Dear Editor,
Since late 2022 and early 2023, following the pandemic period the literature is full of evidence showing the direct correlation between COVID-19 and the growth of neurological disorders. Long Covid effects seem to be concentrated mainly at the central level, affecting people's lives worldwide. An underestimated neurological and psychological disorder is the attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which mainly affects children and adolescents. This clinical condition is manifested by high levels of hyperactivity, inattention and impulsivity, which are completely inappropriate for growth (Pinzon et al., 2022 ; Ferrara et al., 2023).
In Italy, at Asl Napoli 3 SUD, and in Costa Rica, at Hospital Clínica Biblica, a retrospective analysis study has been conducted comparing two populations of more than 1 million people, to demonstrate the steady growth in consumption of drugs used for ADHD (methylphenidate and atomoxetine) between the years 2019 and 2022. An extraction on the companies’ database allowed us to know the actual amounts of defined daily dose (DDD) dispensed. Monitoring over these four years confirmed the strong correlation between pandemic COVID-19 and ADHD.
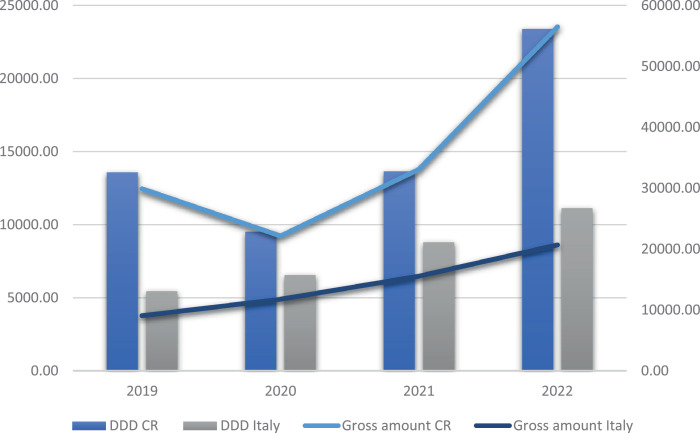
Fig. 1 refers to the situation in both the centers. From 2019 to 2022, DDDs more than doubled with 103.6 percent more prescriptions of methylphenidate and 111.8 percent more of atomoxetine in Asl Napoli 3 Sud. On the other hand, in Clínica Biblica, DDDs grew significantly at about 56% for atomoxetine and 72% for methylphenidate in 2022 compared to the values of 2019. Comparing both medications DDDs and the financial cost expressed as the gross amount in euros, A similar trend is observed that gradually increases up to the maximum value for each item in 2022.
Fig. 1.
Annual comparison of DDD´s and gross amount trends of atomoxetine and methylphenidate for Asl Napoli 3 South and Hospital Clínica Biblica.
ADHD disorder, which affects a small population and whose treatments are not too expensive, unlike other disorders attracts less commercial interest. However, it is a booming disease and it represents a real social and dangerous problem, which affects young population (Valkenburg et al., 2022). In fact, ADHD was already on the rise with the expansion of the use of social networks with youth 'distractions' which created an addiction with consequences on attention deficit (Fayyad et al., 2017).
This report aimed to promote a social alarm of scientific interest worldwide. The ADHD comprehensive clinical management, although the cost of medication is relatively low, illustrates a remarkable economic burden with future social costs, thus appropriate government measures are needed to limit the spread. COVID-19, with its restrictions, has led to serious neurological consequences for people, and it played a crucial role in fostering technological expansion, with also negative consequences for the public. France and the European Commission (European Commission 2023) have already considered inhibiting the use of social networks by 13 to 16-year-olds in an attempt to stem the growth of a less productive population in the future in an increasingly computerized society.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
The authors consent to the publication of the manuscript.
Authors contributions
Conceptualization, FF, EZ, AV - Data curation, FF, EZ, JAV, BS, UT, JPD - Formal analysis, FF, EZ, AV, BS, SA, EN, JPD - Funding acquisition, N/A - Investigation, FF, EZ, AV, AZ - Methodology, EN, UT, JAV, JPD, SA - Project administration, UT, EB - Resources, N/A - Software, N/A - Supervision, RL, EN, UT, EB, GR - Validation, AZ, AV, RL, EN, UT, EB, GR - Visualization, JAV, AZ, RL, BS, UT, EN, EB, GR - Writing - original draft, FF, EZ, AV, JAV, BS, SA, EN, JPD - Writing - review & editing, FF, AV, AZ, RL.
Funding
No funding was received to conduct this study.
Availability of data and materials
Full availability of data and materials. All stated data can be provided on request to the reader.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
The authors declare that the opinions expressed are of a personal nature and do not in any way commit the responsibility of the Administrations to which they belong.
References
- European Commission. https://ec.europa.eu/. (Accessed March 2023).
- Fayyad J., Sampson N.A., Hwang I., Adamowski T., Aguilar-Gaxiola S., Al-Hamzawi A., Andrade L.H., Borges G., de Girolamo G., Florescu S., Gureje O., Haro J.M., Hu C., Karam E.G., Lee S., Navarro-Mateu F., O'Neill S., Pennell B.E., Piazza M., Posada-Villa J., Ten Have M., Torres Y., Xavier M., Zaslavsky A.M., Kessler R.C. WHO World Mental Health Survey Collaborators. The descriptive epidemiology of DSM-IV adult ADHD in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2017;9(1):47–65. doi: 10.1007/s12402-016-0208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara F., Zovi A., Masi M., Langella R., Trama U., Boccellino M., Vitiello A. Long COVID could become a widespread post-pandemic disease? A debate on the organs most affected. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02417-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinzon R.T., Wijaya V.O., Jody A.A., Nunsio P.N., Buana R.B. Persistent neurological manifestations in long COVID-19 syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect Public Health. 2022;15(8):856–869. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkenburg P.M., Meier A., Beyens I. Social media use and its impact on adolescent mental health: an umbrella review of the evidence. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;44:58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Full availability of data and materials. All stated data can be provided on request to the reader.