Abstract
Primary immune deficiencies (PIDs) are genetic disorders impacting the appropriate development or functioning of any portion of the immune system. The broad adoption of high-throughput sequencing has driven discovery of new genes as well as expanded phenotypes associated with known genes. Beginning with the identification of WAS mutations in patients with severe Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome, recognition of WAS mutations in additional patients has revealed phenotypes including isolated thrombocytopenia and X-linked neutropenia. Likewise RAC2 patients present with vastly different phenotypes depending on the mutation–ranging from reticular dysgenesis or severe neutrophil dysfunction with neonatal presentation to later onset common variable immune deficiency. This review examines genotype-phenotype correlations in patients with WAS (Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome) and RAC2 mutations, highlighting functional protein domains, how mutations alter protein interactions, and how specific mutations can affect isolated functions of the protein leading to disparate phenotypes.
Keywords: Wiskott, Aldrich syndrome, RAC2, mutation, genotype–phenotype
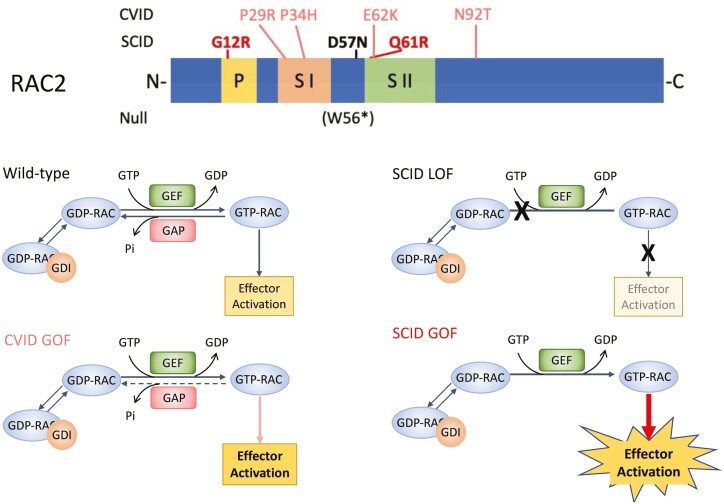
Both gain- and loss-of-function mutations in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) and RAC2 are found throughout the genes and cause immunodeficiencies involving leukocyte actin remodeling. Patient phenotypes differ based on gain or loss of protein function or loss of protein. Identified RAC2 mutations include dominant loss-of-function resulting in severe infantile onset disease similar to leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD-like LOF) in which RAC2 cannot activate downstream effectors (black), dominant gain-of-function causing severe combined immune deficiency (SCID GOF) with constitutively activate RAC2 (bold red), and prolonged activated RAC2 causing common variable immune deficiency (CVID GOF) in which RAC2 fails to rapidly hydrolyze GTP but maintains intrinsic hydrolysis (salmon).
Graphical Abstract
Both gain- and loss-of-function mutations in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) and RAC2 are found throughout the genes, causing immunodeficiencies involving leukocyte actin remodeling. Patient phenotypes differ based on gain or loss of protein function or loss of protein. This review highlights the correlation between WAS and RAC2 mutations and patient presentations and explores the expanding cellular roles recognized for the two proteins.
Introduction
The immune system is dynamic with constant surveillance and response to pathogens: migration toward a wound or infection, phagocytosis, antigen presentation, formation of immune synapse, and cytokine/chemokine signaling are just a few of the ongoing events. A breakdown in any of these may lead to recurrent infections leading a patient to be referred for immune evaluation. In the current era of next-generation, high-throughput sequencing (NGS) recognition of genetic variants is common; the current, curated list of genes causing inborn errors of immunity (IEI) maintained by the International Union of Immunologic Societies currently recognizes variants in 453 genes [1]. Validating pathogenicity and placing these variants in the context of disease phenotypes, however, is frequently challenging. Identification of autosomal recessive mutations, either loss of function (LOF) or null, causing specific diseases has contributed significantly to our understanding of pathways and mechanisms within the immune system. Concurrently, knock-out mouse models and cell lines have been used to evaluate the role of specific proteins in observed cellular phenotypes. In contrast, heterozygous missense mutations require functional validation to prove causality. In silico predictions from NGS data may suggest pathogenicity but exactly how a specific mutation disrupts the gene or protein product requires careful in vitro analysis.
Actin in primary immune deficiencies
Variants identified by whole exome or whole genome sequencing have expanded proteins and pathways recognized to be critical for proper immune homeostasis and activation. Included among these are genes involved in actin cytoskeleton assembly and remodeling which allow migration, phagocytosis, and T- and B-cell receptor signaling (reviewed in Ref. [2]). Actin is present intracellularly in two forms, monomeric or G-actin, and filamentous, F-actin. Rapid assembly of F-actin is required for cellular movement including chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and immune synapse formation while concurrent disassembly at the trailing end replenishes the G-actin pool. Since the recognition of WAS as the disease gene for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) and its role in actin assembly, mutations in more than 20 genes have been identified encoding proteins involved in actin formation and remodeling leading to diseases of immune dysregulation (reviewed in Refs. [2, 3]). This review will focus on two members of the actin-regulatory environment within immune cells, WASP and RAC2. Both are members of the ubiquitously expressed larger protein families, WASP-like proteins and Rho family of GTPases respectively, however, both WASP and RAC2 expression are restricted to hematopoietic compartment.
WASP
WASP protein and actin interaction
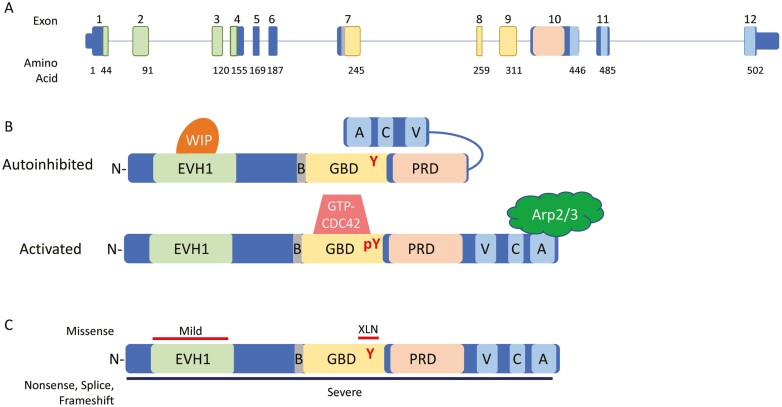
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) is 502 amino acids encoded by the 12 exon WAS gene (Fig. 1A). Several conserved domains are present within the protein including the N-terminal ENA/Vasp homology 1 domain (EVH1), an 11 amino acid basic domain (B), the GTPase binding domain (GBD), a proline rich domain (PRD), and the C-terminal VCA domain complex composed of the verprolin homology region (V), cofilin homology region (C), and acidic sequence (A) (Fig. 1B).
