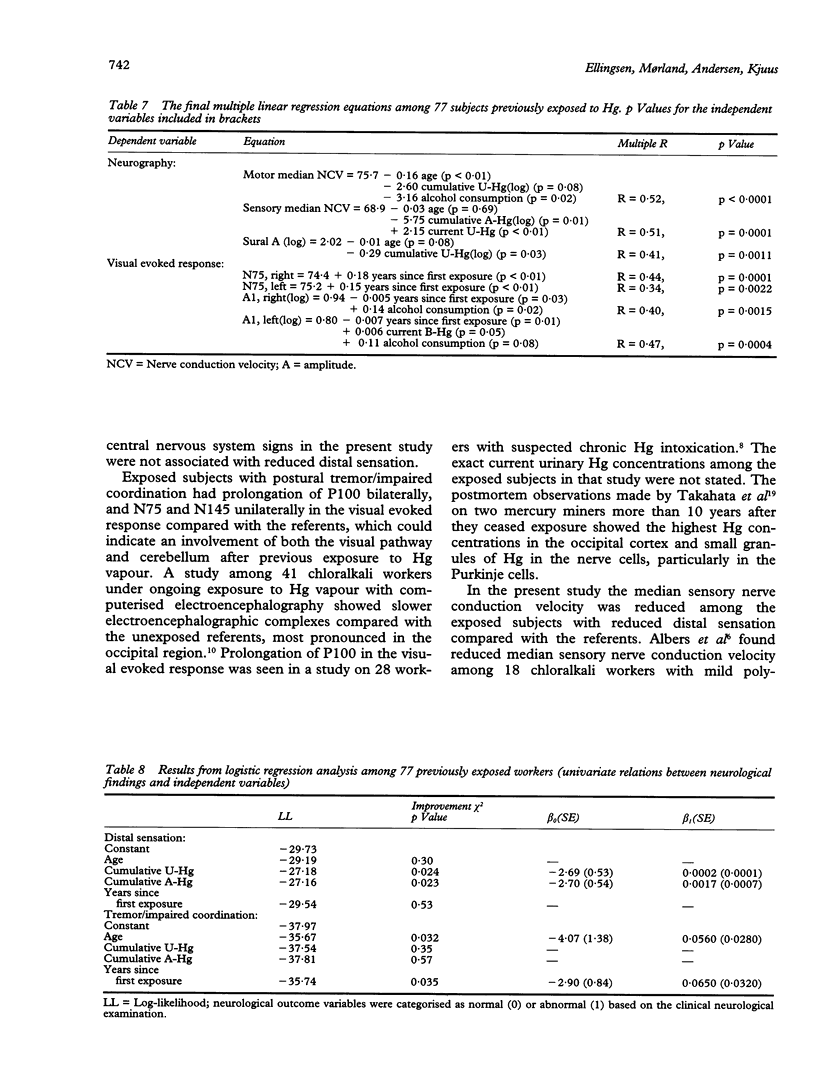
Abstract
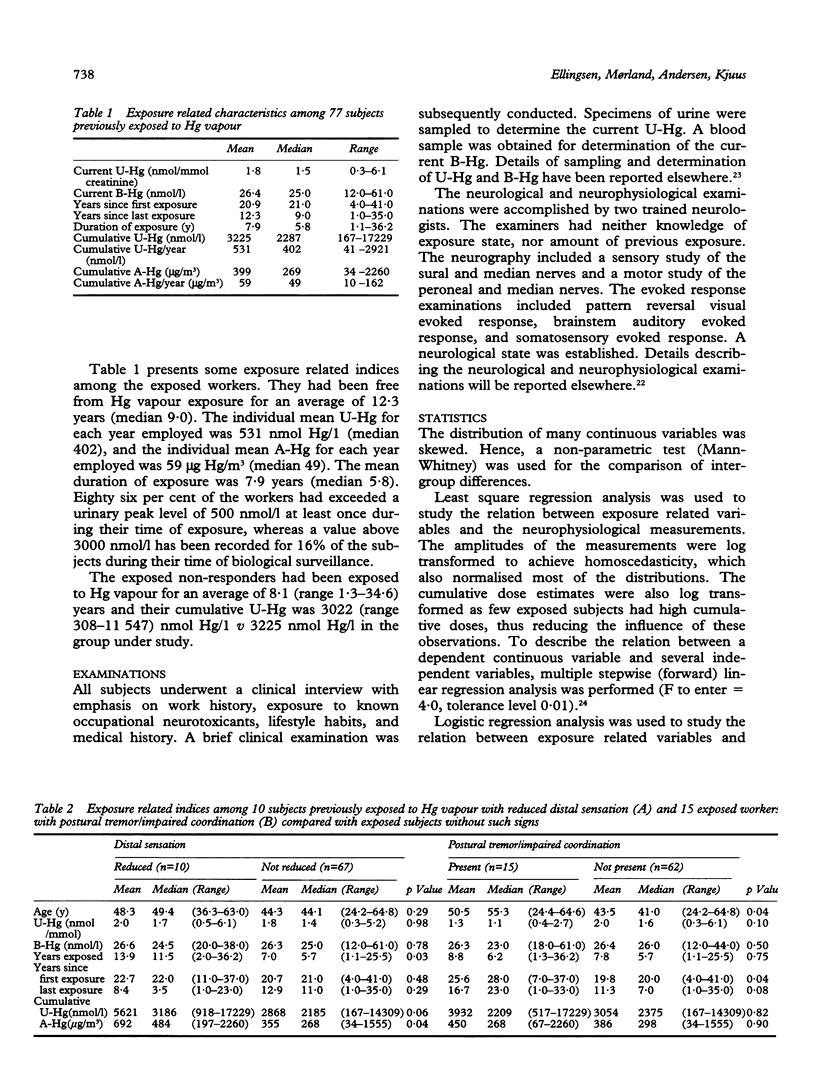
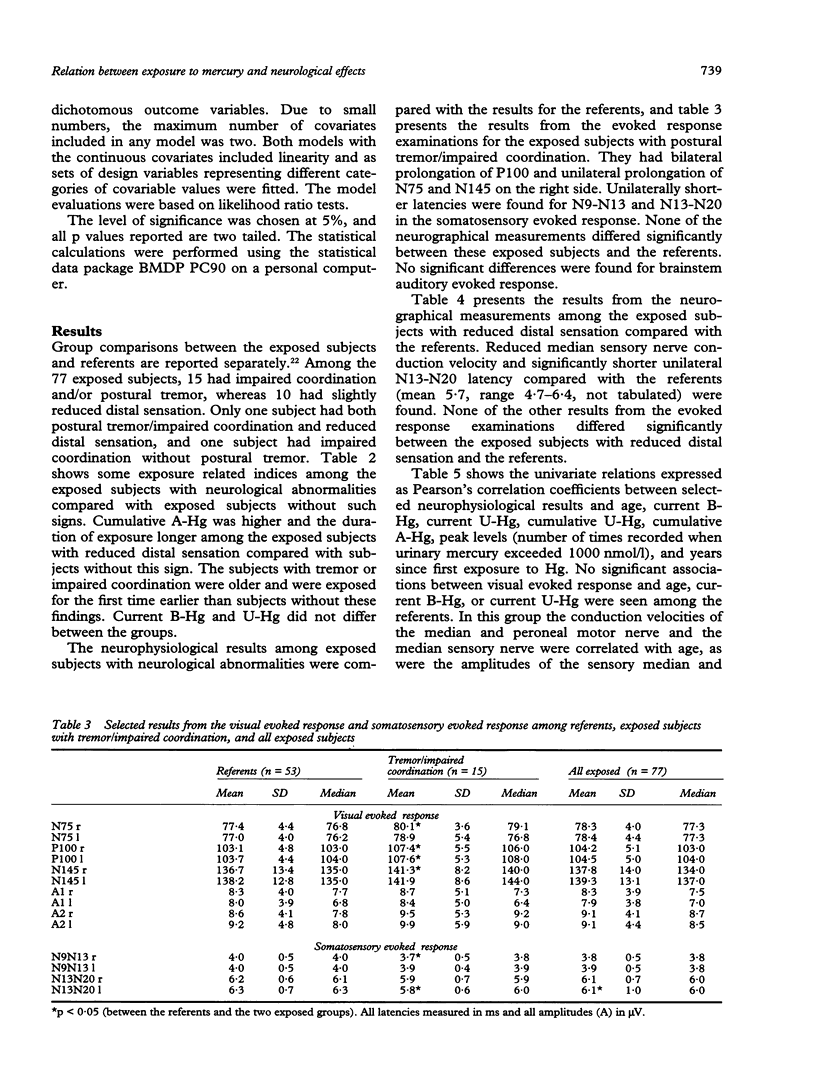
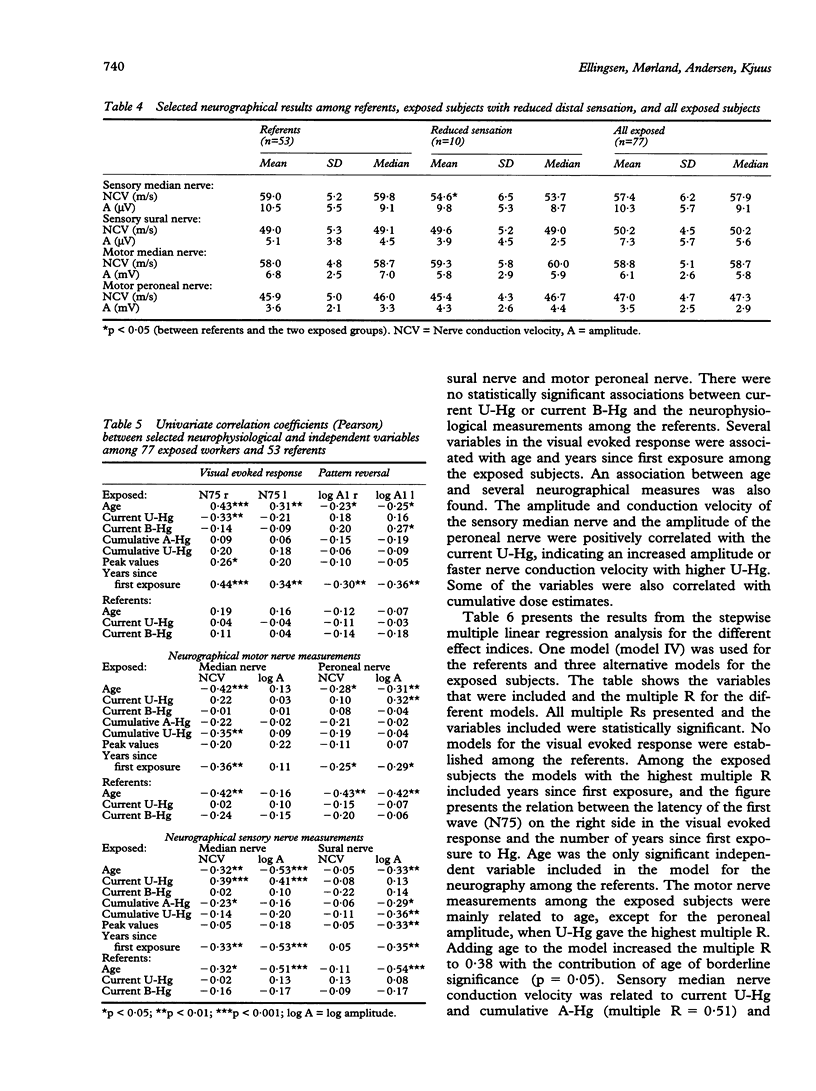
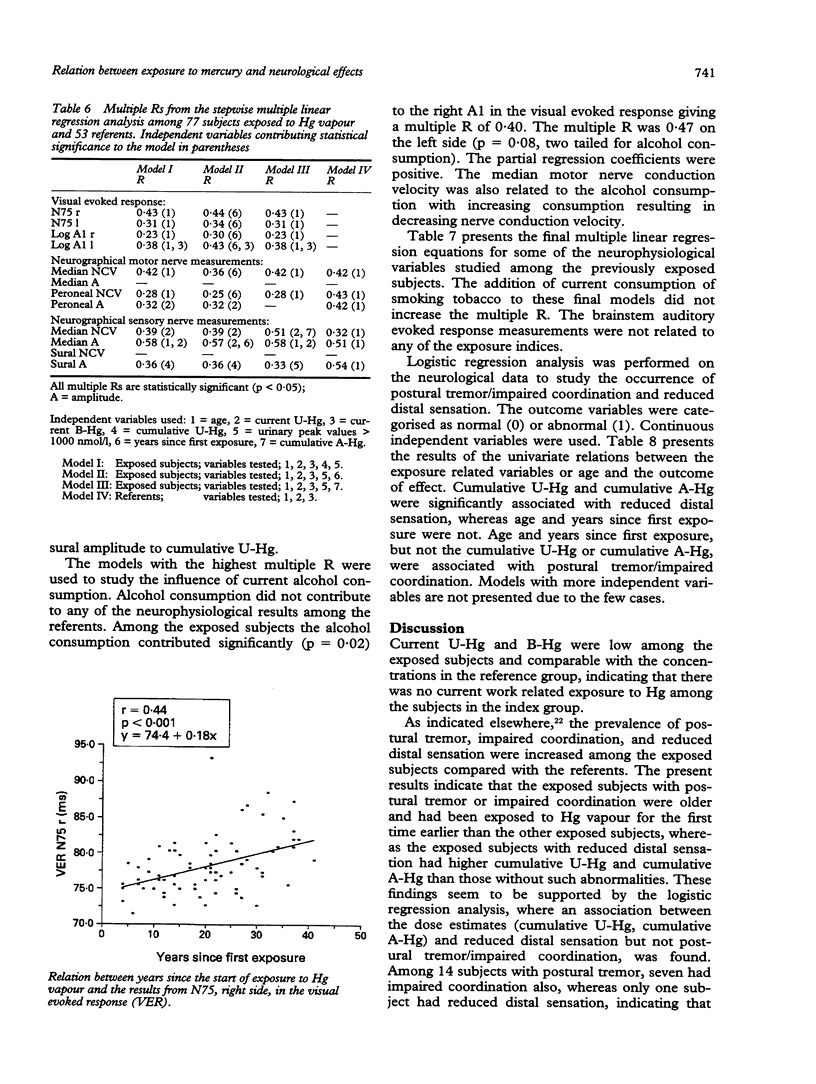
A cross sectional study of aspects of their neurology was carried out on 77 chloralkali workers previously exposed to mercury (Hg) vapour and compared with 53 age matched referents. The chloralkali workers had been exposed for an average of 7.9 years at a concentration of 59 micrograms Hg/m3 in the working atmosphere. The individual mean urinary concentration of Hg for each year of exposure was 531 nmol Hg/1. On average the exposure had ceased 12.3 years before the examinations. Both the median sensory nerve conduction velocity and the amplitude of the sural nerve were associated with measures of cumulative exposure to Hg. An association was also found between years since first exposure to Hg and aspects of the visual evoked response. Previously exposed subjects with postural tremor or impaired coordination also had alterations in visual evoked response. These results may indicate an effect of previous exposure to mercury vapour on the nervous system, possibly in the visual pathway, cerebellum, and the peripheral sensory nerves.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. W., Cavender G. D., Levine S. P., Langolf G. D. Asymptomatic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in workers exposed to elemental mercury. