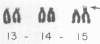Abstract
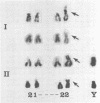
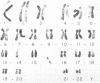
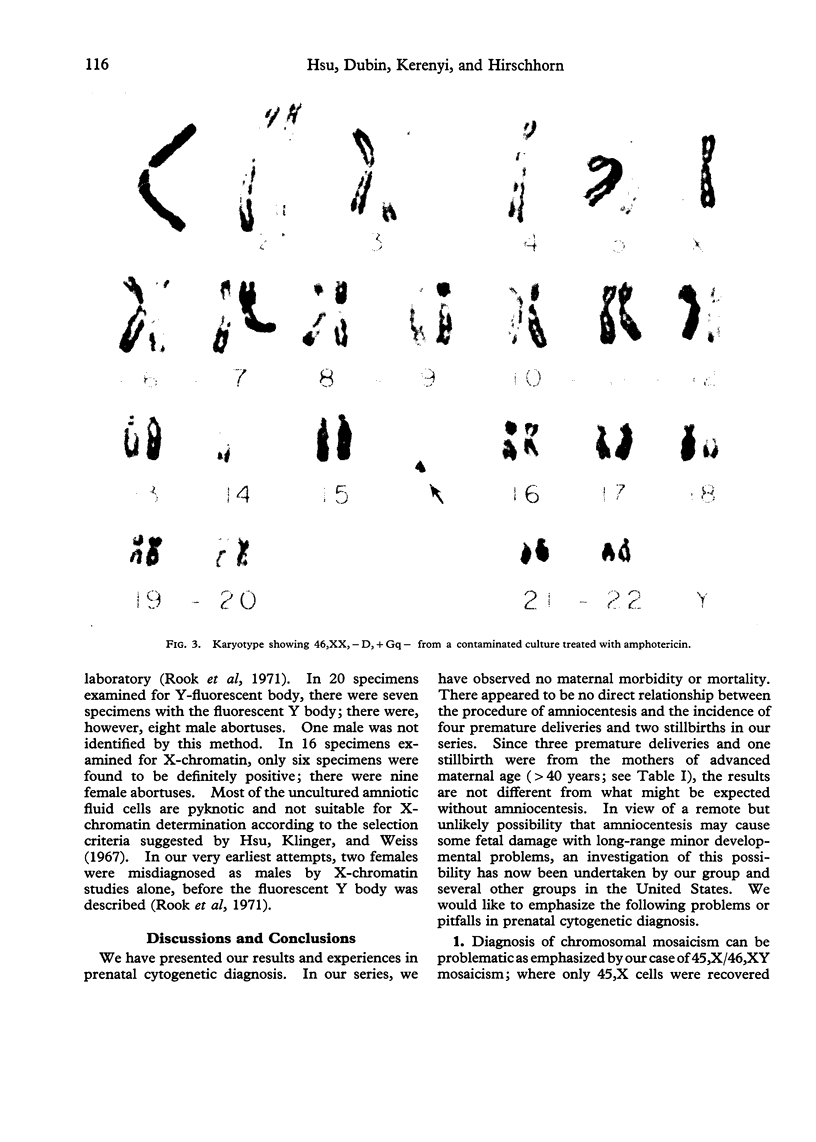
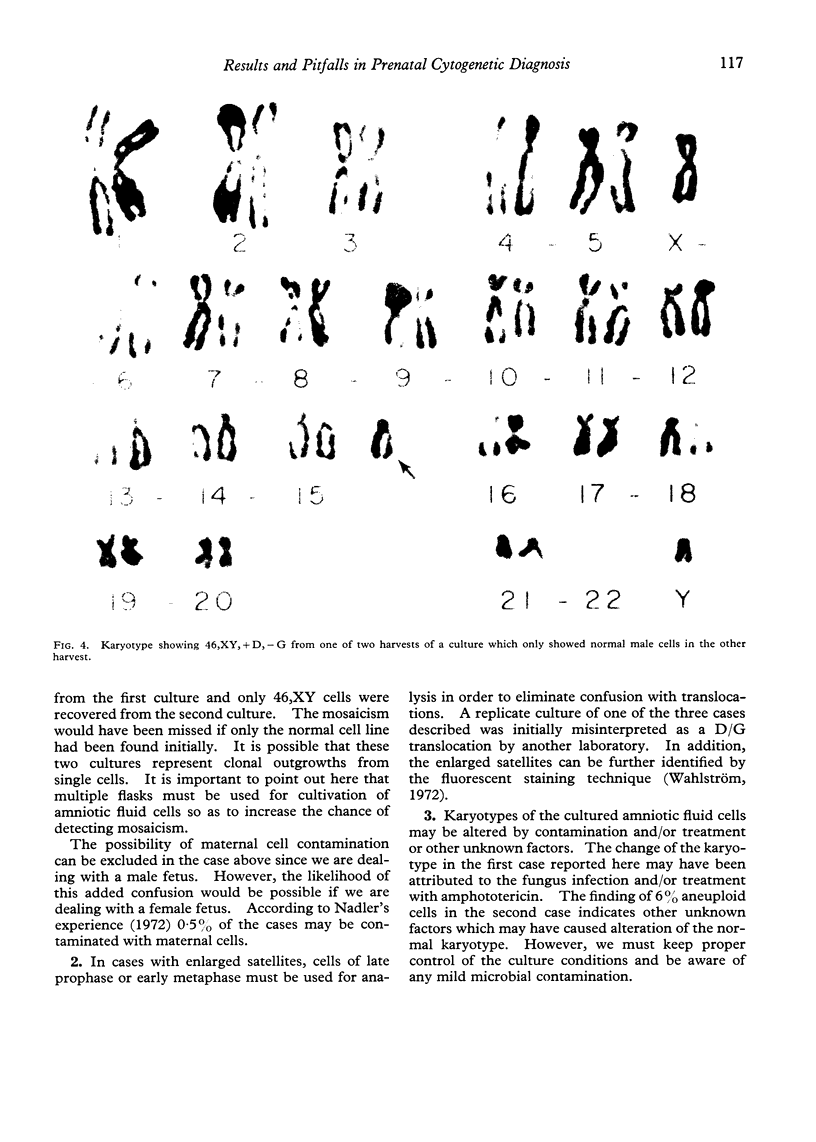
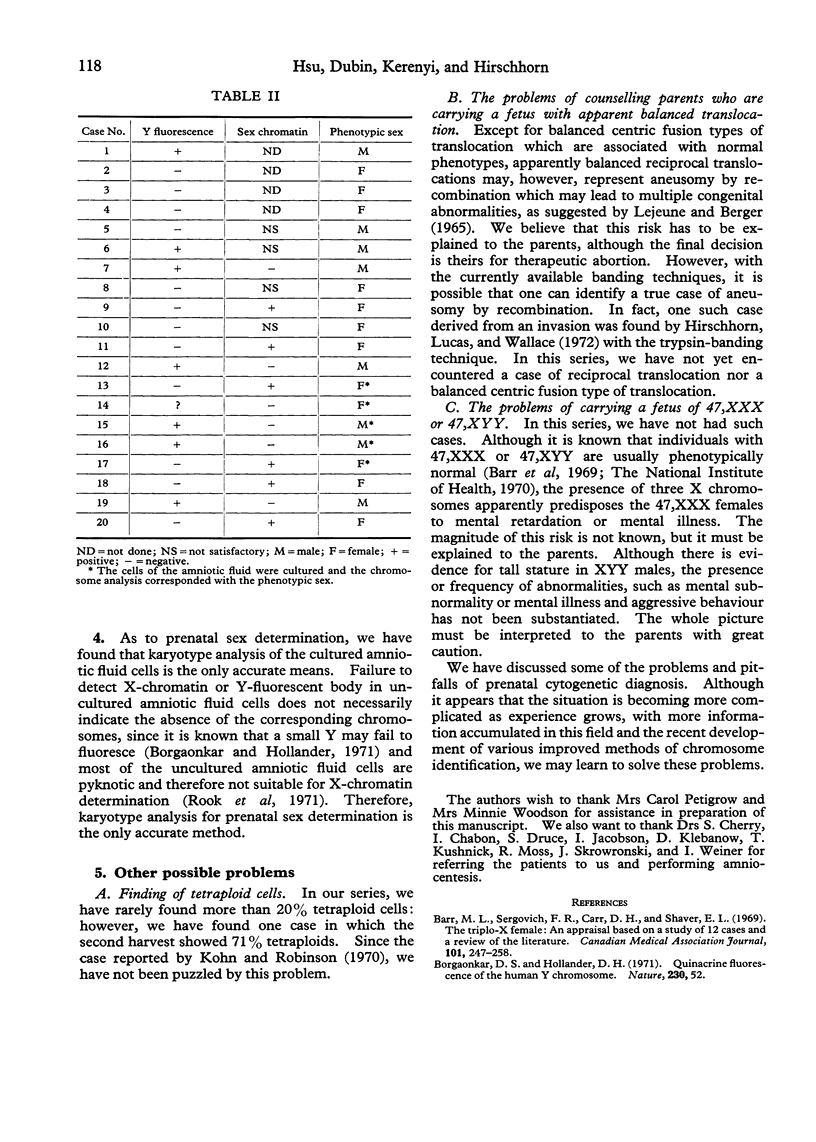
Since 1969, we have cultured over 200 diagnostic amniotic fluids. Of these, 183 were for cytogenetic diagnosis. The chromosome analysis was successful in 168 cases. The indications and the results of the affected fetuses (followed by therapeutic abortion) are: (1) previous child with Down's syndrome: 62 cases (1:47,XX,+21); (2) advanced maternal age: 54 cases (1:47,XXY; 1:45,X/46,XY mosaicism; 1:47,+18); (3) previous child with multiple anomalies: 12 cases; (4) previous child with 47,XY,+18 or 47,+13: five cases; (5) translocation carrier: two cases; (6) parental mosaicism: three cases; (7) X-linked disorders: six cases (3:XY); (8) others: 24 cases. We have found firstly, that for prenatal sex determination, karyotype analysis of the cultured amniotic fluid cells is the only accurate means and that caution must be taken if sex chromatin and Y-fluorescent body determination from the uncultured amniotic fluid cells is used. Secondly, that diagnosis of chromosomal mosaicism can be problematic as exemplified by our case of 45,X/46,XY mosaicism, where only 45,X cells were recovered from the first culture. Thirdly, that in cases with enlarged satellites, cells of late prophase or early metaphase must be used to eliminate confusion with translocations. We encountered