Figure 1:
WAS gene and WASP protein. (A) Genomic schematic for the WAS gene. Exons are numbered above; the number of the last amino acid coded in each exon is shown below. Exons encoding protein domains are colored accordingly. (B) Linear protein cartoon of WAS showing inhibited structure (top) with Y291 buried by folding of VCA domains and activated (bottom) with removal of WIP and binding of GTP-CDC42 allowing interaction with Arp2/3 complex. (C) Location of mutations leading to differing phenotypes. Missense mutations shown on top with red bars corresponding to phenotype, nonsense, splice, and frameshift mutations occur throughout, denoted by black bar below. Abbreviations: N, N-terminus: EVH1, ENA/Vasp homology 1 domain; B, basic domain: GBD, GTPase binding domain; PRD, proline rich domain; V, verprolin homology region; C, cofilin homology region; A, acidic sequence; WIP, WASP interacting protein.
Under basal, autoinhibited conditions, WASP-interacting protein (WIP) is bound to the EVH1 domain. WIP acts as a chaperone for WASP and association with WIP is critical for WASP stability [de la Fuente]. In T cells, the majority of WASP is bound to WIP [4] and T cells from Wip−/− mice have severely decreased levels of WASP [4] indicating appropriate WIP/WASP interaction is critical for proper WASP levels in the cell. Without input signals, WIP-bound-WASP is maintained in a quiescent, autoinhibited state via the C-terminal VCA domain binding to the GBD [5] (Fig. 1B). The structure of the folded protein results in tyrosine-291 (Y291) being located between the GBD and VCA regions, inaccessible to tyrosine kinases [5]. Signals from extracellular receptors causing actin remodeling rely on small GTPases of the Rho family including CDC42, RAC1, and RAC2. Upon activation, these proteins release GDP and bind GTP allowing binding and activation of downstream effectors. Activation of WASP can occur via activated, GTP-bound-CDC42 binding to the GBD causing a conformational change releasing the C-terminus and allowing interaction with Arp2/3 complex [5].
WAS mutations
Mutations in the X-linked gene, WAS, encoding the WASP, are the cause of the allelic diseases WAS [6–9] and X-linked neutropenia (XLN) [10]. Classical WAS patients present with thrombocytopenia, small platelet volume, severe eczema, increased susceptibility to pyogenic and opportunistic infections, and increased risk of autoimmune disease and cancer. Recurrent upper respiratory infections are common while more severe cases have a broader range of pathogens including bacterial, fungal (candidiasis, aspergillosis, Pneumocystis jirovecci), and viral (EBV, HSV, CMV, HPV, VZV) [11–13]. A scoring system was developed [14] with scores ranging from 1 (mildest) to 5 (most severe, including autoimmunity and/or malignancy). In older literature, patients on the more severe end of the spectrum having scores of 3–5 were referred to as WAS. Patients with milder presentation, thrombocytopenia and mild eczema or isolated thrombocytopenia, received the diagnosis of X-linked thrombocytopenia (XLT) and had scores of 1 or 2. It has been shown, however, that XLT patients may progress to a more severe phenotype developing autoimmunity or malignancy; in one large international XLT cohort, 29 of 173 patients (16.8%) exhibited score progression to 5 [15]. Accordingly the disease is now referred to as “severe” or “mild” WAS [13]. Treatment using hematopoietic stem cell transplant [16] or gene therapy [17–20] appears curative, extending the survival of severe WAS patients beyond childhood or early adolescence although ongoing reduced platelet counts have been observed in gene therapy treated patients [17, 20].
More than 400 different mutations have been identified in WAS encompassing all mutation types. Null mutations caused by stop codons, frameshifts, and splice mutations in exons 1 through 10 are common within severe WAS and lead to nonsense-mediated decay of WAS transcript and loss of protein product. Mutations occurring in exons 11 or 12 lead to truncation of the protein, deletion of the acidic region, and loss of Arp2/3 interaction. Missense changes are most frequently observed in the N-terminal EVH1 domain [21] and have been demonstrated to impair WASP–WIP interactions [22] (Fig.1C). WIP is required to stabilize WASP and maintain it in the autoinhibited conformation. Consequently, these missense mutations lead to decreased levels of WASP [4]. Flow cytometric and western blot studies from patients with missense mutations frequently show severely reduced levels of WASP supporting this hypothesis [23, 24]. Grouping patients by presence or absence of normal size WASP provides the strongest genotype/phenotype correlation of disease severity. Protein negative or truncated protein patients present earlier and with more severe disease [11, 12, 25] while protein positive patients present with milder WAS [11, 23]. There have been missense mutations outside of the EVH1 domain reported such as p.A236G [23] and p.M307V [23, 24], however, careful examination reveal they may create new splice donor sites leading to a frameshifting splice defect rather than missense mutation. Consistent with this, there was reduced protein observed by western blot in cells from a patient carrying the p.A236G mutation [23].
In contrast to the loss of function mutations described above, a cluster of missense mutations occur in the GBD region of the protein leading to severe congenital XLN. These patients present with recurrent bacterial infections, severe neutropenia, and monocytopenia, however, they maintain normal platelet counts and volume. The first patients to be described were hemizygous for p.L270P which was demonstrated to create a stable protein [10]. The mutant protein failed to establish the autoinhibited conformation allowing the C-terminal VCA region to be accessible to bind the Arp2/3 complex and drive actin polymerization [10]. The mutant WASP was constitutively active, independent of GTP-bound CDC42 [10] resulting in a “gain of function” (GOF) protein. Additional mutations in males with severe neutropenia, some with myelodysplasia, have been identified in the same region including p.R268W [26], p.S271F [26], p.S272P [27], p.I290T [28], and p.I294T [27]. Bone marrow examination in some patients reveal abnormal megakaryocyte morphology, impaired granulopoiesis, myeloid maturation arrest, and a greater percentage of apoptotic cells [27]. Similar to p.L270P, the variants evaluated exhibited CDC42-independent actin polymerization demonstrated by increased levels of F-actin.
