, most biomarker studies can also be performed [5]. For techniques based on nucleic acid extraction, the threshold of analytical sensitivity, the limit of detection (LOD), of the method used must be known. Each type of technique has different minimum requirements, including 30% tumour cells for direct sequencing, 5% for real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and 20% for next-generation sequencing (NGS) [6]. In addition, the type of mutation can change the sensitivity threshold. Thus, a range of nucleic acid content between 5 and 10% is required to detect point mutations and small insertions or deletions, and a range up to 30% is needed to correctly analyse alterations in the number of copies [6]. Two alternative methods for redundant molecular detection are recommended, if necessary.
Regarding the management of all types of biological samples, protocols that allow both anatomopathological diagnosis and biomarker detection are required.
What biomarkers should be tested for in NSCLC?
Table 1 shows the biomarkers that must be detected in patients with NSCLC, and Table 2 provides other biomarkers of interest in these patients.
Table 1.
Essential biomarkers in NSCLC patients
| Gene/protein | Predictive alteration | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Mutation | PCR: Sanger sequencing, real-time PCR and NGS |
| ALK | Rearrangement | IHC, FISH, real-time PCR and NGS |
| ROS1 | Rearrangement | IHC (screening), FISH, real-time PCR and NGS |
| BRAF V600 | Mutation | Real-time PCR and NGS |
| PD-L1 | Overexpression | IHC |
| NTRK | Rearrangement | IHC (screening), real-time PCR and NGS |
| RET | Rearrangement | FISH, real-time PCR and NGS |
| KRAS | Mutation | PCR: Sanger sequencing, real-time PCR and NGS |
| MET |
Mutation Amplification |
NGS FISH, real-time PCR and NGS |
ALK anaplastic lymphoma kinase, BRAF B-Raf proto-oncogene, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, FISH fluorescence in situ hybridisation, IHC immunohistochemistry, KRAS kirsten rat sarcoma virus, MET mesenchymal epithelial transition factor, NGS next-generation sequencing, NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer, NTRK neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase, PCR polymerase chain reaction, PD-L1 programmed death ligand-1, RET rearranged during transfection, ROS1 c-ros oncogene 1
Table 2.
Other biomarkers of interest in NSCLC patients
| Gene/protein | Predictive alteration | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| HER2 |
Mutation Amplification |
NGS FISH, real-time PCR, NGS |
| TMB | Mutations | NGS |
| STK11 | Mutation | NGS |
| KEAP1 | Mutation | NGS |
| MSI | Pattern of hypermutation | IHC, PCR, NGS |
FISH fluorescence in situ hybridisation, HER2 human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, IHC immunohistochemistry, KEAP1 Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, MSI microsatellite instability-high, NGS next-generation sequencing, NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer, PCR polymerase chain reaction, STK11 serine/threonine kinase 11, TMB tumour mutation burden
EGFR
Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene are identified in approximately 10–16% of NSCLCs, with a higher frequency among patients with adenocarcinoma and nonsmoking patients [7]. The most frequent mutations that are directly related to sensitivity to anti-EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) affect exon 19 and consist of deletions that preserve the reading frame (in-frame deletions) between codons 746 and 759 (amino acids leucine, arginine, glutamate and alanine, LREA) (45–50%), followed by missense point mutations in exon 21, with substitution of the amino acid leucine with arginine at position 858 (L858R) (35–45%). Several EGFR-TKIs have been approved for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic disease and EGFR-activating mutations (exon 19 deletion, L858R) [8], including osimertinib (the preferred option in most guidelines), gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib and dacomitinib. Osimertinib is also approved as an adjuvant treatment after complete surgical resection in adult patients with EGFR-activating mutations [9].
Other mutations, such as insertions in exon 20, should also be detected due to their different effects in the disease, and treatment requirements [9].
In relation to the methodology, the clinical tests for EGFR detection should be able to detect all the individual mutations that have been reported with a frequency of at least 1% in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Highly sensitive methods are recommended. Regarding the result reports, the mutations that have been detected and the sensitivity of the detection methods used should be specified, among other data [3].
The initial recommendations for the diagnosis of mutations in EGFR have undergone some changes, including the fact that any cytological sample with adequate cellularity and preservation can be used, the need to use techniques with high sensitivity compared to Sanger sequencing as the reference method and the lack of sensitivity of IHC for the diagnosis of mutations in clinical practice [7].
Most patients with sensitizing EGFR mutations (exon 19 deletion and exon 21 mutations, L858R) receive an anti-EGFR TKI regimen, with the most frequent molecular mechanism of acquired resistance being the EGFR T790M mutation in patients receiving first- or second-generation anti-EGFR TKIs (50–60% of cases). Techniques that can detect this mutation in at least 5% of viable cells should be used, including new digital PCR methods [10].
The mechanisms leading to acquired resistance against TKIs vary, including intragenic mutations, gene amplification or fusion and functional adaptation with histological transformation. Accordingly, mechanisms of acquired resistance should be monitored using tumour biopsy or liquid biopsy (LB) [11].
ALK
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements are present in 2–5% of advanced NSCLCs [9]. These tumours are arising more often in younger patients, and females with or without minimal prior tobacco smoking exposure. The disease is frequently aggressive in its clinical course and presents with thromboembolic events, and metastases in the liver, serosal surfaces and brain are common [12]. Outcomes, including survival, are dramatically improved with specific ALK TKIs and, at present, median overall survival for stage IV patients frequently exceeds 5 years. Crizotinib was the first drug approved in this context and, since then, second- (ceritinib, alectinib and brigatinib) and third-generation (lorlatinib) TKIs are available in the European Union for the treatment of untreated patients and for those following progression on prior inhibitors [13]. The benefit of individual drugs in these pretreated patients depends on the mechanism of resistance, which frequently involves acquired mutations in the ALK kinase [14].
The histological types eligible for ALK rearrangement tests should include all adenocarcinomas, carcinomas with non-squamous histological evidence and squamous tumours in patients younger than 50 years of age and/or with low or no tobacco exposure (i.e. < 10 pack-years) [15]. The key methods for detecting ALK gene rearrangement are IHC, FISH and NGS. At present IHC represents a fast, reliable and cost-effective method to detect ALK fusions [16]. Its use in cytology smears is quite controversial, although recent studies have proven the suitability of the method [5]. The most commonly used antibodies for detecting rearrangements are D5F3 (Ventana® ALK [D5F3] CDx Assay, Tucson, Arizona, USA) and 5A4 (Novocastra®, Leica Biosystems®, Buffalo Grove, Illinois, USA), although the latter is not included in a diagnostic kit [17]. The cecal appendix is suitable as both a positive and a negative control. It must be fixed and processed under the same conditions as the patient sample. A positive tumour case can also be used as a control.
The role of FISH as the optimal standard methodology is currently controversial, although there are automated reader algorithms approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that greatly increase reliability [18]. When there is a positive IHC result as manifested by strong granular cytoplasmic staining with either of the 5A4 or D5F3 antibodies, confirmation by a second technique is not mandatory [15]. However, it is strongly advisable in cases that are inconclusive. This diagnostic redundancy is also helpful if unusual FISH staining is found [19].
Lastly, the methods based on NGS and RNA assays are highly specific and there are numerous studies that demonstrate their value for detecting fusions in patients who show negative results with other techniques [19]. Variant testing for specific rearrangements in ALK, which may provide some useful information in terms of predicting response to specific inhibitors, does not yet have sufficient data for recommendation, although it could be useful in the future [9, 14, 19]. In some circumstances, LB may replace tissue tumour biomarker analysis, and ALK profiling in circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) may serve as a treatment guiding tool [20, 21].
ALK mutations are emerging as important resistance mechanisms to ALK TKIs, and ALK mutation testing in this scenario may provide crucial treatment guiding information as newer-generation ALK TKIs display different efficacies against different ALK mutations [22].