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1168–1174. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. W., Kallenbach L. R., Fine L. J., Langolf G. D., Wolfe R. A., Donofrio P. D., Alessi A. G., Stolp-Smith K. A., Bromberg M. B. Neurological abnormalities associated with remote occupational elemental mercury exposure. Ann Neurol. 1988 Nov;24(5):651–659. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman L. J., Sauter S. L., Henning R. A., Dodson V. N., Reddan W. G., Matthews C. G. Differences in frequency of finger tremor in otherwise asymptomatic mercury workers. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Dec;47(12):838–843. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.12.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg R. L., Vogt R. L., Smith A. B., Brondum J., Brightwell W. S., Hudson P. J., McManus K. P., Hannon W. H., Phipps F. C. Effects of elemental mercury exposure at a thermometer plant. Am J Ind Med. 1991;19(4):495–507. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700190407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsen D. G., Holland R. I., Thomassen Y., Landro-Olstad M., Frech W., Kjuus H. Mercury and selenium in workers previously exposed to mercury vapour at a chloralkali plant. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Aug;50(8):745–752. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.8.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer R. F., de Ribaupierre Y., Guillemin M. P., Berode M., Lob M. Measurement of hand tremor induced by industrial exposure to metallic mercury. Br J Ind Med. 1983 May;40(2):204–208. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves R. J., Evans J. G., Janota I., Magos L., Cavanagh J. B. Persistent mercury in nerve cells 16 years after metallic mercury poisoning. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;14(6):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1988.tb01336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He F. S., Zhow X. R., Lin B. X., Xiung Y. P., Chen S. Y., Zhang S. L., Ru J. Y., Deng M. H. Prognosis of mercury poisoning in mercury refinery workers. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1984 Apr;13(2 Suppl):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh J. B., Greenwood M. R., Clarkson T. W., Allen J., Demuth S. The effect of ethanol on the fate of mercury vapor inhaled by man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosta L., Byrne A. R., Zelenko V. Correlation between selenium and mercury in man following exposure to inorganic mercury. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):238–239. doi: 10.1038/254238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm O., Pratt H. Subclinical effects of exposure to inorganic mercury revealed by somatosensory-evoked potentials. Eur Neurol. 