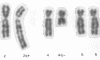Abstract
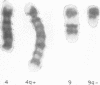
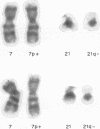
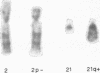
Five cases of chromosome imbalance resulting from 3:1 disjunction of reciprocal translocations are described. A review of the literature suggests this phenomenon is more common than has previously been recognized.
Full text
PDF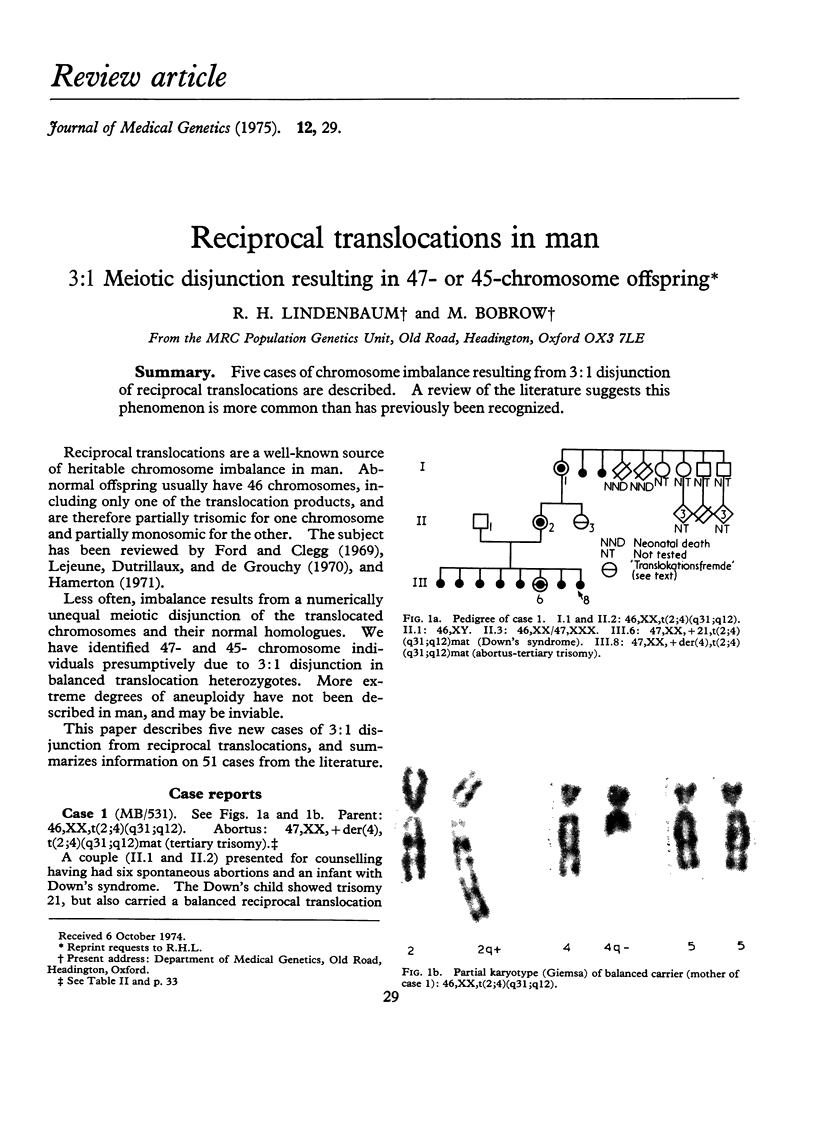

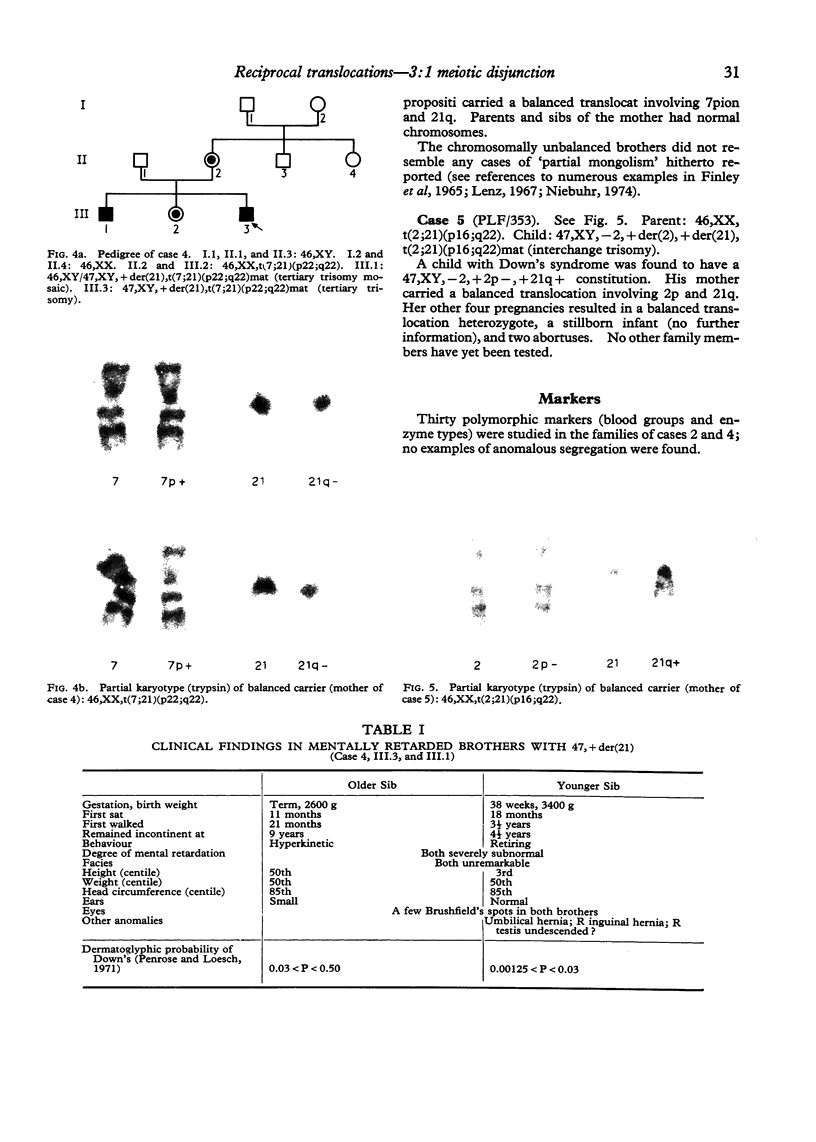
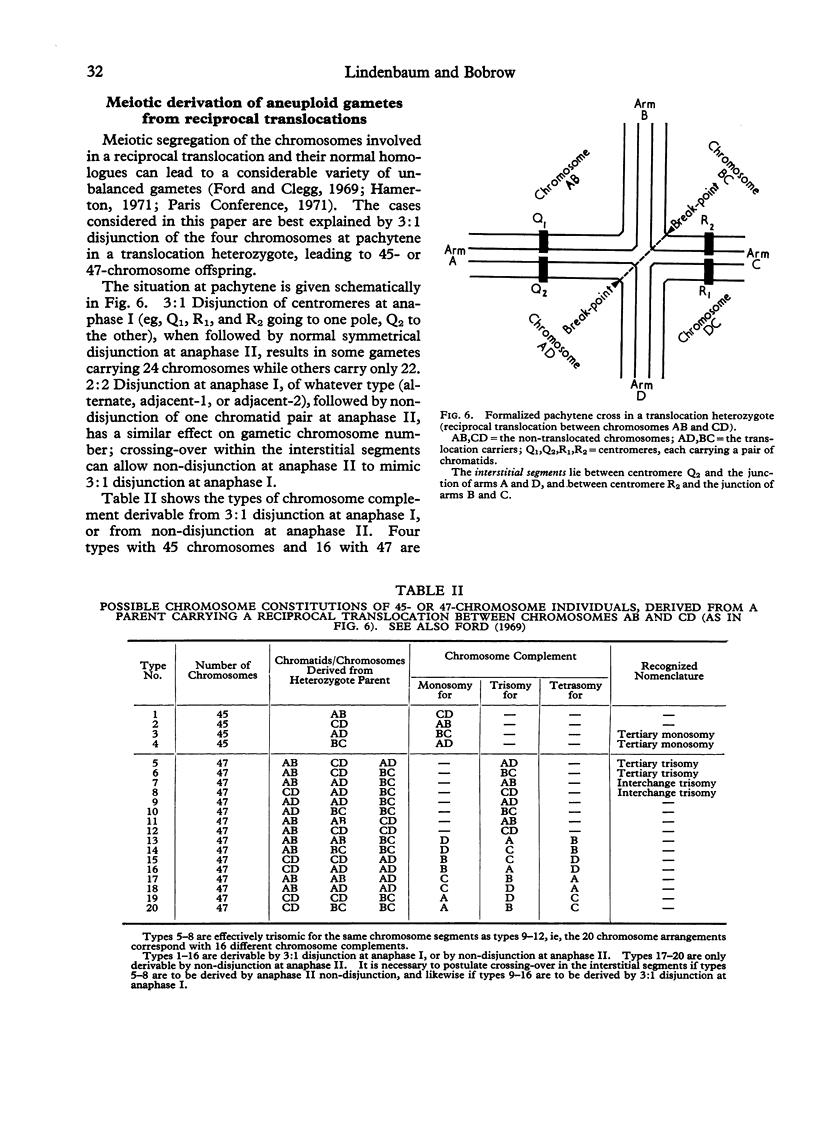

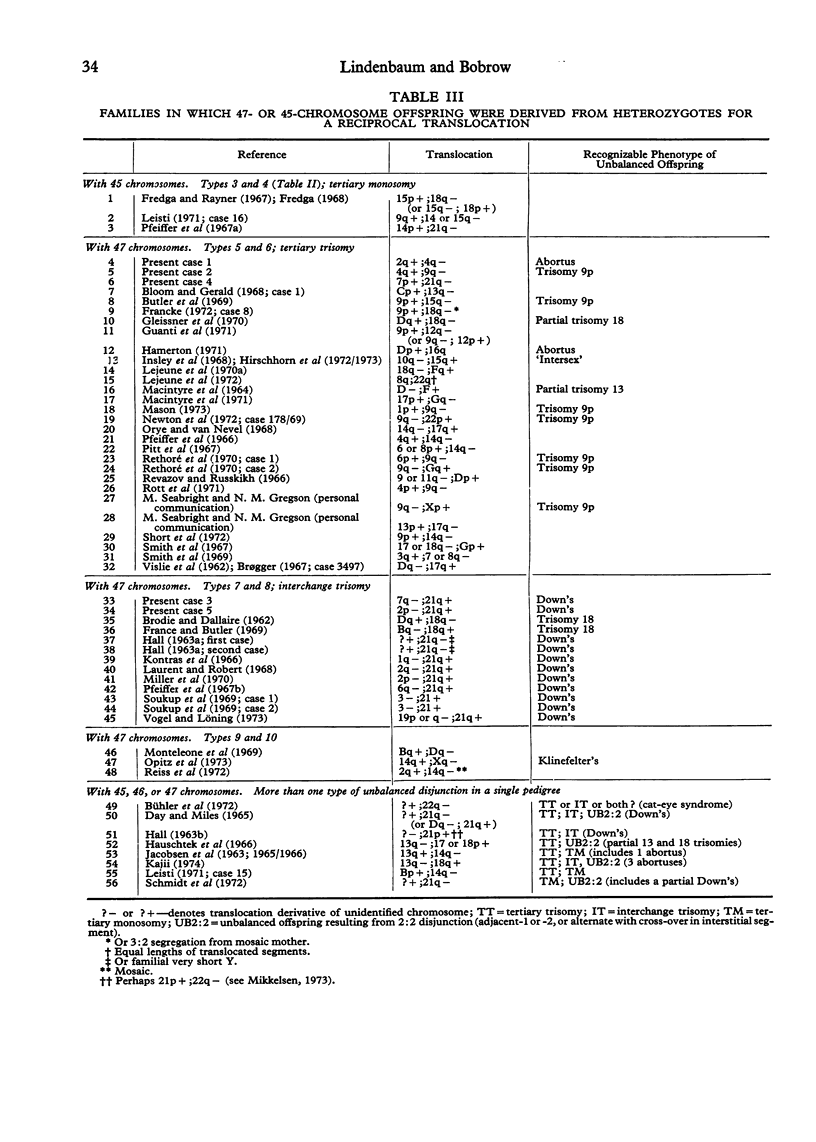






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A (15;18) translocation, unbalanced, 45 chromosomes. Human Genetic Mutant Cell Repository, Camden, N.J., identification No. GM-17. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(5):370–371. doi: 10.1159/000130477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aarskog D. A new cytogenetic variant of translocation Down's syndrome. Cytogenetics. 1966;5(1):82–87. doi: 10.1159/000129886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIESELE J. J., SCHMID W., LAWLIS M. G. Mentally retarded schizoid twin girls with 47 chromosomes. Lancet. 1962 Feb 24;1(7226):403–405. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLANK C. E. Apert's syndrome (a type of acrocephalosyndactyly)-observations on a British series of thirty-nine cases. Ann Hum Genet. 