ROS1
The c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) encodes a receptor with tyrosine kinase activity. Activating gene rearrangements with several partner genes are found in approximately 1% of NSCLCs, particularly those arising in young, nonsmoking patients [23]. These tumours are frequently associated with thrombotic events and have the propensity to develop central nervous system (CNS) metastases [24]. ROS1 fusions occur almost exclusively in adenocarcinomas, frequently in those with a solid component and signet-ring cells [25]. This histological profile is also typical of tumours harbouring an ALK translocation. Indeed, both receptors have a 77% similarity in their ATP-binding domain.
Crizotinib was the initial TKI approved for the first- or second-line treatment of stage IV lung cancer patients with ROS1 rearrangement [26]. More recently, TKIs such as lorlatinib, entrectinib and repotrectinib are being studied but are not yet approved for this indication [27].
Currently, it is recommended to carry out ROS1 testing in patients with advanced stage lung adenocarcinoma, regardless of the clinical characteristics. ROS1 testing is not recommended in squamous cell carcinoma, except in low or light smokers [27]. Three technologies are used to detect the following ROS1 rearrangements: IHC, cytogenetic techniques, particularly FISH [9], and molecular techniques such as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and particularly NGS [15, 19]. IHC is generally recommended as a screening method and positive cases should be confirmed with another orthogonal method (e.g., FISH or NGS), due to the variable specificity of the two commercially available antibodies (D4D6, Cell Signalling Technology and SP384, Ventana Medical Systems®) [3, 15, 28]. The specimen for analysis should include at least 20 tumour cells and each laboratory should validate its own interpretation range [15, 19, 28]. An external control must be available, other than cecal appendix, and it is advisable also to have a positive tumour control. The existence of positive peritumoural reactive pneumocytes has also been considered as a control. Of note, ROS1 expression, typically focal, can be found in up to one-third of tumours without underlying ROS1 rearrangements, but with other genomic alterations (e.g., mutations of EGFR, kirsten rat sarcoma virus [KRAS], BRAF or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 [HER2], and ALK rearrangements) [28, 29]. In addition, non-specific immunostaining has also been observed in the histological subtype of infiltrating mucinous adenocarcinoma and in non-tumour tissue [30].
FISH is one of the reference techniques. It uses dual-colour break-apart probes and a count of at least 50 tumour cells is recommended [15, 28, 30, 31]. A tumour should be considered positive when at least 50% of tumour cells have break-apart signals (separated by ≥ 1 signal diameter), and/or 3’ isolated signals (frequently marked with green fluorochrome) [30]. False positives and false negatives have been described, attributable to both methodological and biological causes [30, 32]. Last, NGS technologies (DNA or RNA-based), have shown high sensitivity and specificity in tumour samples and also in ctDNA [20, 21].
BRAF
Mutations of the B-Raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) are observed in 2% of lung carcinomas, are exclusive to other tumour types and appear mostly in adenocarcinomas, especially of the papillary type (80%) [33]. The most frequent mutation is BRAFV600E (Val600Glu) (50%), which predominates in women and may entail greater tumour aggressiveness, while the rest are more common in men or patients who smoke [34]. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the FDA approved dabrafenib and trametinib after their efficacy was demonstrated in phase II clinical trials in patients with the BRAFV600 mutation [9]. In the case of the FDA, the approval includes the need to detect the mutation with the NGS Oncomine Dx Target Test® panel [35].
Currently, any PCR method with adequate sensitivity and quality to identify BRAF mutations is allowed. However, detection of this mutation individually is not recommended, so this mutation is usually studied in NGS panels, which analyse at least exons 11 and 15 of that gene.
PD-L1
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), programmed cell death protein-1/ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors and to a lesser extent cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) blockers, have proven to be an effective strategy in the treatment of lung cancer, NSCLC and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), over the past 15 years [36]. At present, randomized clinical trial data support them as the standard treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, whether in monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy [37]. More recently, PD-1/PD-L1 blockade has been shown to be also effective in the adjuvant and neo-adjuvant context in patients with early disease [38, 39]. Although PD-L1 is far from being an ideal biomarker, the magnitude of benefit from PD-1/PD-L1 blockers in monotherapy is related to the tumour expression of PD-L1 [38]. In contrast, PD-L1 expression does not predict the efficacy of combination regimens of chemotherapy plus PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, PD-1 plus CTLA-4 blockers or chemotherapy plus PD-1 plus CTLA-4 blockers [37].
PD-L1 testing is based on IHC, currently the only validated predictive test. The diversity of IHC assays and cut-off points that define a positive result have been a source of confusion and have driven a number of harmonizing efforts by the scientific community [40, 41]. Current guidelines for the determination of the PD-L1 biomarker recommend the usual pre-analytical conditions of IHC testing. PD-L1 expression is evaluated by determining the percentage of tumour cells with partial or full membrane staining of any intensity.
There are several PD-L1 clones available for IHC testing. The four most widely used in pathology laboratories are 22C3 and 28–8 by Agilent (which share the Autostainer LINK 48® diagnostic platform by Agilent®), SP263 by MedImmune®/Ventana®, and SP142 by Spring®/Bioscience®/Ventana® (which share the Ventana® BenchMark diagnostic platform) [1]. The performance characteristics of the 22C3 and 28–8 assays appear to be similar based on side-by-side evaluation in retrospective cohorts. SP263 and E1L3N, used in routine practice but not approved as companion diagnostic tests, can show comparable patterns of staining to the approved assays when properly validated. The one consistent outlier has been the SP142 assay, which shows lower tumour cell staining, despite the fact that SP142 antibody recognizes identical or nearly identical epitopes as SP263 and E1L3N [42]. The SP142 assay was reportedly optimized for both tumour cell and immune cell scoring. However, its performance as an immune cell marker is further confounded by poor interobserver agreement in the interpretation of immune cell expression [43].
Regarding sample selection, if more than one tissue block is available for a given tumour, the most representative sample should be tested. More than one block may be tested when the reporting pathologist determines that additional testing is necessary to establish the tumour’s PD-L1 status. If additional blocks from the same sample are tested, the results from all tested blocks should be combined as though testing had been carried out in a single paraffin block [44].
It is not uncommon for the only material available to come from cytology samples. In these cases, it should be noted that the use of PD-L1 IHC kits that are validated for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) biopsy samples, and not specifically for cytology samples, may be used if the cytology samples were processed according to the same pre-analytical conditions as required by the kits [45].
NTRK
Fusions of neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) can be present in a wide variety of tumours, in both adults and paediatric patients, with the estimated frequency in NSCLC being less than 1%. Most are found in adenocarcinomas, and the most frequently involved gene is NTRK1 [9].
No clinical or pathological data characterise affected patients, but identifying them is crucial since tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitors (iTRKs) are available, such as larotrectinib and entrectinib, which have been approved by the EMA and the FDA for the treatment of tumours with NTRK fusions [46]. Despite the marked efficacy, resistance often develops, and clinical results for second-generation iTRKs are already available [47].
Two following strategies are recommended to detect these alterations: NGS with a panel including the study of the three genes (i.e., NTRK1, 2 and 3), and an adequate number of rearrangement pairs, or screening by IHC with mandatory subsequent confirmation of all positive results obtained by NGS [48, 49].
RET
Fusions of the gene rearranged during transfection (RET) are observed in different types of tumours, with a frequency of 1–2% in NSCLC, mainly in adenocarcinomas in nonsmoking patients. KIF5B is the most frequent rearrangement pair [50]. The presence of calcifications in the form of psammoma bodies should suggest RET fusions [51].
Currently, selective inhibitors are available, such as selpercatinib and pralsetinib, which have high response rates, although their approval by regulatory agencies for first-line treatment in patients with advanced disease is conditional on the results obtained in ongoing phase III studies [52, 53].
The optimal detection method for RET fusion is NGS, but FISH or PCR can also be used [54]. Regarding the design of an efficient fusion search algorithm in RET, it is important to consider the following: (1) NGS based on the study of RNA is more sensitive than if only DNA is studied, and (2) the results of FISH can be difficult to interpret [55, 56].