Neutrophils from murine XLN models carrying mutations corresponding to p.L270P and p.I294T, demonstrated constitutive phosphorylation of Y293 (corresponding to human Y291), increased cytoplasmic and cortical F-actin, and increased membrane ruffling [29]. Lymphocytes from XLN mice are capable of chemokine-directed migration equivalent to wild-type mouse lymphocytes, however, both T and B cells exhibit reduced spreading, a cytoskeletal response to T- or B-cell receptor activation [30]. Further, both T- and B-XLN cells had increased receptor-induced apoptosis and increased genomic instability compared to wild-type [30].
RAC2
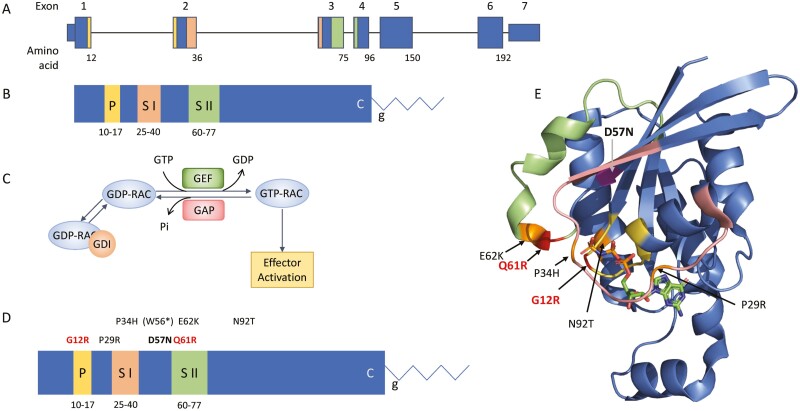
RAC2 is a member of the RHO-subfamily of GTP hydrolases. The RAC2 gene is 7 exons spanning 19 000 bases on chromosome 22 (Fig. 2A). It encodes a highly conserved protein of 192 amino acids with several domains and motifs critical to its function (Fig. 2B) including the phosphate binding loop, and the Switch I and Switch II domains—unstructured regions which undergo conformational shifts upon nucleotide binding and interact with downstream effectors such as p67phox[31] and PLCγ2 [32, 33]. Post-translational processing includes addition of a c-terminal geranyl–geranyl moiety at the CXXL prenylation motif. GTP hydrolases are small proteins which cycle between guanine diphosphate (GDP) bound inactive and guanine triphosphate (GTP) bound active states allowing them to act as on/off switches and activating downstream effector proteins. In the absence of input signals, the C-terminal geranyl–geranyl group will bind to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor (GDI) which prevents nucleotide binding and membrane association. Extracellular signals through G-protein coupled receptors or receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of guanine exchange factors (GEFs) such as DOCK2 [34], PREX1, and VAV1 [35] which release GDP-RAC2 from the GDI protein and remove GDP allowing the binding of GTP (GTP-RAC2) [36, 37] (Fig. 2C). The active RAC2 then binds to downstream effectors such as p67phox inducing activation of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase [31] or PAK1 leading to changes in actin cytoskeleton [38]. GTP-RAC2 is then bound by GAP proteins which drive GTP → GDP hydrolysis inactivating the protein. The GEF/GAP-mediated nucleotide binding and hydrolysis is rapid, a critical feature for actin remodeling and cellular movement.
Figure 2:
RAC2 gene and protein. (A) Genomic schematic for RAC2. Exons are numbered above; the number of the last amino acid codon in each exon is shown below. Exon 7 is untranslated. (B) Linear protein cartoon of RAC2 showing locations of specific domains. P, P-loop (yellow); S I, Switch I domain (peach); S II, Switch II domain (green); C, CXXL prenylation motif; g, geranylgeranyl moiety. (C) RAC2 bound to GDI is unable to interact with effectors. Release from GDI and interaction with GEFs removes GDP allowing binding of GTP. RAC2-GTP can then interact with downstream effectors. RAC2-GAP interactions lead to hydrolysis of GTP. (D) Reported RAC2 mutations shown on linear RAC2 protein with domains noted. Mutations in bold are constitutively active (red) or inactive (black). Mutation in parenthesis undergoes nonsense-mediated decay and does not result in a protein product. The remaining activating mutations maintain intrinsic GTP hydrolysis. (E) Three-dimensional structure of the related RAC1 (3TH5) [39] showing domains colored as in B and location of mutations. GTP shown as sticks.
RAC2 mutations
The initial RAC2 mutation, p.D57N, was identified in an infant who presented in the first weeks of life with severe bacterial infections, poor wound healing, and neutrophilia resembling leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) [40] (Table 1, Fig. 2D). Western blot analysis revealed decreased total RAC2 protein in patient neutrophils. [41]. Biochemical studies demonstrated the mutant protein was able to bind GEF proteins, however, GEF binding did not increase GDP-GTP exchange [42]. Further, p.D57N had a high rate of GTP dissociation preventing activation and resulting in a protein with minimal activity [42]. In 2010 a second patient was identified via newborn screening [43, 44] having severely reduced T-cell receptor excision circle (TRECs) a hallmark of recent thymic emigrants. Functional studies on the p.D57N patient neutrophils demonstrated impaired chemotaxis, reduced phagocytosis of opsonized erythrocytes and defective adhesion and rolling on GlyCAM-1 [40]. One primary downstream effector of RAC2 is the NADPH oxidase component, p67phox [31]. Stimulation of neutrophils with the formyl peptide Met-Leu-Phe (fMLF) will activate RAC2 through its G-protein coupled receptor, FPR1, leading to assembly and activation of the NADPH oxidase complex and production of superoxide. Studies using p.D57N expression constructs showed decreased superoxide production in response to fMLF, impaired chemotaxis and defective GTP binding [40]. Expressing the mutation in Rac2-deficient, Rac1-sufficient NIH/3T3 cells impacted cellular activity as revealed by altered cell growth, morphology, and membrane ruffling indicating the mutation is dominant-negative [40].
