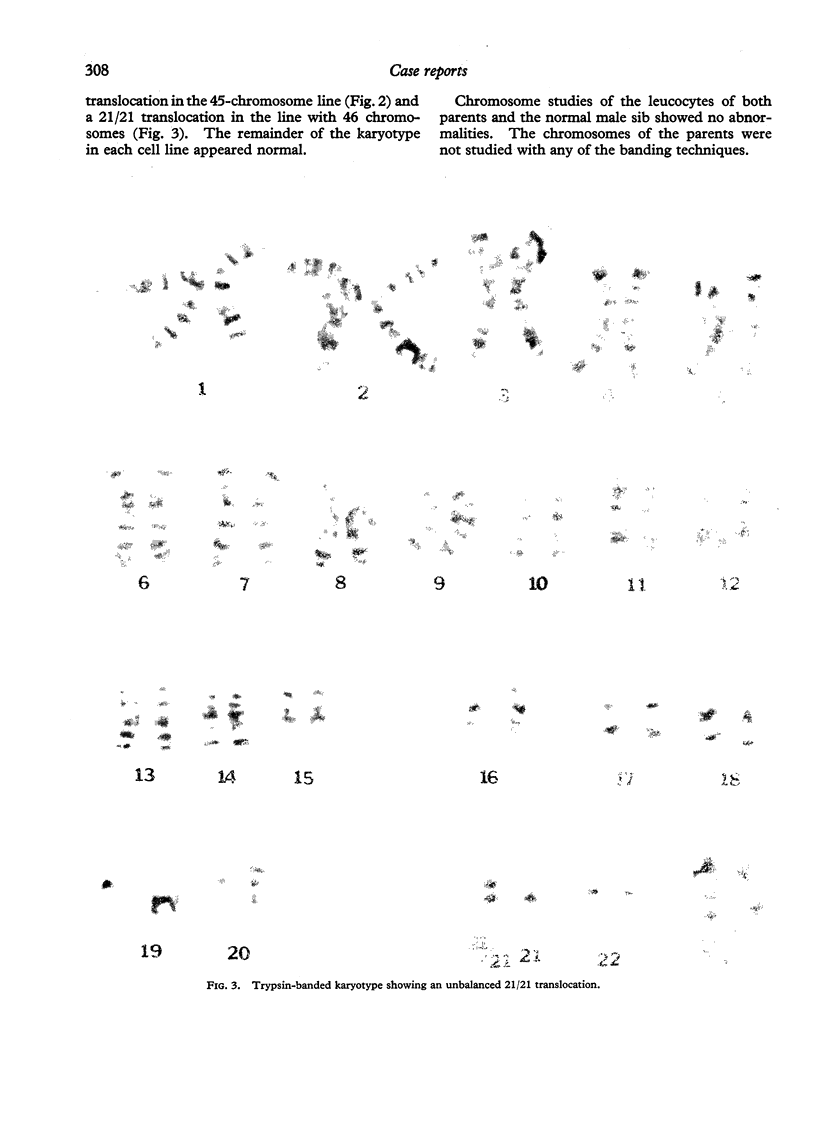
Abstract
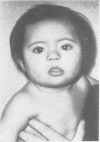
A female infant with Down's syndrome was found to be a chromosomal mosaic with two cell lines in both blood and skin cells. One line carried a balanced 15/21 translocation, and the other line was effectively trisomic for chromosome 21 with a 21/21 translocation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Seabright M. The use of proteolytic enzymes for the mapping of structural rearrangements in the chromosomes of man. Chromosoma. 1972;36(2):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00285214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELLWEGER H., ABBO G. Chromosomal mosaicism and mongolism. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):827–827. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]