KRAS
Mutations in KRAS are identified in 25% of patients with NSCLC. They are found in all histological subtypes of adenocarcinoma, although they are more common in the invasive mucinous variant. They are also detected in 5% of squamous tumours [57]. Their presence confers biological and clinical heterogeneity and may have no prognostic value [58].
Mutations in KRAS are usually located in codons 12, 13 and 61. Mutations in codon 12 account for 80% of cases and are generally substitutions of glycine by cysteine (KRASG12C), valine (KRASG12V) or aspartic acid (KRASG12D), with frequencies of 10–13%, 5 and 4%, respectively [59]. KRASG12C and KRASG12V mutations are usually related to smoking and activate the RalGDS/Ral/FLIP pathway, while the KRASG12D mutation is more typical in nonsmoking patients and seems to activate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways. In addition, KRASG12C shows greater phosphorylation of ERK1/2.
More than 50% of NSCLCs with KRAS mutations present another mutation, and three subgroups can be established: the KP subgroup has mutations in tumour protein 53 (TP53) and represents 40% of cases; the KL subgroup, where serine/threonine kinase 11 (STK11), Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) or liver kinase B1 (LKB1) is identified, is usually associated with low percentages of PD-L1; and the KC subgroup, which is characterized by inactivation of CDK2A/B, is associated with a mucinous histology [60, 61]. In contrast, it is very rare to find EGFR mutations, thus KRAS and EGFR mutations are considered mutually exclusive.
The used technique to identify KRAS mutations is usually PCR. Thus far, their detection in isolation is not recommended, but should be included in NGS panels [62].
After years without effective therapies, several inhibitors have been developed that have shown activity in phase II trials against the KRASG12C mutation, such as sotorasib and adagrasib [63, 64]; therefore, they have been approved by the FDA, although the benefit of these agents in monotherapy or in combination, and to which patients they should be administered, are being studied in phase III trials.
MET
Oncogenic activation of the mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET) gene in NSCLC can occur mainly by amplification (1–5%) or by the presence of mutations in exon 14 (3–4%) that reduce degradation of the MET protein [9]. In NSCLC with a sarcomatoid morphology, the frequency of mutations in exon 14 can be up to 22% [65]. Between 5 and 20% of patients with EGFR mutations acquire resistance to EGFR-TKIs through MET amplification [9].
Currently, the results of several clinical trials demonstrate the activity and tolerability of oral drugs such as capmatinib, tepotinib and savolitinib in patients with mutations in exon 14, and capmatinib and tepotinib have already been approved by the EMA [9]. Conjugated antibodies such as telisotuzumab vedotin, bispecific antibodies such as amivantamab and others are also being studied in patients with MET amplification.
The technique of choice to study MET amplification is FISH, since it allows an estimation of the increase in the number of copies and clonal amplification with more precision. Due to the heterogeneity of mutations in exon 14, the optimal detection method in this case is NGS. An NGS panel with sufficient coverage should be used. To avoid false-negative results, an RNA panel is recommended [9]. MET overexpression by amplification or mutation of the gene can be detected, but the predictive value of MET IHC is still controversial [7, 9].
HER2
Overexpression, amplification and mutations of HER2 can be found in NSCLC, which are identified in 3–38%, 3% and 1–4% of patients, respectively [66]. The most frequent mutations are insertions in exon 20 (the tyrosine kinase domain), with the insertion/duplication of the four amino acids tyrosine, valine, methionine and alanine (YVMA) at codon 776 (YVMA 776–779 ins) being the most frequent (80–90%) [66, 67]. These mutations are mainly associated with patients with adenocarcinoma, nonsmoking patients and women [68]. The most recent data suggest that these mutations are the best predictors of a clinical benefit with anti-HER2 therapies (e.g., trastuzumab deruxtecan), regardless of the type of mutation and the presence of overexpression and amplification [67].
Regarding the methodologies for evaluating HER2 status, DNA- or RNA-based NGS is the most appropriate method to select patients compared to IHC and FISH [67]. Amplification has been described as a resistance mechanism following targeted treatments [66].
Immune biomarkers with potential value
The tumour mutation burden (TMB) refers to the number of somatic mutations present in the tumour, excluding polymorphisms and germline mutations from all variants, expressed per megabase in the studied exome. The mutations acquired by tumour cells may lead to abnormal protein structure, and consequently, to the expression of neoantigens that can elicit an immunotherapy response. Interestingly, there is no clear correlation between the expression of PD-L1 and TMB [69]. Many studies have shown that high TMB in tumours results in a better therapeutic effect with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy, including in some lung cancers [69], but there is no definitive validation for the use of this immunotherapy in clinical practice. However, exploratory analysis of the Keynote 042 trial suggests that among patients with tumours expressing PD-L1 in ≥ 50% of cells, only those whose TMB was higher than the median exhibited any therapeutic benefit with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors as compared to chemotherapy [70]. In fact, TMB is not a reliable predictor of outcome for NSCLC or SCLC treated with chemotherapy plus ICI blockade or dual immuno-oncology regimens.
With regard to testing for TMB, targeted NGS is considered to be a good alternative to more complex massive sequencing, and some recent data have validated the use of large panels [71, 72]. Harmonization studies are still required to validate the interconnectivity between different NGS studies, the heterogeneity of the numbers of included genes, horizontal coverage, the required optimal depth, the chemical sequencing type and the bioinformatic algorithms used [71]. If eventually drugs are approved based on TMB cut-offs, the harmonization efforts underway could be very useful. Detection of TMB in the blood (bTMB) is feasible, but robust data on its clinical utility are still lacking.
Microsatellite instability-high/deficient MisMatch repair (MSI-H/dMMR) predicts the efficacy of ICIs in gastric cancer and colon cancer. However the incidence of MSI-H/dMMR in lung cancer is low [73], and further investigation is needed to determine whether MSI-H/dMMR can be used as a predictive biomarker in this context. At present, the standard measure commonly used to judge MSI-H is the Bethesda method [74]. Of note, patients with MSI-H have a higher probability of having high TMB, but not vice versa [75].
The predictive role of genomic aberrations underlying lung cancer have also been investigated [76]. Gene alterations typically perceived as associated with immunotherapy response include those in TP53 or KRAS, and on the contrary aberrations affecting EGFR, ALK, ROS, RET, KEAP1 or LKB1 are less likely to be associated to checkpoint blockade benefit [61, 76]. In any case, at present, the available data do not support treatment recommendations based only on those genomic determinations.
Tumour inflammatory biomarkers such as related gene signatures or tissue cell content (T cell subtypes, myeloid cells, etc.) are investigational at present as they are peripheral blood-related immunotherapy and microbiome efficacy biomarkers.
Prioritizing the use of biological samples to achieve an accurate diagnosis
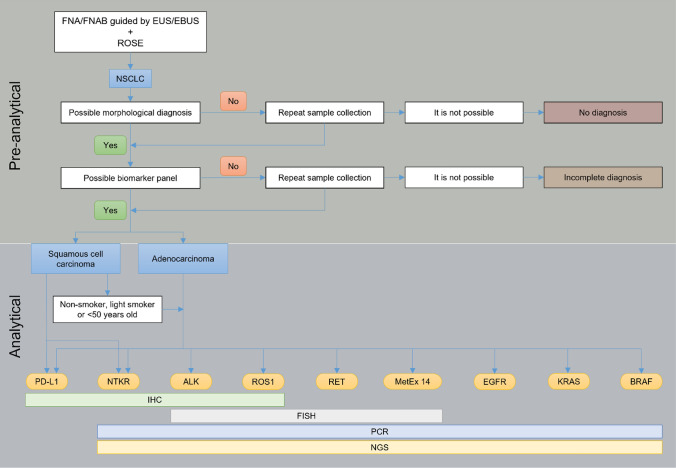
A high percentage of patients with NSCLC are diagnosed in advanced stages. These patients are not eligible for surgery; thus, the diagnosis is established through small biopsies and cytological samples. The development of imaging techniques that guide fine needle aspiration (FNA) and fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) allows the acquisition of high-quality samples in the quantities necessary to perform a complete diagnosis, both morphologically and via biomarkers (Fig. 1) [5].