Table 1:
reported RAC2 mutations
| cDNA | Protein | Age at presentation | Presentation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.169C > A | p.D57N | 1 mo | LAD-like | [40, 41] |
| c.169C > A | p.D57N | NBS | LAD-like | [43, 44] |
| c.168G > A# | p.W56* | 1 yr | CVID | [45] |
| c.168G > A# | p.W56* | 7 yr | CVID | [45] |
| c.86C > G | p.P29R | 1 yr | CVID | [46] |
| c.101C > A | p.P34H | 2 yr | CVID | [47] |
| c.101C > A | p.P34H | 2 yr | CVID | [47] |
| c.101C > A | p.P34H | 2 yr | CVID | [47] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | 2 mo | CVID | [48] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | NBS | CVID | [48] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | 4 yr | CVID | [48] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | n.d. | CVID | [49] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | 9 yr | CVID | [49] |
| c.184G > A | p.E62K | 1.5 yr | CVID | [49] |
| c.275A > C | p.N92T | 4 mo | CVID | [50] |
| c.34G > A | p.G12R | 3 d | SCID | [51] |
| c.34G > A | p.G12R | 10 d | SCID | [51] |
| c.34G > A | p.G12R | 9 d | SCID | [51] |
| c.182A > G | p.Q61R | 2 d | SCID | [52] |
# homozygous, NBS, newborn screening; n.d., not determined.
Subsequently a sibling pair from a consanguineous family homozygous for p.W56* [45] was identified. This mutation occurs early in the transcript and is predicted to cause nonsense-mediated decay leading to absence of any RAC2 protein (Fig. 2D). In contrast to patients with dominant LOF mutation, these homozygous-null siblings presented as young children (Table 1) with recurrent upper and lower respiratory infections leading to the development of bronchiectasis. Immunologically, they are notable for both T- and B-cell lymphopenia. Similar to the second p.D57N patient, these two had reduced TRECs compared to age-matched controls [45]. Importantly, no immune phenotype was reported for the parents, both carriers of p.W56*.
The first gain-of-function RAC2 mutation was identified in a 3 member, 2-generation family carrying a Switch I domain mutation, p.P34H [47] (Table 1). Subsequently, 6 patients from 4 families were identified carrying the Switch II domain mutation, p.E62K [48, 49]. Two additional isolated cases have been reported carrying p.N92T [50] and p.P29R [46] (Table 1). Phenotypically, the patients were diagnosed with common variable immune deficiency (CVID) with all but one characterized by recurrent respiratory infections including sinusitis and pneumonias, frequently leading to bronchiectasis. Three of the p.E62K patients were from a single, three-generation family in which the father and grandfather both underwent lung transplantation due to recurrent respiratory infections leading to structural lung disease and end-stage pulmonary failure [49]. One p.E62K patient was detected by newborn screening due to absent TRECS [48], however, all patients tested exhibited significant T- and B-cell lymphopenia [48, 49].
In contrast to the p.D57N patients, evaluation of RAC2-GOF patient neutrophils revealed excess superoxide production in response to fMLF [46–48, 50] indicating an activating mutation. Compared to wild-type RAC2, cells transfected with p.E62K exhibited elevated basal superoxide production [48, 50], increased AKT phosphorylation without stimulation [48] and increased PAK1-protein binding domain-associated RAC2 [48, 49], all of which are indicative of active, GTP-bound RAC2 [47, 48]. Biochemical studies on isolated protein revealed the p.E62K mutation maintained intrinsic rates of GDP-GTP exchange and GTP hydrolysis, however, both GEF-mediated nucleotide exchange and GAP-mediated GTP hydrolysis were impaired by the mutation resulting in sustained GTP—RAC2 association and prolonged RAC2-driven activation of downstream effectors [48]. Highlighting the role of RAC2 in actin cytoskeletal formation, several studies using primary patient cells revealed visible intracellular vacuoles, increased macropinocytosis, increased levels of F-actin, and impaired chemotaxis [48]. These findings are consistent with an active RAC2 molecule that permits continued actin polymerization due to its dependence on intrinsic rather than GAP-mediated GTP hydrolysis.
In 2020, Lagresle-Peyrou and colleagues [51] identified 3 individuals from 2 families who presented in the first week of life with sepsis, profound pancytopenia, and hypoplastic bone marrow (Table 1). They were diagnosed with reticular dysgenesis (RD), a form of severe combined immunodeficiency in which patients lack both T cells and neutrophils. Genetic evaluation identified a heterozygous RAC2 mutation, c.34G>A, p.G12R. An additional patient was reported by Stern and colleagues [52] who presented at 2 days with RD and a RAC2 mutation, c.182A > G, p.Q61R. Transduction of CD34+ human cord blood cells with RAC2 p.G12R impaired cell proliferation compared to WT-transduced cells with p.G12R cells exhibiting altered mitochondrial membrane potentials, increased apoptosis, and reduced differentiation [51]. Western blot of transduced cells showed equivalent levels of mutant and wild-type RAC2 protein indicating normal stability of the mutant protein [51]. Functional studies performed using p.Q61R revealed increased superoxide production in the absence of stimulation and a more than 10-fold increase in superoxide production in response to PMA [52]. Unlike CVID RAC2-GOF mutations, mutations at G12 and Q61 are comparable to well characterized, somatic RAS mutations. The third most common somatic KRAS mutation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is p.G12R while p.Q61R is seen in more than 40% of NRAS and HRAS mutated cancers [53]. Both mutations lead to loss of GAP-mediated GTP hydrolysis and a high rate of nucleotide exchange resulting in constitutively active proteins [53, 54]. The profound effects of constitutively active mutations on mitochondria and hematopoietic stem cells leads to loss of both bone marrow cellularity and circulating lymphoid and myeloid cells and drives the phenotype observed in these 4 patients.