three cases of enlarged satellites—one in the D group and two in the G group—and all three resulted in normal infants. Fourthly, that the karyotype may be altered by contamination and/or treatment or other unknown factors. We have observed two such cases where each mother delivered a normal infant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr M. L., Sergovich F. R., Carr D. H., Saver E. L. The triplo-X female: an appraisal based on a study of 12 cases and a review of the literature. Can Med Assoc J. 1969 Sep 6;101(5):247–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar D. S., Hollander D. H. Quinacrine fluorescence of the human Y chromosome. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):52–52. doi: 10.1038/230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertner M., Hsu L. Y., Martin J., Hirshhorn K. The use of amniocentesis for prenatal genetic counseling. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1970 Nov;46(11):916–921. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Klinger H. P., Weiss J. Influence of nuclear selection criteria on sex chromatin frequency in oral mucosa cells of newborn females. Cytogenetics. 1967;6(5):371–382. doi: 10.1159/000154941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Strauss L., Dubin E., Hirschhorn K. Prenatal diagnosis of trisomy 18. Pathologic findings in 20-week conceptus. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Feb;125(2):290–292. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160020098020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardon N. B., Chernay P. R., Hsu L. Y., Martin J. L., Hirschhorn K. Problems in prenatal diagnosis resulting from chromosomal mosaicism. Clin Genet. 1972;3(2):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn G., Robinson A. Tetraploidy in cells cultured from amniotic fluid. Lancet. 1970 Oct 10;2(7676):778–779. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J., Burger R. Sur deux observations familiales de translocations complexes. Ann Genet. 1965;8(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisgar F., Gertner M., Cherry S., Hsu L. Y., Hirschhorn K. Prenatal chromosome analysis. Nature. 1970 Jan 17;225(5229):280–281. doi: 10.1038/225280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Littlefield J. W., Kanfer J. N., Kolodny E. H., Shih V. E., Atkins L. Prenatal genetic diagnosis (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 24;283(26):1441–1447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012242832605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A., Hsu L. Y., Gertner M., Hirschhorn K. Identification of Y and X chromosomes in amniotic fluid cells. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):53–53. doi: 10.1038/230053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström J. Identification by fluorescence of apparently extra human F chromosomes as G chromosomes with giant satellites. Hereditas. 1972;71(1):154–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1972.tb01014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]