Fig. 1.
Update of the small sample diagnostic algorithm in patients with NSCLC. ALK anaplastic lymphoma kinase, BRAF B-Raf proto-oncogene, EBUS endobronchial ultrasound, EUS endoscopic ultrasound, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, FISH fluorescence in situ hybridisation, FNA fine needle aspiration, FNAB fine needle aspiration biopsy, IHC immunohistochemistry, KRAS kirsten rat sarcoma virus, MetEx 14 mesenchymal epithelial transition factor exon 14, NGS next-generation sequencing, NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer, NTRK neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase, PCR polymerase chain reaction, PD-L1 programmed death ligand-1, ROS1 c-ros oncogene 1, RET rearranged during transfection, ROSE rapid on site evaluation
International guidelines recommend that regardless of the type of sample [77]: (1) a precise morphological diagnosis should be determined (i.e., NSCLC subtype); (2) the diagnosis of NSCLC not otherwise specified (NSCLC-NOS) should account for less than 10% of diagnoses with small samples/cytology; (3) IHC/immunocytochemistry (ICC) should be used judiciously; and iv) samples should be saved for biomarker studies.
In the case of FNA/FNAB guided by imaging techniques, the use of rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) is recommended. In addition to assessing whether a sample is sufficiently adequate to facilitate a diagnostic approach, ROSE also allows control of the entire pre-analytical phase and in situ preparation of the sample for analysis of the necessary biomarkers according to the preliminary diagnostic impression [5, 78].
In the case of cytological samples, samples should be handled in situ for proper processing by the following: (1) smears with immediate 96% alcohol fixation; (2) air-dried smears stained with Giemsa®/Diff-Quik®; (3) cell blocking; and (4) washing a needle in liquid cytology fixative (which provides good RNA conservation).
All these types of cytological samples are useful for biomarker detection by IHC/ICC, FISH and PCR-based techniques [5, 79–81].
IHC/ICC offers excellent results, which are comparable to those obtained by cell block biopsy and in smears previously stained with Papanicolaou. Unstained cytological smears stained with Giemsa®/Diff-Quik® and Papanicolaou are excellent substrates for FISH. Whole nuclei are analysed and, therefore, the signals observed are real, with no truncation effect due to the cutting of the paraffin samples. Moreover, DNA and RNA are of better quality in samples not fixed in formalin.
Molecular studies are usually less challenging on surgical specimens due to a greater amount of tissue. However, difficulty remains, and surgical pieces should be adequately fixed within 24–48 h. Necrotic areas should be avoided, and detection should be performed on samples with at least 30% viable tumour cellularity. In addition, the pieces should be adequately cut according to macroscopic protocols (e.g., white paper on pathology), including sufficient number of sections of the tumour. Tumours no larger than 3 cm should be included in their entirety. A good histological study is the first biomarker, since it will determine the histological subtype and guide further molecular detection (superimposable to that indicated above for small biopsy and cytology). Some histological subtypes are associated with different molecular alterations, although any clinical or histological variable should not be considered exclusive for biomarker detection in lung cancer. Another debate concerns molecular detection in tumours with different histological subtypes (a very common occurrence in adenocarcinomas). In these cases, testing samples corresponding to the most frequent subtype would be convenient, and detection in secondary subtypes can be added, especially if they present mucinous differentiation, in clear cells or signet-ring cells or in the presence of psammoma bodies.
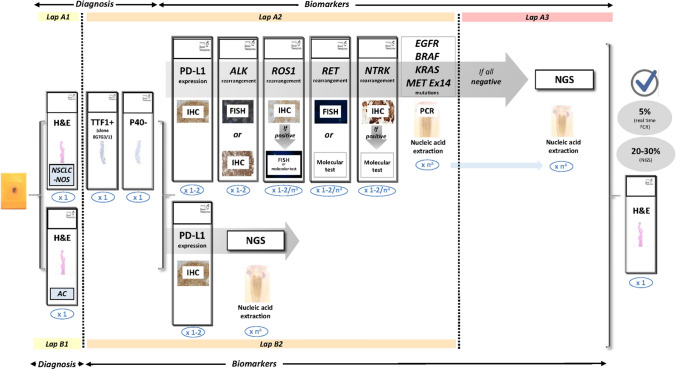
For all the biomarker analysis methods cited above, Fig. 2 shows an update of the protocol to be followed to analyse a biological sample of NSCLC.
Fig. 2.
Updated protocol for multiple biomarker testing on samples from patients with NSCLC. The number of sections for each test is shown in blue. aThe requirements for nucleic acid extraction for individual molecular testing or for extended genetic panels (NGS) are variable. Figure modified from Conde et al. (confidential, submitted). AC adenocarcinoma, ALK anaplastic lymphoma kinase, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, FISH fluorescence in situ hybridisation, H&E haematoxylin and eosin, IHC immunohistochemistry, KRAS kirsten rat sarcoma virus, MET mesenchymal epithelial transition factor, NGS next-generation sequencing, NTRK neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase, NSCLC-NOS non-small-cell lung carcinoma—not otherwise specified, PCR polymerase chain reaction, RET rearranged during transfection, ROS1 c-ros oncogene 1, PD-L1 programmed death ligand-1
The role of NGS in NSCLC
In recent years, the need for multigenic tests in patients with lung cancer has increased, including alterations in oncogenic factors, computations or resistance mechanisms [82]. NGS allows the sequencing of long and complex genes and multiple genes in a patient sample to identify alterations in factors and targets, minimizing the use of tissues in a short period and their use in daily clinical practice.
The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) has established recommendations on whether multigenic tumour NGS can be used and how to profile metastatic cancers following the classification of the Scale for Clinical Actionability of Molecular Targets (ESCAT) [83]. ESCAT is a framework that classifies the correspondence between a drug and genomic alterations according to their ability to act at the following three levels [84]: (1) from the perspective of public health; (2) from the perspective of academic clinical research centres; and (3) at the level of each individual patient.
With regard to lung cancer, the general recommendations for daily practice consider that a tumour or plasma sample from a patient with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC is profiled using NGS technology to detect level I ESCAT alterations (the alteration-drug pairing is associated with a better outcome in clinical trials, ready for routine use). The tests should include EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, RET, HER2, NTRK, KRAS and MET. In addition, for clinical research centres, multigene sequencing is strongly recommended for innovative drugs and clinical trials, as opposed to use in individual patients, for whom few clinically significant findings are expected with NGS [83].
Selection of the size of the NGS panel depends on the type of alterations to be studied, the response time required and the costs that can be expected [85, 86]. Each service should implement the panel that best meets its needs and be very familiar with its coverage to be able to expand molecular studies if the initial results are completely negative. Thus, to identify treatable fusions, the use of RNA panels is recommended because they are more sensitive than those that exclusively use DNA [87].
The starting nucleic acids are obtained mainly from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples (including both tissue samples and cell blocks from cytological samples) or from the nucleic acids present in the plasma. In the first stage of sample preparation, an exhaustive review of all the material from each patient is essential for the selection of the most appropriate paraffin block considering the pre-analytical variables (insufficient fixation and all fixatives that are not neutral buffered formalin at 10% must be avoided) and the percentage of tumour cellularity (optimal cutoff point: equal to or greater than 30%) [88].
The two methodological approaches of NGS most implemented in clinical practice are bridge amplification (Illumina®, San Diego, CA, USA) and emulsion PCR (ThermoFisher Scientific®, Waltham, MA, USA), which each have strengths and weaknesses. Among the advantages of Illumina® bridge amplification, this method allows identification of unknown alterations and the use of larger gene panels, while ThermoFisher Scientific® emulsion PCR requires less starting material and yields molecular results with shorter response times [54, 89].