A comparison of reported RAC2 mutations is provided in Table 1. The constitutively active GOF mutations which prevent both GAP-mediated and intrinsic hydrolysis are adjacent to the GTP binding site (Fig. 2E). The LOF p.D57N mutation impedes binding of GTP preventing the active form of the protein and activation of downstream effectors. The recognized CVID GOF missense mutations occur within the disordered Switch I and Switch II domains with the exception of the p.N92T mutation which is adjacent to Switch II in the three-dimensional structure. The switch regions undergo conformational change upon binding of GTP allowing effector interactions. Functional studies performed on p.E62K have shown hinderance of GAP interactions leading to decreased GAP-mediated hydrolysis while maintaining intrinsic hydrolysis [48]. The homozygous p.W56* leading to total loss of RAC2 in the patients reveals some level of redundancy for RAC2, possibly via the closely related, ubiquitously expressed, RAC1.
Cellular roles for WASP and RAC2
While examination of altered WASP function for individual mutations has been performed, broader roles of WASP in immune cells are recognized. Dysregulated actin cytoskeleton impacts cellular migration and podosome formation of leukocytes. Actin-intense immune cell events such as immune synapse formations in T cells [55, 56], B cells [57], NK cells [58], and dendritic–/NK-cell interactions [59] have all been demonstrated to be disrupted in WASP-deficient cells. Defective autophagy and mitophagy was seen in cells from Was-deficient mice and WAS patients [60] including reduced actin cages surrounding disrupted mitochondria [60]. Consistent with this finding, WAS patient cells exhibited fragmented mitochondria rather than extensive mitochondrial networks indicating a role for WAS in maintenance of mitochondrial homeostasis [61]. While the above roles for WASP are cytoplasmic and membrane related, a critical role for WASP in the nucleus has also been demonstrated. Altered TH0 – TH1 transition was demonstrated to be caused by decreased WASP binding and altered epigenetic programming at the TBX21 promoter with subsequent decreased TBX21 transcript under TH1 promoting conditions [62]. Subsequently it was demonstrated that WASP is required for hSWI/SNF-complex chromatin remodeling that occurs during TH0 – TH1 transition [63]. Recently, Yuan et al. [64] demonstrated a role for WASP as a regulator of RNA splicing and transcriptional control of splicing factors. Examination of the broader dysregulated transcriptome in patients with WAS mutations may help further elucidate underlying mechanisms for patient phenotypes.
Given the recent identification of RAC2 mutations and still limited numbers of reported RAC2 patients, the breadth of studies performed remains small. It is possible that RAC2 patients may also exhibit similar cellular phenotypes as WAS patients surrounding autophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, and transcriptional regulation. Already RAC2 regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis has been demonstrated. Constitutively active RAC2 G12R patient fibroblasts demonstrated disrupted mitochondrial network [51], downregulation of RAC2 in BCR-ABL leukemic progenitor/stem cells caused a decreased in mitochondrial membrane potential [65], and T cells from patients deficient in the RAC2 GEF, DOCK2, have mitochondrial defects [66]. Certainly additional studies will extend identified roles for RAC2.
Assessment of identified variants
Variants identified by NGS can be evaluated across four criteria—transcript, protein, function and location, and effect on cellular function. Some or all of these assays may be used to determine pathogenicity. While in silico analysis provides a prediction of the change in coding sequence, it frequently ignores the effect of the nucleotide change on transcriptional regulation. As mentioned above, careful examination of the p.A236G and p.M307V WAS variants suggests the mutations lead to a splicing defect rather than a missense change. In this case, amplification of full-length WAS cDNA from patient cells can determine the primary transcript produced and quantitative RT-PCR may be used to demonstrate reduced or absent WAS transcript levels. The effect of a variant on the protein can be evaluated using western blotting to determine the presence and size of the target protein as well as examination of markers of activation such as pAKT for activating RAC2 mutations [48, 49]. Flow cytometry requires fewer cells than western blots and can be used to quantify relative protein levels, activation of target proteins, or presence of F-actin although it cannot determine the size of the mutant protein. Determination of the relative level of WASP or RAC2 protein does not itself indicate gain or loss of function, additional assays are necessary to demonstrate the effect of the variant on the protein. Using either patient cells or transfection assays, immunoprecipitation may be performed to look for protein binding partners such as PAK1-RAC2 binding, WIP-WASP, or WASP-Arp2/3. Additional assays for examining protein-specific functions that have been reported include GDP/GTP exchange and GTP hydrolysis for RAC2 [48].
Since both WASP and RAC2 participate in actin formation, the effect of the mutant protein on actin remodeling is often demonstrated by microscopy. Fluorescent microscopy can visualize immune synapse formation, presence of F-actin under basal or stimulated conditions, actin cages surrounding damaged mitochondria [61], membrane ruffling, formation of macropinosomes, or uptake of FITC-dextran [48]. Time-lapse video of cellular chemotaxis allows not only a quantitative analysis of how quickly cells migrate but also a qualitative analysis of leading and trailing edges of the cells, again a marker of actin assembly/disassembly [48].
Further assays involving the role of WASP or RAC2 in the nucleus and effect on transcription or epigenetics rely on high-throughput, NGS techniques such as RNA-Seq for quantification of transcripts, ChIP-Seq for DNA binding and epigenetic alterations, or ATAC-Seq to demonstrate alterations of chromatin accessibility. As more evidence accumulates for the role of actin within the nucleus, additional assays will likely demonstrate expanded roles for WASP and possibly RAC2 in the regulation of target transcriptional programs.
Broader considerations
The first identification of WAS mutations occurred almost three decades ago leading to several large cohort studies exploring range of mutations, protein expression, and in vitro function as well as describing genotype/phenotype correlations [11, 12, 16, 23]; in contrast, <20 RAC2 patients have been reported [40, 43–52]. Studies which expand clinical phenotypes of identified RAC2 patients and correlate in vitro functional studies with presentation and disease course are still lacking. Additionally, it is likely that patients with mutations in other WASP- or RAC2-interacting proteins will be identified. Recognizing phenotypic differences and similarities among these patients will emphasize particular roles each protein plays in actin regulation. One example of a RAC2-interacting genes is the RAC2 GEF, DOCK2. Bi-allelic DOCK2 mutations lead to immune deficiency and altered cytoskeleton dynamics [67] but have additional, non-hematopoietic findings including increased viral replication in patient fibroblasts [67].
