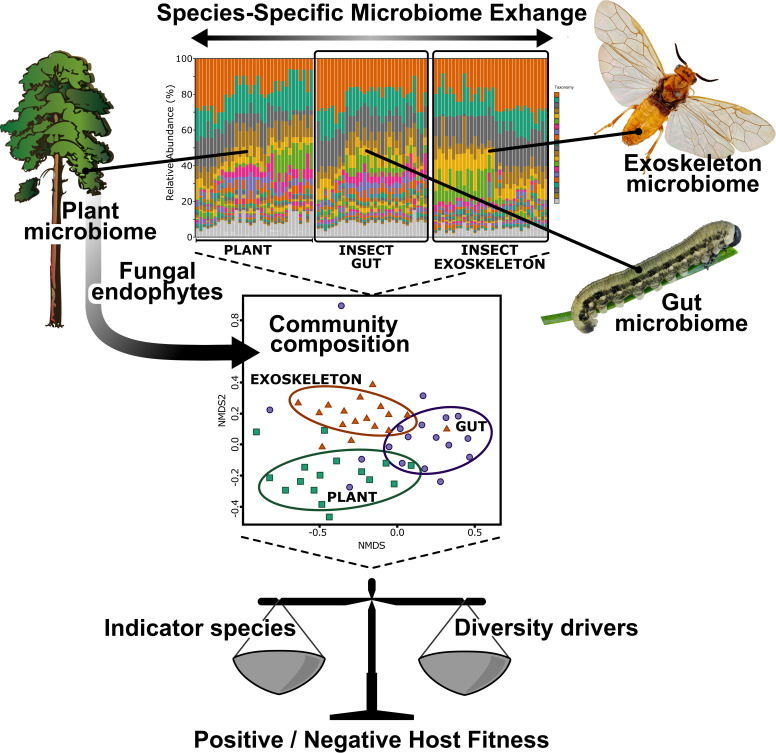
FIG 1.
Microbiome exchange and the interactions between microbial communities of plants and insect herbivores. The microbial interaction between each species of plant and insect is likely highly specific and dependent on the insect’s feeding mode and environmental conditions. Endophytic fungi may play an important role by producing secondary metabolites that are toxic to the insect herbivores. However, together with endophytic bacteria, they can also become part of the insect gut microbiome. Experiments revealing the microbial community structures will enable the identification of the drivers of diversity and the indicator strains for increasing or reducing the fitness of each host as well as the further manipulation of the microbiome exchange.