The molecular findings obtained should be reflected in the NGS results report, together with the relevant conclusions regarding the tumour of each patient. The results should be discussed in a multidisciplinary committee, since increasing evidence indicates that this practice improves clinical outcomes [90].
The role of liquid biopsy in NSCLC
The concept of LB encompasses tests performed on a sample of peripheral blood or other biological fluid with the objective of detecting circulating tumour cells (CTCs) or fragments of nucleic acids from a tumour, such as circulating free DNA (cfDNA), ctDNA, circulating exosomes, platelet RNA and circulating tumour RNA (ctRNA), which can be isolated from blood (plasma) or urine, pleural fluids, ascites, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and saliva. LB has high specificity (96%), but its sensitivity is only 66% [91]. Therefore, a negative result is not definitive and requires tissue confirmation.
Therefore, its role is complementary to biopsy, and current recommendations are based on two clinical contexts when a tissue sample is limited or insufficient: (a) detection of molecular sensitive alterations and (b) detection of resistance mechanisms after progression on a TKI [21, 92]. A third context would be treatment efficacy monitoring based on the ctDNA load for minimal residual disease (MRD), an attractive approach that is not yet well established technically (quantification units need to be established), but where fluctuating levels of circulating nontumour DNA can affect the results [92]. Its use in early diagnosis presents difficulties due to low sensitivity in localized disease. Essentially, the greatest development has been in EGFR mutations, but currently, LB is being incorporated into tests for other molecular alterations, although the detection of gene rearrangements from circulating RNA continues to be a technical challenge awaiting resolution [21].
Some technical requirements of LB are the need for larger than usual blood volumes (two 10-ml tubes). Plasma is preferred rather than serum for nucleic acid extraction. The maximum waiting time until plasma extraction is 2 h for tubes with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and 3 days for tubes with special preservatives (Streck®). Blood should not be frozen before plasma extraction. DNA extraction should be performed with protocols designed for small and fragmented DNA [92]. Notably, up to 10% of people over 65 years of age present clonal haematopoiesis phenomena that may be misinterpreted as false-positive findings [93].
The use of techniques with high sensitivity, such as digital PCR, is recommended. In the case of NGS, good agreement is evident for tissue results, except for the variants that are found with an allelic frequency lower than 1% [94]. However, tools such as the unique molecular identifier (UMI) can be used to optimize detection. Two commercial NGS platforms (Guardant360® and FoundationOne Liquid CDx) have FDA approval for the analysis of solid tumours, including lung carcinomas [21].
In short, LB will be progressively incorporated into molecular diagnosis, treatment monitoring, MRD detection and early diagnosis as soon as prospective studies confirm its clinical utility.
Main requirements for implementing good quality control
Molecular testing is becoming an essential diagnostic tool and a part of standard management in cancer patients. Both laboratories and pathologists face new challenges in order to meet this novel requirement in patient care. Pathology laboratories must incorporate reliable methods to ensure optimal sample quality and processing to reduce the risk of errors in molecular biology tests [95]. Furthermore, practicing pathologists need to go beyond diagnosis and classification in order to produce information that will be required to guide treatment accurately and to do so in a timely manner [96].
The results of predictive biomarkers often determine which therapy (e.g., chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy) patients receive. Laboratory errors may therefore result in wrong or suboptimal treatment decisions and consequently harm the patient. To assure high-quality testing, laboratories must have a quality assurance system in place and comply with relevant international standards from certified organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the College of American Pathologists (CAP), or the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) (Table 3) [96–100].
Table 3.
Examples of European quality assurance schemes
| Supplier | Name | Starting material | Aim | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMQN | Molecular testing of cfDNA in plasma for EGFR gene mutations (pilot) | Plasma containing cfDNA | Mutations in the EGFR gene | 5 mock clinical cases with matching samples |
| Molecular testing in lung cancer | Mix of real tissue and artificial FFPE materials | Mutations in the EGFR, PIK3CA, KRAS and BRAF genes | 10 mock clinical cases with matching samples | |
| DNA Sequencing – NGS (vSomatic) | DNA sample derived from FFPE material | Any NGS strategy can be used | 1 mock clinical case with matching samples | |
| Oncogene panel testing | Rolled sections of FFPE materials | Mutations in the EGFR, PIK3CA, KRAS, HRAS, NRAS, KIT, TP53 and BRAF genes | 3 mock clinical cases with matching samples | |
| ESP | ALK FISH | Slides | ALK rearrangements | 5 resections, 5 digital cases |
| ALK IHC | Slides | ALK rearrangements | 5 resections | |
| EGFR, KRAS (optional), BRAF (optional) | Slides/rolled sections | Mutations | 10 resection specimens, possible cell-line | |
| ROS1 FISH | Slides | ROS1 rearrangements | 5 resections or possibly cell-lines, 5 digital cases | |
| ROS1 IHC | Slides | ROS1 rearrangements | 5 resections or possibly cell-lines | |
| PD-L1 | Slides | PD-L1 overexpression | 8 resections (TMAs) and 4 digital cases | |
| MET EQA scheme (ex 14 skipping) for DNA and RNA | Slides/rolled sections | MET exon 14 mutations | 5 resections | |
| NordiQC | Companion PD-L1 | Slides | PD-L1 overexpression | 1 preparation with multiple cases + 1 in-house case |
| SEAP | ALKanza MODULE | Slides | ALK rearrangements | 1 slide with 4 cases + 1 in house |
| EGFR | Slides/rolled sections | EGFR mutations | 4 consecutive slides | |
| UKNQEQAS | NSCLC ALK IHC | Slides | ALK and ROS1 rearrangements | 1 slide with several cases + 1 in house |
| NSCLC ALK/ROS1 FISH (pilot) | Slides | ALK and ROS1 rearrangements | 1 slide with several cases + 1 in house | |
| NSCLC PD-L1 IHC (pilot) | Slides | PD-L1 overexpression | 1 slide with several cases + 1 in house | |
| Gen QA | Lung cancer | Slides/rolled sections | EGFR, ALK (optional), KRAS (optional), BRAF (optional) | 5–4 cases |
| ctDNA (pilot) | Plasma | EGFR mutations | 5 cases | |
| Additional lung cancer biomarkers | Slides/rolled sections | ROS1, RET and MET (amplification) | 4 cases |
ALK anaplastic lymphoma kinase, BRAF B-Raf proto-oncogene, cfDNA circulating free DNA, ctDNA circulating tumour DNA, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, FFPE formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded, FISH fluorescence in situ hybridisation, HRAS Harvey Rat sarcoma virus, IHC immunohistochemistry, KIT proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase, KRAS kirsten rat sarcoma virus, MET mesenchymal epithelial transition factor, NGS next-generation sequencing, NRAS neuroblastoma ras viral oncogene homolog, NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer, PD-L1 programmed death ligand-1, PIK3CA phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha, RET rearranged during transfection, ROS1 c-ros oncogene 1, TMAs tissue microarrays, TP53 tumour protein 53
Progress in personalized medicine is limited, in part, because of the lack of standardized European and international documentation and insufficient guidelines for pre-analytical workflows. The pre-analytical process has recently been examined in some detail by the SPIDIA® project (http://www.spidia.eu). The following data were considered necessary to issue a report in accordance with good practice guidelines (Table 4) [96]: (1) patient identification: the patient must be identified correctly—laboratories require a minimum of two unique patient identifiers plus a unique sample identifier on the request form and the report; (2) reporting style and content: long reports are rarely read in full, and length matters; one page or, better still, single-screen reports are preferred, provided that they are legible. Clear presentation of the results, the test(s) performed, and any limitations of the tests (e.g., whether all possible mutations or a selection of the more common ones were tested) must be included; (3) interpretation: the result of the test must be described and be provided with an appropriate interpretation, particularly when this involves a treatment decision; (4) integrated reporting: the need for integrating patients’ results is widely acknowledged. As gene panel testing becomes more widespread, the results of different gene tests should be merged into a single report. Also, results from several pathology specialties on individual patients need to be integrated into the same report.