Expanding beyond the demonstrated epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of target genes by WASP, more recently nuclear actin was shown to be required for RNA polymerase II clustering and colocalization at serum-response genes [68]. This demonstration of actin involvement in transcription opens the possibility of altered transcriptional regulation in other actinopathies including RAC2. Specific studies such as single cell RNA-Seq, ChIP-Seq, and ATAC-Seq will be required to determine cell-type-specific and target-gene-specific effects of these mutations. To date, only LOF WAS has been evaluated in this way. It will be interesting to see whether the effect of GOF WAS or activating RAC2 mutations on transcription parallel their effects on actin polymerization.
Conclusions
The diverse mutations identified in WAS and RAC2 and the accompanying phenotypes highlight an additional layer of mutation-related pathology (Table 2). Null mutations leading to absent protein highlight required functions which are not compensated by other proteins. In the case of WAS, these mutations lead to a severe phenotype with early onset while in RAC2, due to some compensation by RAC1, the phenotype is less severe although still significant. Truncation mutations deleting the C-terminus of WASP identify critical functions of the deleted domains as highlighted by WAS mutations deleting the acidic region critical for Arp2/3 binding. Missense mutations impact interactions with protein partners: WIP or CDC42 for WASP, GEFs or GAPs for RAC2. RAC2 missense changes may also directly affect binding of the guanine nucleotide which dictates conformation and activity of the protein. In both genes, resulting actin assembly defects have significant effects on immune cell stability, migration, and response to extracellular stimuli. Consistent for both WASP and RAC2 GOF mutations is increased levels of F-actin, impaired cellular migration and, in the case of constitutively active RAC2 and GOF WAS, increased apoptosis. The difference in severity of phenotypes between WASP and RAC2 null patients suggests some compensation for RAC2, possibly via RAC1, that is not present for WASP. One additional factor for RAC2 mutations is the impact of the mutation on intrinsic hydrolysis of GTP. Mutations leading to stable proteins which abrogate intrinsic hydrolysis such as p.G12R and p.Q61R, result in constitutively active proteins with profound effects on all leukocytes evidenced by bone marrow hypoplasia. The disease presentations observed across WAS and RAC2 mutated patients highlight the need to evaluate each genetic variant for its impact on transcript level, protein size and stability, protein activity and binding partners, and effect on cellular function. Thorough studies evaluating mutation effects from transcript through protein function will continue to expand our knowledge beyond isolated genes by recognizing cellular and biologic phenotypes overlapping with other genetic disorders thus allowing recognition of additional genes contributing to genetic heterogeneity.
Table 2:
comparison of phenotypes by mutation type
| Null | Truncation | LOF | Transient GOF | Constitutive GOF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAS disease presentation | Severe WAS | Severe WAS | Mild WAS, may progress to severe | NR | X-linked neutropenia |
| Specific phenotypes | Thrombocytopenia, small platelet volume, severe eczema, susceptibility to pyogenic infections, increased incidence of autoimmune disease, and cancer | Thrombocytopenia ± mild eczema | Severe neutropenia, monocytopenia, normal platelet volume, recurrent bacterial infections, myelodysplasia | ||
| RAC2 disease presentation | CVID | NR | Neonatal LAD-like | CVID | Neonatal SCID, reticular dysgenesis |
| Specific phenotypes | Decreased T cells, decreased B cells, decreased TRECs, recurrent respiratory infections | Neutrophiia, severe bacterial infections, poor wound healing, decreased T cells, decreased TRECs, decreased neutrophil chemotaxis, decreased superoxide to fMLF | Decreased T cells, decreased B cells, decreased TRECs, increased superoxide to fMLF, impaired chemotaxis, increased F-actin | Severe pancytopenia, hypoplastic bone marrow, sepsis, altered mitochondrial function, increased superoxide at baseline, and after PMA | |
NR, not reported.
Acknowledgements
None.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- CMV
cytomegalovirus
- CVID
common variable immune deficiency
- EBV
Epstein-Barr virus
- EVH1
ENA/Vasp homology 1
- fMLF
formyl-methionine-leucine-phenylalanine
- GBD
GTPase binding domain
- GDI
GDP-disssociation inhibitor
- GDP
guanine diphosphate
- GEF
guanine exchange factor
- GOF
gain of function
- GTP
guanine triphosphate
- HPV
human Pappiloma virus
- HSV
herpes simplex virus
- IEI
inborn errors of immunity
- LAD
leukocyte adhesion deficiency
- LOF
loss of function
- n.d.
not determined
- NBS
newborn screening
- NGS
next-generation sequencing
- NR
not reported
- PID
primary immune deficiency
- PRD
proline rich domain
- RD
reticular dysgenesis
- TREC
T-cell receptor excisin circle
- WAS
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- WASP
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein
- WIP
WASP-interacting protein
- XLN
X-linked neutropenia
- XLT
X-linked thrombocytopenia
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Funding
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Author contributions
Not applicable.
Clinical trial registration
Not applicable.
The animal research adheres to the ARRIVE guidelines
https://arriveguidelines.org/arrive-guidelines—Not applicable.