1960 May;24:151–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1959.tb01728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREIBART S., MELLMAN W. J., EBERLEIN W. R. DEVELOPMENTAL RETARDATION ASSOCIATED WITH AN UNBALANCED 13-15/18 TRANSLOCATION. Cytogenetics. 1964;3:252–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE H. R., DALLAIRE L. The E syndrome (trisomy 17-18) resulting from a maternal chromosomal translocation. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Sep 8;87:559–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass H. N., Crandall B. F., Marcy S. M. Two different chromosome abnormalities resulting from a translocation carrier father. J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;83(6):1034–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belling J., Blakeslee A. F. On the Attachment of Non-Homologous Chromosomes at the Reduction Division in Certain 25-Chromosome Daturas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1926 Jan;12(1):7–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.12.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belling J., Blakeslee A. F. The Configurations and Sizes of the Chromosomes in the Trivalents of 25-Chromosome Daturas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1924 Mar;10(3):116–120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.10.3.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeslee A. F. Distinction between Primary and Secondary Chromosomal Mutants in Datura. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1924 Mar;10(3):109–116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.10.3.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. E., Gerald P. S. Localization of genes on chromosome 13: analysis of two kindreds. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Nov;20(6):495–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Madan K. The effects of various banding procedures on human chromosomes, studied with acridine orange. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(3):143–156. doi: 10.1159/000130449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov N. P., Kuleshov N. P., Chebotarev A. N., Alekhin V. I., Midian S. A. Population cytogenetic investigation of newborns in Moscow. Humangenetik. 1974 May 17;22(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00278453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar D. S., McKusick V. A., Farber P. A. An inherited small extra chromosome: a mother with 46,XX,t(17;22)(pl;ql) and a son with 47,XY,+der(22)mat. J Med Genet. 1973 Dec;10(4):379–384. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar S., Schimke R. N., Thomas H. Report of five unrelated patients with a small, metacentric, extra chromosome or fragment. J Genet Hum. 1971 Sep;19(3):207–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. J., Eades S. M., France N. E. Transmission of a translocation t(Cp+; Dq-) through three generations; including an example of probable trisomy for the short arm of the C group chromosome No. 9. Ann Genet. 1969 Mar;12(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler E. M., Méhes K., Müller H., Stalder G. R. Cat-eye syndrome, a partial trisomy 22. Humangenetik. 