1985;24(4):237–243. doi: 10.1159/000115801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langauer-Lewowicka H., Kazibutowska Z. Multimodality evoked potentials in occupational exposure to metallic mercury vapour. Pol J Occup Med. 1989;2(2):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langolf G. D., Chaffin D. B., Henderson R., Whittle H. P. Evaluation of workers exposed to elemental mercury using quantitative tests of tremor and neuromuscular functions. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1978 Dec;39(12):976–984. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. P., Cavender G. D., Langolf G. D., Albers J. W. Elemental mercury exposure: peripheral neurotoxicity. Br J Ind Med. 1982 May;39(2):136–139. doi: 10.1136/oem.39.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lille F., Hazemann P., Garnier R., Dally S. Effects of lead and mercury intoxications on evoked potentials. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1988;26(1-2):103–116. doi: 10.3109/15563658808995401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nylander M., Friberg L., Lind B. Mercury concentrations in the human brain and kidneys in relation to exposure from dental amalgam fillings. Swed Dent J. 1987;11(5):179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piikivi L., Tolonen U. EEG findings in chlor-alkali workers subjected to low long term exposure to mercury vapour. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Jun;46(6):370–375. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.6.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels H., Abdeladim S., Braun M., Malchaire J., Lauwerys R. Detection of hand tremor in workers exposed to mercury vapor: a comparative study of three methods. Environ Res. 1989 Aug;49(2):152–165. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(89)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro I. M., Cornblath D. R., Sumner A. J., Uzzell B., Spitz L. K., Ship I. I., Bloch P. Neurophysiological and neuropsychological function in mercury-exposed dentists. Lancet. 1982 May 22;1(8282):1147–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R., Valciukas J. A., Rosenman K. D. Peripheral neurotoxicity in workers exposed to inorganic mercury compounds. Arch Environ Health. 1987 Jul-Aug;42(4):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Vorwald A. J., Patil L. S., Mooney T. F., Jr Effects of exposure to mercury in the manufacture of chlorine. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1970 Nov-Dec;31(6):687–700. doi: 10.1080/0002889708506315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroom F. Q., Greer M. Mercury vapour intoxication. Brain. 1972;95(2):305–318. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