References
- 1. Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Franco JL, Holland SM, et al. Human Inborn errors of immunity: 2022 update on the classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies expert committee. J Clin Immunol 2022, 1, 35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Sprenkeler EGG, Webbers SDS, Kuijpers TW.. When Actin is not actin’ like it should: a new category of distinct primary immunodeficiency disorders. J Innate Immun 2021, 13, 3–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Papa R, Penco F, Volpi S, Gattorno M.. Actin remodeling defects leading to autoinflammation and immune dysregulation. Front Immunol 2021, 11, 604206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. de la Fuente MA, Sasahara Y, Calamito M, Anton IM, Elkhal A, Gallego MD, et al. WIP is a chaperone for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 926–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kim AS, Kakalis LT, Abdul-Manan N, Liu GA, Rosen MK.. Autoinhibition and activation mechanisms of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein. Nature 2000, 404, 151–8. doi: 10.1038/35004513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Derry JMJ, Ochs HD, Francke U.. Isolation of a novel gene mutated in Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. Cell 1994, 78, 635–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Villa A, Notarangelo L, Macchi P, Mantuano E, Cavagni G, Brugnoni D, et al. X-linked thrombocytopenia and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome are allelic diseases with mutations in the WASP gene. Nat Genet 1995, 9, 414–7. doi: 10.1038/ng0495-414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kolluri R, Shehabeldin A, Peacocke M, Lamhonwah A-M, Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Weissman SM, et al. Identification of WASP mutations in patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and isolated thrombocytopenia reveals allelic heterogeneity at the WAS locus. Hum Mol Genet 1995, 4, 1119–26. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.7.1119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Zhu Q, Zhang M, Blaese RM, Derry JM, Junker A, Francke U, et al. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and X-linked congenital thrombocytopenia are caused by mutations of the same gene. Blood 1995, 86, 3797–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Devriendt K, Kim AS, Mathijs G, Frints SG, Schwartz M, Van den Oord JJ, et al. Constitutively activating mutation in WASP causes X-linked severe congenital neutropenia. Nat Genet 2001, 27, 313–7. doi: 10.1038/85886 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Imai K, Morio T, Zhu Y, Jin Y, Itoh S, Kajiwara M, et al. Clinical course of patients with WASP gene mutations. Blood 2004, 103, 456–64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Sullivan KE, Mullen CA, Blaese RM, Winkelstein JA.. A multiinstitutional survey of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Pediatr 1994, 125, 876–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Candotti F. Clinical manifestations and pathophysiological mechanisms of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Clin Immunol 2018, 38, 13–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ochs HD, Filipovich AH, Veys P, Cowan MJ, Kapoor N.. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: diagnosis, clinical and laboratory manifestations, and treatment. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009, 15, 8485–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.10.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Albert MH, Bittner TC, Nonoyama S, Notarangelo LD, Burns S, Imai K, et al. X-linked thrombocytopenia (XLT) due to WAS mutations: clinical characteristics, long-term outcome, and treatment options. Blood 2010, 115, 3231–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-239087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Moratto D, Giliani S, Bonfim C, Mazzolari E, Fischer A, Ochs HD, et al. Long-term outcome and lineage-specific chimerism in 194 patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome treated by hematopoietic cell transplantation in the period 1980-2009: an international collaborative study. Blood 2011, 118, 1675–84. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-319376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Aiuti A, Biasco l, Scaramuzza S, Ferrua F, Cicalese MP, Baricordi C, et al. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Science 2013, 341, 1233151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Ferrua F, Cicalese MP, Galimberti S, Giannelli S, Dionisio F, Barzaghi F, et al. Lentivral haemopoietic stem cell or progenitor cell gene therapy for treatment of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: interim results of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1/2 clinical study. Lancet Haematol 2019, 6, e239–e253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Magnani A, Semeraro M, Adam F, Booth C, Dupré L, Morris EC, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of lentiviral hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell gene therapy for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Nat Med 2022, 28, 71–80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hacein-Bey Abina S, Gaspar HB, Blondeau J, Caccavelli L, Charrier S, Buckland K, et al. Outcomes following gene therapy in patients with severe Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. JAMA 2015, 313, 1550–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Ochs HD, Thrasher AJ.. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006, 117, 725–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Stewart DM, Tian L, Nelson DL.. Mutations that cause the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome impair the interaction of Wiskott=Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) with WASP interacting protein. J Immunol 1999, 162, 5019–24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.162.8.5019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Jin Y, Mazza C, Christie JR, Giliani S, Fiorini M, Mella P, et al. Mutations of the Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP): hotspots, effect on transcription, and translation and phenotype/genotype correlation. Blood 2004, 104, 4010–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Suri D, Rikhi R, Jindal AK, Rawat A, Sudhakar M, Vignesh P, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: a multi-institutional experience from India. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 627651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Ochs HD. Mutations of the Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome Protein affect protein expression and dictate the clinical phenotypes. Immunol Res 2009, 44, 84–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. He M, Saeed MB, Record J, Keszei M, Gonçalves Pinho L, Vasconcelos-Fontes L, et al. Overactive WASp in X-linked neutropenia leads to aberrant B-cell division and accelerated plasma cell generation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2022, 149, 1069–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ancliff PJ, Blundell MP, Cory GO, Calle Y, Worth A, Kempski H, et al. Two novel activating mutations in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein result in congenital neutropenia. Blood 2006, 108, 2182–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-010249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Beel K, Cotter MM, Blatny J, Bond J, Lucas G, Green F, et al. A large kindred with X-linked neutropenia with an I294T mutation of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene. Br J Haematol 2009, 144, 120–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Keszei M, Record J, Kritikou JS, Wurzer H, Geyer C, Thiemann M, et al. Constitutive activation of WASp n X-linked neutropenia renders neutrophils hyperactive. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 4115–31. doi: 10.1172/jci64772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Westerberg LS, Meelu P, Baptista M, Eston MA, Adamovich DA, Cotta-de-Almeida V, et al. Activating WASP mutations associated with X-linked neutropenia result in enhanced actin polymerization, altered cytoskeletal responses, and genomic instability in lymphocytes. J Exp Med 2010, 207, 1145–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Knaus UG, Heyworth PG, Evans T, Curnutte JT, Bokoch GM.. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac2. Science 1991, 254, 1512–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Walliser C, Retlich M, Harris R, Everett KL, Josephs MB, Vatter P, et al. Rac regulates its effector phospholipase Cγ2 through interaction with a split pleckstrin homology domain. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 30351–62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m803316200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Bunney TD, Opaleye O, Roe SM, Vatter P, Baxendale RW, Walliser C, et al. Structural insights into formation of an active signaling complex between Rac and Phospholipase C Gamma 2. Mol Cell 2009, 34, 223–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Nishihara H, Maeda M, Tsuda M, Makino Y, Sawa H, Nagashima K, et al. DOCK2 mediates T cell receptor-induced activation of Rac2 and IL-2 transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002, 296, 716–20. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00931-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lawson CD, Donald S, Anderson KE, Patton DT, Welch HCE.. P-Rex1 and Vav1 cooperate in the regulation of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-dependent neutrophil responses. J Immunol 2011, 186, 1467–76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J.. GEF means go: turning on Rho GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005, 6, 167–80. doi: 10.1038/nrm1587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Cherfils J, Zeghouf M.. Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol Rev 2013, 93, 269–309. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM, Gill GN.. Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 1999, 1, 253–9. doi: 10.1038/12963 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Krauthammer M, Kong Y, Ha BH, Evans P, Bacchiocchi A, McCusker JP, et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic RAC1 mutations in melanoma. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 1006–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Williams DA, Tao W, Yang F, Kim C, Gu Y, Mansfield P, et al. Dominant negative mutation of the hematopoietic-specific Rho GTPase, Rac2, is associated with a human phagocyte immunodeficiency. Blood 2000, 96, 9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ambruso DR, Knall C, Abell AN, Panepinto J, Kurkchubasche A, Thurman G, et al. Human neutrophil immunodeficiency syndrome is associatated with an inhibitory Rac2 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 4654–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Gu Y, Jia B, Yang FC, D'Souza M, Harris CE, Derrow CW, et al. Biochemical and biological characterization of a human Rac2 GTPase mutant associated with phagocytic immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 15929–38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m010445200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Routes JM, Grossman WJ, Verbsky J, Laessig RH, Hoffman GL, Brokopp CD, et al. Statewide newborn screening for severe T-cell lymphopenia. JAMA 2009, 302, 2465–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Accetta D, Syverson G, Bonacci B, Reddy S, Bengtson C, Surfus J, et al. Human phagocyte defect caused by a Rac2 mutation detected by means of neonatal screening for T-cell lymphopenia. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011, 127, 535–8.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.10.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Alkhairy OK, Rezaei N, Graham RR, Abolhassani H, Borte S, Hultenby K, et al. RAC2 loss-of-function mutation in 2 siblings with characteristics of common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015, 135, 1380–1384.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Zhang L, Chen Z, Li W, Liu Q, Wang Y, Chen X, et al. Combined immunodeficiency caused by a novel de novo gain-of-function RAC2 mutation. J Clin Immunol 2022, 42, 1280–1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Lougaris V, Chou J, Beano A, Wallace JG, Baronio M, Gazzurelli L, et al. A monoallelic activating mutation in RAC2 resulting in a combined immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2019, 143, 1649–1653.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Hsu AP, Donkó A, Arrington ME, Swamydas M, Fink D, Das A, et al. Dominant activating RAC2 mutation with lymphopenia, immunodeficiency, and cytoskeletal defects. Blood 2019, 133, 1977–88. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-11-886028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Smits BM, Lelieveld PHC, Ververs FA, Turkenburg M, de Koning C, van Dijk M, et al. A dominant activating RAC2 variant associated with immunodeficiency and pulmonary disease. Clin Immunol 2020, 212, 108248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Sharapova SO, Haapaniemi E, Sakovich IS, Kostyuchenko LV, Donkó A, Dulau-Florea A, et al. Heterozygous activating mutation in RAC2 causes infantile-onset combined immunodeficiency with susceptibility to viral infections. Clin Immunol 2019, 205, 1–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Lagresle-Peyrou C, Olichon A, Sadek H, Roche P, Tardy C, Da Silva C, et al. A gain-of-function RAC2 mutation is associated with bone-marrow hypoplasia and an autosomal dominant form of severe combined immunodeficiency. Haematologica 2021, 106, 404–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Stern H, Donko A, Shapiro T, Hsu AP, Leto TL, Holland SM, et al. A novel RAC2 variant presenting as Severe Combined immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol 2021, 41, 473–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Hobbs GA, Der CJ, Rossman KL.. RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J Cell Sci 2016, 129, 1287–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Lu S, Jang H, Nussinov R, Zhang J.. The structural basis of oncogenic mutations G12, G13 and Q61 in small GTPase K-Ras4B. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 21949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Badour K, Zhang J, Shi F, McGavin MK, Rampersad V, Hardy LA, et al. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein acts downstream of CD2 and the CD2AP and PSTPIP1 adaptors to promote formation of the immunological synapse. Immunity 2003, 18, 141–54. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00516-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Dupre L, Aiuti A, Trifari S, Martino S, Saracco P, Bordignon C, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein regulates lipid raft dynamics during immunological synapse formation. Immunity 2002, 17, 157–66. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00360-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Meyer-Bahlburg A, Becker-Herman S, Humblet-Baron S, Khim S, Weber M, Bouma G, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein deficiency in B cells results in impaired peripheral homeostasis. Blood 2008, 112, 4158–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-140814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Orange JS, Ramesh N, Remold-O’Donnell E, Sasahara Y, Koopman L, Byrne M, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein is rerquired for NK cell cytotoxicity and colocalizes with actin to NK cell-activating immunologic synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 11351–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Burns S, Cory GO, Vainchenker W, Thrasher AJ.. Mechanisms of WASp-mediated hematologic and immunoligc disease. Blood 2004, 104, 3454–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1678 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Lee PP, Lobato-Márquez D, Pramanik N, Sirianni A, Daza-Cajigal V, Rivers E, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein regulates autophagy and inflammasome activity in innate immune cells. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Rivers E, Rai R, Lötscher J, Hollinshead M, Markelj G, Thaventhiran J, et al. Wiskott Aldrich syndrome protein regulates non-selective autophagy and mitochondrial homeostasis in human myeloid cells. Elife 2020, 9, e55547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Taylor MD, Sadhukhan S, Kottangada P, Ramgopal A, Sarkar K, D’Silva S, et al. Nuclear role of WASp in the pathogenesis of dysregulated TH1 immunity in human Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Sci Transl Med 2010, 2, 37ra44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Sarkar K, Sadhukhan S, Han S-S, Vyas YM.. Disruption of hSWI/SNF complexes in T cells by WAS mutations distinguishes X-linked thrombocytopenia from Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood 2014, 124, 3409–19. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-587642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Yuan B, Zhou X, Suzuki K, Ramos-Mandujano G, Wang M, Tehseen M, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein forms nuclear condensates and regulates alternative splicing. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Capala ME, Maat H, Bonardi F, van den Boom V, Kuipers J, Vellenga E, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in human leukemic stem/progenitor cells upon loss of RAC2. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0128585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Alosaimi MF, Shendi H, Beano A, El-Marsafy A, Geha RS, Chou J.. T-cell mitochondrial dysfunction and lymphopenia in DOCK2-deficient patients. J Allerg Clin Immunol 2019, 144, 306–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Dobbs K, Domínguez Conde C, Zhang SY, Parolini S, Audry M, Chou J, et al. Inherited DOCK2 deficiency in patients with early-onset invasive infections. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 2409–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Wei M, Fan X, Ding M, Li R, Shao S, Hou Y, et al. Nuclear actin regulates inducible transcription by enhancing RNA polymerase II clustering. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaay6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.