1972;15(2):150–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00295742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. H. Chromosomes and abortion. Adv Hum Genet. 1971;2:201–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Putnam T. I. An 18p21q translocation in a patient with presumptive "monosomy G". Am J Dis Child. 1972 Dec;124(6):908–910. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110180110016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Robson E. B., Buckton K. E., Jacobs P. A., Polani P. E. Segregation of genetic markers in families with chromosome polymorphisms and structural rearrangements involving chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):261–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAY R. W., MILES C. P. FAMILIAL DOWN'S SYNDROME WITH UNDETECTED TRANSLOCATION. J Pediatr. 1965 Sep;67:399–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Capoa A., Allen F. H., Jr, Gold A. P., Koenigsberger R., Miller O. J. Presumptive C-15 translocation and familial large Y identified by autoradiography. J Med Genet. 1969 Mar;6(1):89–94. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Chapelle A., Koivisto M., Schröder J. Segregating reciprocal (4;21) (q21;q21) translocation with proposita trisomic for parts of 4q and 21. J Med Genet. 1973 Dec;10(4):384–389. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.4.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Jonasson J., Laurèn K., Lejeune J., Lindsten J., Petersen G. B., Saldaña-Garcia P. An unbalanced 4q-21q translocation identified by the R but not by the G and Q chromosome banding techniques. Ann Genet. 1973 Mar;16(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINLEY S. C., FINLEY W. H., ROSECRANS C. J., PHILLIPS C. EXCEPTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN A MONGOLOID CHILD OF A FAMILY WITH A 13-15/PARTIAL 21 (D-PARTIAL G) TRANSLOCATION. N Engl J Med. 1965 May 27;272:1089–1092. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196505272722102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
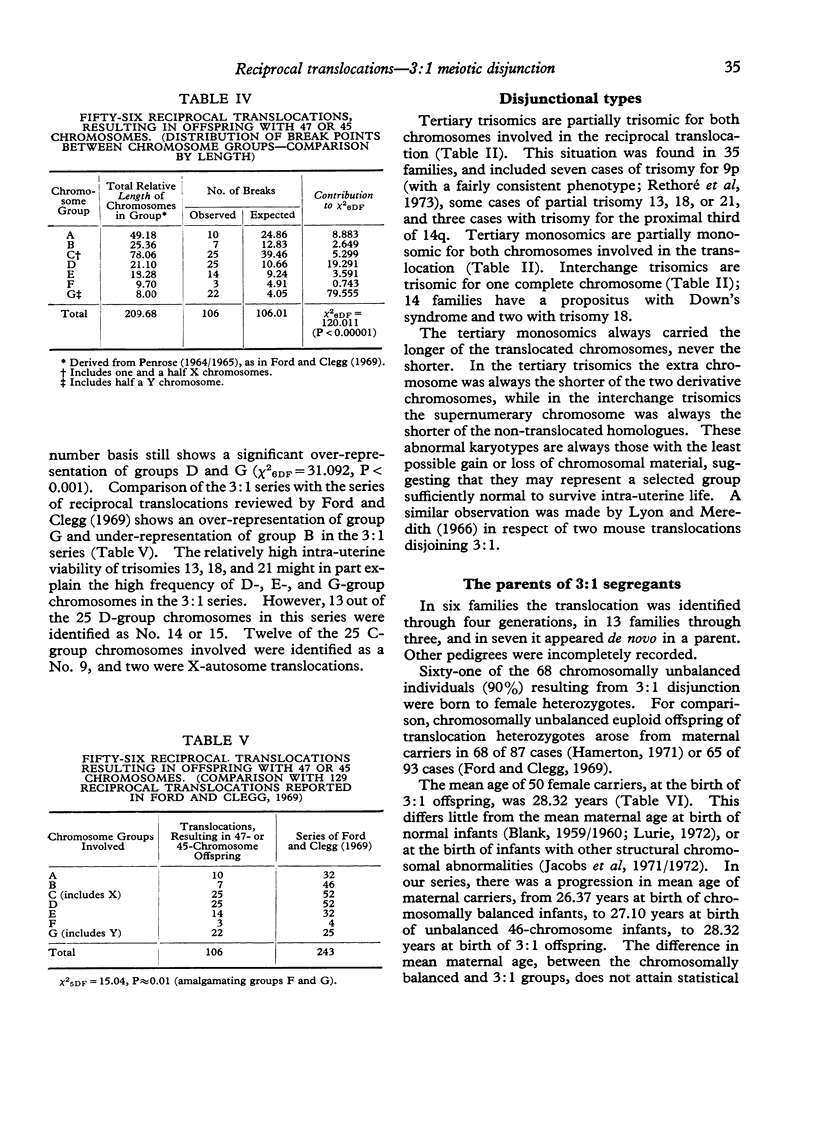
- Ford C. E., Clegg H. M. Reciprocal translocations. Br Med Bull. 1969 Jan;25(1):110–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraccaro M., Herin P., Hultén M., Ivemark B. I., Jonasson J., Lindsten J., Tiepolo L., Zetterqvist P. Structural abnormalities of chromosome 18. 3. Two G-18 translocations, one identified AS 22-18. Ann Genet. 1972 Jun;15(2):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- France N. E., Butler L. J. Trisomy 18 associated with a familial translocation t(Bq-; 18q+). Ann Genet. 1969 Mar;12(1):46–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Quinacrine mustard fluorescence of human chromosomes: characterization of unusual translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;24(2):189–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
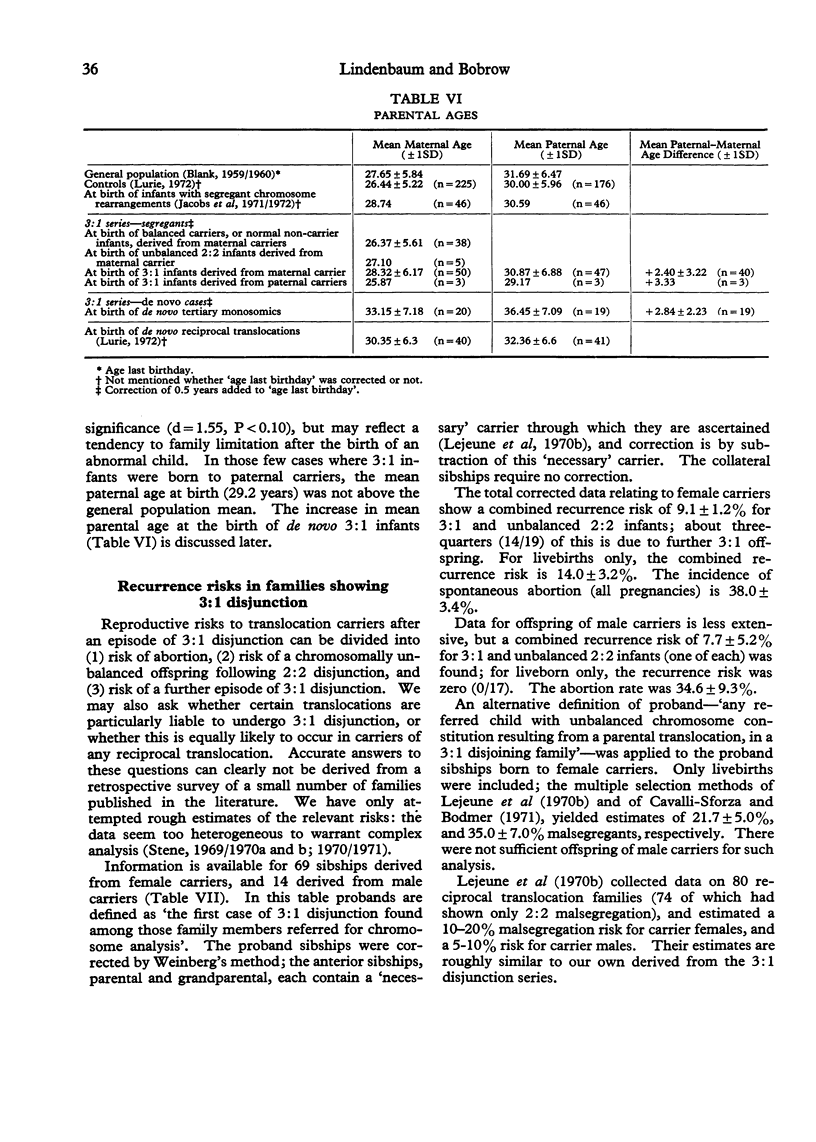