Table 4.
Proposed pathology results report content
| Identification of the patient and the doctor who ordered the test (or, failing that, the authorising person) |
| Pathological diagnosis |
|
Type of specimen submitted Previous treatment (yes/no) Timing of biopsy (initial/relapse/progression) Date on which the specimen was collected |
| The external code in the case of referral centres |
| The medium in which the specimen was received (fresh, frozen, paraffin-embedded, etc.) |
| The anatomical origin of the specimen |
| The order date, the specimen receipt date and the date on which the results were issued |
| The biomarker test method used, specifying detectable mutations and/or other abnormalities. In the case of commercial kits, the commercial name, the batch number and whether they are an approved ‘in vitro diagnostics’ product should be stated |
|
Name of the platform used and expiration date of the product The quality of the sample, specifying the percentage of cancer cells and whether the sample was enriched by micro- or macrodissection, as well as DNA concentration and purity |
| Comments about the adequate or inadequate nature of the sample |
| The test result, defining the type of molecular abnormality detected or the absence of molecular abnormalities |
| Identification of the professional responsible for the test (all phases) |
| Identification of the laboratory supervisor (optional) |
| Any additional information or comments of interest to the doctor who ordered the test |
| Accreditation or participation in quality programs |
Surgical Pathology services should obtain accreditation on quality assurance. We believe that all laboratories providing molecular pathology services should have laboratory accreditation according to ISO 15189 or their national equivalent. Accreditation provides patients, staff, service users and commissioners with evidence of laboratory competence.
Conclusions
Currently, in patients with NSCLC, a clear genomic diagnostic strategy that allows the establishment of optimal therapeutic indications for each must be defined.
With this objective, in the new consensus of the SEOM and the SEAP, the following recommendations are proposed: (1) EGFR, BRAF, KRAS and MET mutations, ALK, ROS1, RET and NTRK translocations and PD-L1 expression must be detected in NSCLC; (2) other emerging biomarkers such as the HER2 mutation and immune biomarkers such as TMB, MSI, STK11 and KEAP1 are recommended, especially if NGS is available; (3) molecular detection can be performed at any stage of NSCLC or in clinically selected patients, and new therapeutic indications that require this information can be established; (4) the availability of NGS strongly facilitates molecular diagnosis in a precise and effective manner, and its use should be immediately generalized; (5) LB has an increasing role in molecular diagnosis, especially if tissue is limited, and its role in the follow-up of treatment is also promising, both in MRD detection and early diagnosis; (6) a tumour sample must be appropriately analysed for correct prioritization of the molecular detection test to be performed, and good quality control throughout the process is essential; (7) adequate multidisciplinary collaboration between the different professionals involved is needed to achieve the highest quality in the diagnostic process and in the detection of the best therapeutic approach for each patient with NSCLC at any stage of the disease.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the editorial assistance of Beatriz Gil-Alberdi of HealthCo Trials (Madrid, Spain) in the drafting of this manuscript.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors participated in the writing of the first draft of the manuscript, commented on following draft versions and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
SEOM and SEAP acknowledge the financial support for this project in the form of unrestricted collaboration in the logistics from AstraZeneca and Roche.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest related with this project.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Footnotes
The original online version of this article was revised to correct Figure 2 caption.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
2/8/2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: 10.1007/s12094-023-03103-x
References
- 1.Garrido P, Conde E, de Castro J, Gómez-Román JJ, Felip E, Pijuan L, et al. Updated guidelines for predictive biomarker testing in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a National Consensus of the Spanish Society of Pathology and the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020;22(7):989–1003. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02218-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Canberk S, Engels M. Cytology samples and molecular biomarker testing in lung cancer-advantages and challenges. Virchows Arch. 2021;478(1):45–57. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02995-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Aisner DL, Arcila ME, Beasley MB, Bernicker EH, et al. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(3):323–358. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, Novello S, Smit EF, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(Suppl 4):iv192–iv237. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lozano MD, Echeveste JI, Abengozar M, Mejías LD, Idoate MA, Calvo A, et al. Cytology smears in the era of molecular biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer: doing more with less. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142(3):291–298. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0208-RA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Angulo B, Conde E, Suárez-Gauthier A, Plaza C, Martínez R, Redondo P, et al. A comparison of EGFR mutation testing methods in lung carcinoma: direct sequencing, real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(8):e43842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.IASLC. IASLC Atlas of EGFR testing in lung cancer—guidebook. 2017. https://www.iaslc.org/research-education/publications-resources-guidelines/iaslc-atlas-egfr-testing-lung-cancer-guidebook. Accessed Apr 2022.
- 8.Majem M, Juan O, Insa A, Reguart N, Trigo JM, Carcereny E, et al. SEOM clinical guidelines for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (2018) Clin Transl Oncol. 2019;21(1):3–17. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1978-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tan AC, Tan DSW. Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(6):611–625. doi: 10.1200/jco.21.01626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nizamaddin SK, Mehrotra M, Nadhim ASH, Luthra R, Roy-Chowdhuri S. Detection of EGFR T790M mutation by droplet digital polymerase chain reaction in lung carcinoma cytology samples. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020 doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0411-OA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reita D, Pabst L, Pencreach E, Guérin E, Dano L, Rimelen V, et al. Molecular mechanism of EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: application to biological diagnostic and monitoring. Cancers (Basel). 2021 doi: 10.3390/cancers13194926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zugazagoitia J, Biosca M, Oliveira J, Olmedo ME, Dómine M, Nadal E, et al. Incidence, predictors and prognostic significance of thromboembolic disease in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 2018 doi: 10.1183/13993003.02431-2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Peng L, Zhu L, Sun Y, Stebbing J, Selvaggi G, Zhang Y, et al. Targeting ALK rearrangements in NSCLC: current state of the art. Front Oncol. 2022;12:863461. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.863461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lin JJ, Riely GJ, Shaw AT. Targeting ALK: precision medicine takes on drug resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(2):137–155. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.cd-16-1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Aisner DL, Arcila ME, Beasley MB, Bernicker EH, et al. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142(3):321–346. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0388-CP. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thunnissen E, Allen TC, Adam J, Aisner DL, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, et al. Immunohistochemistry of pulmonary biomarkers: a perspective from members of the Pulmonary Pathology Society. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142(3):408–419. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0106-SA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Conde E, Hernandez S, Prieto M, Martinez R, Lopez-Rios F. Profile of Ventana ALK (D5F3) companion diagnostic assay for non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2016;16(6):707–713. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2016.1172963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Conde E, Suárez-Gauthier A, Benito A, Garrido P, García-Campelo R, Biscuola M, et al. Accurate identification of ALK positive lung carcinoma patients: novel FDA-cleared automated fluorescence in situ hybridization scanning system and ultrasensitive immunohistochemistry. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(9):e107200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Conde E, Rojo F, Gómez J, Enguita AB, Abdulkader I, González A, et al. Molecular diagnosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: expert opinion on ALK and ROS1 testing. J Clin Pathol. 2022;75(3):145–153. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2021-207490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mack PC, Banks KC, Espenschied CR, Burich RA, Zill OA, Lee CE, et al. Spectrum of driver mutations and clinical impact of circulating tumor DNA analysis in non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of over 8000 cases. Cancer. 2020;126(14):3219–3228. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rolfo C, Mack P, Scagliotti GV, Aggarwal C, Arcila ME, Barlesi F, et al. Liquid biopsy for advanced NSCLC: a Consensus Statement from the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16(10):1647–1662. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mondaca S, Lebow ES, Namakydoust A, Razavi P, Reis-Filho JS, Shen R, et al. Clinical utility of next-generation sequencing-based ctDNA testing for common and novel ALK fusions. Lung Cancer. 2021;159:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Drilon A, Jenkins C, Iyer S, Schoenfeld A, Keddy C, Davare MA. ROS1-dependent cancers—biology, diagnostics and therapeutics. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(1):35–55. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0408-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Muñoz-Unceta N, Zugazagoitia J, Manzano A, Jiménez-Aguilar E, Olmedo ME, Cacho JD, et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients with advanced lung cancer harboring rearrangements in ROS1. Eur J Cancer. 2020;141:193–198. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boland JM, Wampfler JA, Jang JS, Wang X, Erickson-Johnson MR, Oliveira AM, et al. Pulmonary adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell features: a comprehensive study from 3 distinct patient cohorts. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38(12):1681–1688. doi: 10.1097/pas.0000000000000280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shaw AT, Ou SH, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Solomon BJ, Salgia R, et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(21):1963–1971. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Remon J, Pignataro D, Novello S, Passiglia F. Current treatment and future challenges in ROS1- and ALK-rearranged advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;95:102178. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Conde E, Hernandez S, Martinez R, Angulo B, De Castro J, Collazo-Lorduy A, et al. Assessment of a new ROS1 immunohistochemistry clone (SP384) for the identification of ROS1 rearrangements in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma: the ROSING study. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(12):2120–2132. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wiesweg M, Eberhardt WEE, Reis H, Ting S, Savvidou N, Skiba C, et al. High prevalence of concomitant oncogene mutations in prospectively identified patients with ROS1-positive metastatic lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(1):54–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.08.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bubendorf L, Büttner R, Al-Dayel F, Dietel M, Elmberger G, Kerr K, et al. Testing for ROS1 in non-small cell lung cancer: a review with recommendations. Virchows Arch. 2016;469(5):489–503. doi: 10.1007/s00428-016-2000-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kalemkerian GP, Narula N, Kennedy EB, Biermann WA, Donington J, Leighl NB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for the selection of patients with lung cancer for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(9):911–919. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.76.7293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhao J, Chen X, Zheng J, Kong M, Wang B, Ding W. A genomic and clinicopathological study of non-small-cell lung cancers with discordant ROS1 gene status by fluorescence in-situ hybridisation and immunohistochemical analysis. Histopathology. 2018;73(1):19–28. doi: 10.1111/his.13492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Planchard D, Johnson BE. BRAF adds an additional piece of the puzzle to precision oncology-based treatment strategies in lung cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142(7):796–797. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2018-0088-ED. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nguyen-Ngoc T, Bouchaab H, Adjei AA, Peters S. BRAF alterations as therapeutic targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(10):1396–1403. doi: 10.1097/jto.0000000000000644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Odogwu L, Mathieu L, Blumenthal G, Larkins E, Goldberg KB, Griffin N, et al. FDA approval summary: dabrafenib and trametinib for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancers harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Oncologist. 2018;23(6):740–745. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Doroshow DB, Bhalla S, Beasley MB, Sholl LM, Kerr KM, Gnjatic S, et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(6):345–362. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Reck M, Remon J, Hellmann MD. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(6):586–597. doi: 10.1200/jco.21.01497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Felip E, Vallieres E, Zhou C, Wakelee H, Bondarenko I, Sakai H, et al. LBA9—IMpower010: sites of relapse and subsequent therapy from a phase III study of atezolizumab vs best supportive care after adjuvant chemotherapy in stage IB-IIIA NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(suppl_5):S1283–S1346. doi: 10.1016/annonc/annonc741. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Forde PM, Chaft JE, Smith KN, Anagnostou V, Cottrell TR, Hellmann MD, et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(21):1976–1986. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1716078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hirsch FR, McElhinny A, Stanforth D, Ranger-Moore J, Jansson M, Kulangara K, et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for lung cancer: results from phase 1 of the blueprint PD-L1 IHC Assay Comparison Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(2):208–222. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tsao MS, Kerr KM, Kockx M, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, Botling J, et al. PD-l1 immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life clinical samples: results of Blueprint Phase 2 Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(9):1302–1311. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.05.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rimm DL, Han G, Taube JM, Yi ES, Bridge JA, Flieder DB, et al. A prospective, multi-institutional, pathologist-based assessment of 4 immunohistochemistry assays for PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(8):1051–1058. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vennapusa B, Baker B, Kowanetz M, Boone J, Menzl I, Bruey JM, et al. Development of a PD-L1 complementary diagnostic immunohistochemistry assay (SP142) for atezolizumab. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2019;27(2):92–100. doi: 10.1097/pai.0000000000000594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cheung CC, Barnes P, Bigras G, Boerner S, Butany J, Calabrese F, et al. Fit-for-purpose PD-L1 biomarker testing for patient selection in immuno-oncology: guidelines for clinical laboratories from the Canadian Association of Pathologists-Association Canadienne Des Pathologistes (CAP-ACP) Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2019;27(10):699–714. doi: 10.1097/pai.0000000000000800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang H, Agulnik J, Kasymjanova G, Wang A, Jiménez P, Cohen V, et al. Cytology cell blocks are suitable for immunohistochemical testing for PD-L1 in lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(6):1417–1422. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Doebele RC, Drilon A, Paz-Ares L, Siena S, Shaw AT, Farago AF, et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30691-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Garrido P, Hladun R, de Álava E, Álvarez R, Bautista F, López-Ríos F, et al. Multidisciplinary consensus on optimising the detection of NTRK gene alterations in tumours. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021;23(8):1529–1541. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02558-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hechtman JF. NTRK insights: best practices for pathologists. Mod Pathol. 2022;35(3):298–305. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00913-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rojo F, Colomer R, López-Ríos F, Bautista F, Álvarez R, de Álava E, et al. Multidisciplinary consensus on optimizing the detection of NTRK gene alterations in tumours. Rev Esp Patol. 2021;54(4):250–262. doi: 10.1016/j.patol.2021.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Belli C, Anand S, Gainor JF, Penault-Llorca F, Subbiah V, Drilon A, et al. Progresses toward precision medicine in RET-altered solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(23):6102–6111. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-20-1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mukhopadhyay S, Pennell NA, Ali SM, Ross JS, Ma PC, Velcheti V. RET-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas with lymphangitic spread, psammoma bodies, and clinical responses to cabozantinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(11):1714–1719. doi: 10.1097/jto.0000000000000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Drilon A, Oxnard GR, Tan DSW, Loong HHF, Johnson M, Gainor J, et al. Efficacy of selpercatinib in RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(9):813–824. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gainor JF, Curigliano G, Kim DW, Lee DH, Besse B, Baik CS, et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): a multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(7):959–969. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Belli C, Penault-Llorca F, Ladanyi M, Normanno N, Scoazec JY, Lacroix L, et al. ESMO recommendations on the standard methods to detect RET fusions and mutations in daily practice and clinical research. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Conde E, Hernandez S, Sanchez E, Regojo RM, Camacho C, Alonso M, et al. Pan-TRK immunohistochemistry: an example-based practical approach to efficiently identify patients with NTRK fusion cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021;145(8):1031–1040. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2020-0400-RA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yang SR, Aypar U, Rosen EY, Mata DA, Benayed R, Mullaney K, et al. A performance comparison of commonly used assays to detect RET fusions. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(5):1316–1328. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-20-3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(8):1623–1640. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ferrer I, Zugazagoitia J, Herbertz S, John W, Paz-Ares L, Schmid-Bindert G. KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: from biology to therapy. Lung Cancer. 2018;124:53–64. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Veluswamy R, Mack PC, Houldsworth J, Elkhouly E, Hirsch FR. KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: biology, developmental therapeutics, and molecular testing. J Mol Diagn. 2021;23(5):507–520. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Scheffler M, Ihle MA, Hein R, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Scheel AH, Siemanowski J, et al. K-ras mutation subtypes in NSCLC and associated co-occuring mutations in other oncogenic pathways. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(4):606–616. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Skoulidis F, Heymach JV. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19(9):495–509. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0179-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Reck M, Carbone DP, Garassino M, Barlesi F. Targeting KRAS in non-small-cell lung cancer: recent progress and new approaches. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(9):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ou SI, Jänne PA, Leal TA, Rybkin II, Sabari JK, Barve MA, et al. First-in-human phase I/IB dose-finding study of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in patients with advanced KRAS(G12C) solid tumors (KRYSTAL-1) J Clin Oncol. 2022 doi: 10.1200/jco.21.02752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Skoulidis F, Li BT, Dy GK, Price TJ, Falchook GS, Wolf J, et al. Sotorasib for lung cancers with KRAS p.G12C mutation. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(25):2371–2381. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2103695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Liu X, Jia Y, Stoopler MB, Shen Y, Cheng H, Chen J, et al. Next-generation sequencing of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma reveals high frequency of actionable MET gene mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(8):794–802. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.62.0674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zhao J, Xia Y. Targeting HER2 alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer: a comprehensive review. JCO Precis Oncol. 2020;4:411–425. doi: 10.1200/po.19.00333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Li BT, Smit EF, Goto Y, Nakagawa K, Udagawa H, Mazières J, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(3):241–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2112431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mazières J, Barlesi F, Filleron T, Besse B, Monnet I, Beau-Faller M, et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(2):281–286. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science. 2015;348(6230):124–128. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Herbst RS, Lopes G, Kowalski DM, Nishio M, Wu YL, de Castro Junior G, et al. LBA79—association between tissue TMB (tTMB) and clinical outcomes with pembrolizumab monotherapy (pembro) in PD-L1-positive advanced NSCLC in the KEYNOTE-010 and -042 trials. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:v916–v917. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz394.077. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Büttner R, Longshore JW, López-Ríos F, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Normanno N, Rouleau E, et al. Implementing TMB measurement in clinical practice: considerations on assay requirements. ESMO Open. 2019;4(1):e000442. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2018-000442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ramos-Paradas J, Hernández-Prieto S, Lora D, Sanchez E, Rosado A, Caniego-Casas T, et al. Tumor mutational burden assessment in non-small-cell lung cancer samples: results from the TMB(2) harmonization project comparing three NGS panels. J Immunother Cancer. 2021 doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hause RJ, Pritchard CC, Shendure J, Salipante SJ. Classification and characterization of microsatellite instability across 18 cancer types. Nat Med. 2016;22(11):1342–1350. doi: 10.1038/nm.4191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Umar A, Boland CR, Terdiman JP, Syngal S, de la Chapelle A, Rüschoff J, et al. Revised Bethesda guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96(4):261–268. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Vanderwalde A, Spetzler D, Xiao N, Gatalica Z, Marshall J. Microsatellite instability status determined by next-generation sequencing and compared with PD-L1 and tumor mutational burden in 11,348 patients. Cancer Med. 2018;7(3):746–756. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Guaitoli G, Tiseo M, Di Maio M, Friboulet L, Facchinetti F. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021;10(6):2890–2916. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aggarwal C, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, Version 1.2020. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(12):1464–1472. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Manzo JL, Cuda J, Pantanowitz L, Xing J, Yu J, Beasley HS, et al. Clinical trial cytology: use of on-site evaluation of small biopsy and FNA samples for clinical trials and biomarker research studies. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018 doi: 10.1002/cncy.22001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Malapelle U, Pepe F, Pisapia P, Altimari A, Bellevicine C, Brunnström H, et al. Reference standards for gene fusion molecular assays on cytological samples: an international validation study. J Clin Pathol. 2021 doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2021-207825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lozano MD, Abengozar-Muela M, Echeveste JI, Subtil JC, Bertó J, Gúrpide A, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression on direct Pap-stained cytology smears from non-small cell lung cancer: comparison with cell blocks and surgical resection specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019;127(7):470–480. doi: 10.1002/cncy.22155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Tejerina E, Garca Tobar L, Echeveste JI, de Andrea CE, Vigliar E, Lozano MD. PD-L1 in cytological samples: a review and a practical approach. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021;8:668612. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.668612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yates LR, Seoane J, Le Tourneau C, Siu LL, Marais R, Michiels S, et al. The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) precision medicine glossary. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):30–35. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Mosele F, Remon J, Mateo J, Westphalen CB, Barlesi F, Lolkema MP, et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: a report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(11):1491–1505. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Mateo J, Chakravarty D, Dienstmann R, Jezdic S, Gonzalez-Perez A, Lopez-Bigas N, et al. A framework to rank genomic alterations as targets for cancer precision medicine: the ESMO Scale for Clinical Actionability of molecular Targets (ESCAT) Ann Oncol. 2018;29(9):1895–1902. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.(SEAP-IAP) SEdAP-IAoP. Libro Blanco de la Anatomía Patológica en España 2021. 7 ed. 2021.
- 86.Donoghue MTA, Schram AM, Hyman DM, Taylor BS. Discovery through clinical sequencing in oncology. Nat Cancer. 2020;1(8):774–783. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-0100-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.(NCCN) NCCN. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines). Non-small cell lung cancer Version 3.2022—March 16, 2022. 2022. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf.
- 88.Jennings LJ, Arcila ME, Corless C, Kamel-Reid S, Lubin IM, Pfeifer J, et al. Guidelines for validation of next-generation sequencing-based oncology panels: a Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology and College of American Pathologists. J Mol Diagn. 2017;19(3):341–365. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Yohe S, Thyagarajan B. Review of clinical next-generation sequencing. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141(11):1544–1557. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0501-RA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lamping M, Benary M, Leyvraz S, Messerschmidt C, Blanc E, Kessler T, et al. Support of a molecular tumour board by an evidence-based decision management system for precision oncology. Eur J Cancer. 2020;127:41–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Merker JD, Oxnard GR, Compton C, Diehn M, Hurley P, Lazar AJ, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis in patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists joint review. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(16):1631–1641. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.76.8671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rolfo C, Mack PC, Scagliotti GV, Baas P, Barlesi F, Bivona TG, et al. Liquid biopsy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a statement paper from the IASLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(9):1248–1268. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Razavi P, Li BT, Brown DN, Jung B, Hubbell E, Shen R, et al. High-intensity sequencing reveals the sources of plasma circulating cell-free DNA variants. Nat Med. 2019;25(12):1928–1937. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0652-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Schwaederlé MC, Patel SP, Husain H, Ikeda M, Lanman RB, Banks KC, et al. Utility of genomic assessment of blood-derived circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(17):5101–5111. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Dufraing K, Fenizia F, Torlakovic E, Wolstenholme N, Deans ZC, Rouleau E, et al. Biomarker testing in oncology—requirements for organizing external quality assessment programs to improve the performance of laboratory testing: revision of an expert opinion paper on behalf of IQNPath ABSL. Virchows Arch. 2021;478(3):553–565. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02928-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Cree IA, Deans Z, Ligtenberg MJ, Normanno N, Edsjö A, Rouleau E, et al. Guidance for laboratories performing molecular pathology for cancer patients. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67(11):923–931. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Cheung CC, D'Arrigo C, Dietel M, Francis GD, Fulton R, Gilks CB, et al. Evolution of quality assurance for clinical immunohistochemistry in the era of precision medicine: Part 4: tissue tools for quality assurance in immunohistochemistry. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017;25(4):227–230. doi: 10.1097/pai.0000000000000469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Cheung CC, D'Arrigo C, Dietel M, Francis GD, Gilks CB, Hall JA, et al. Evolution of quality assurance for clinical immunohistochemistry in the era of precision medicine: Part 1: fit-for-purpose approach to classification of clinical immunohistochemistry biomarkers. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017;25(1):4–11. doi: 10.1097/pai.0000000000000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.ISO 15189:2012. Medical laboratories—requirements for quality and competence. 2012.
- 100.Torlakovic EE, Cheung CC, D'Arrigo C, Dietel M, Francis GD, Gilks CB, et al. Evolution of quality assurance for clinical immunohistochemistry in the era of precision medicine—Part 2: immunohistochemistry test performance characteristics. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2017;25(2):79–85. doi: 10.1097/pai.0000000000000444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Not applicable.