- Fredga K. Identification by autoradiography of the chromosomes involved in a familial 15-18 translocation. Hereditas. 1968;60(1):129–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1968.tb02197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredga K., Rayner S. Mitotic and meiotic studies of a familial reciprocal translocation between autosomes 15 and 18 in man. Hereditas. 1967;58(3):303–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1967.tb02159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Nielsen J. Chromosome studies in 5,049 consecutive newborn children. Clin Genet. 1973;4(4):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAVSON K. H., HAGBERG B., FINLEY S. C., FINLEY W. H. An apparently identical extra autosome in two severely retarded sisters with multiple malformations. Cytogenetics. 1962;1:32–41. doi: 10.1159/000129711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
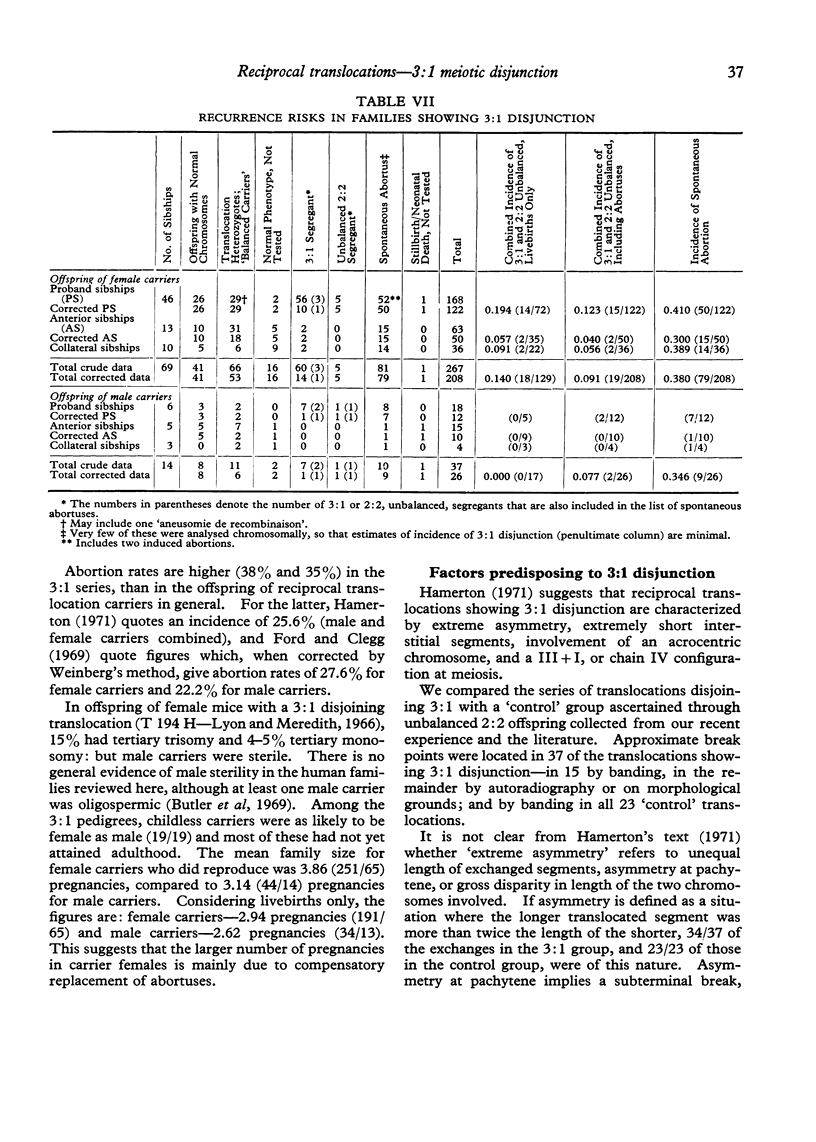
- Gilgenkrantz S., Charles J. M., Cabrol C., Mauuary G., Vigneron C. Délétion du bras court du 18 par translocation t(22-;18p+) avec déficit en IgA. Etude cytogénétique avec autoradiographie et fluorescence. Ann Genet. 1972 Dec;15(4):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraud F., Hartung M., Mattei J. F., Mattie M. G. t(7-; 21q-plus) et trisomie 21 familiale. Ann Genet. 1974 Mar;17(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleissner M., Schwanitz G., Rott H. D. Partielle Trisomie E18 (E18 q--) als Folge einer balancierten Translokation D-E bei der Mutter. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1970 Jul;118(7):441–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL B. Down's syndrome (mongolism) with a morphological Philadelphia chromosome. Lancet. 1963 Mar 9;1(7280):558–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMERTON J. L., GIANNELLI F., POLANI P. E. CYTOGENETICS OF DOWN'S SYNDROME (MONGOLISM). I. DATA ON A CONSECUTIVE SERIES OF PATIENTS REFERRED FOR GENETIC COUNSELLING AND DIAGNOSIS. Cytogenetics. 1965;4:171–185. doi: 10.1159/000129853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOEFNAGEL D., BENIRSCHKE K., MAVALWALA J., BROWNHILL L. UNUSUAL DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ASSOCIATED WITH CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES. J Ment Defic Res. 1963 Dec;7:90–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1963.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschteck E., Mürset G., Prader A., Bühler E. Siblings with different types of chromosal aberrations due to D-E-translocation of the mother. Cytogenetics. 1966;5(5):281–294. doi: 10.1159/000129904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn K., Lucas M., Wallace I. Precise identification of various chromosomal abnormalities. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Apr;36(4):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insley J., Rushton D. I., Jones H. W. An intersexual infant with an extra chromosome. Ann Genet. 1968 Jun;11(2):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSEN P., DUPONT A., MIKKELSEN M. TRANSLOCATION IN THE 13-15 GROUP AS A CAUSE OF PARTIAL TRISOMY AND SPONTANEOUS ABORTION IN THE SAME FAMILY. Lancet. 1963 Sep 14;2(7307):584–585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92673-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L., Barr M. A 45,XY,5-15-,t(5q15q) cri-du-chat child. J Med Genet. 1970 Jun;7(2):161–163. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Frackiewicz A., Law P. Incidence and mutation rates of structural rearrangements of the autosomes in man. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;35(3):301–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Melville M., Ratcliffe S., Keay A. J., Syme J. A cytogenetic survey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 May;37(4):359–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen P., Mikkelsen M., Froland A., Dupont A. Familial transmission of a translocation between two non-homologous large acrocentric chromosomes. Clinical, cytogenetic and autoradiographic studies. Ann Hum Genet. 1966 May;29(4):391–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1966.tb00537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James Kirkwood Slater. Lancet. 1965 Oct 16;2(7416):797–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontras S. B., Currier G. J., Cooper R. F., Ambuel J. P. Maternal transmission of a 21/1 translocation associated with Down's syndrome. J Pediatr. 1966 Oct;69(4):635–639. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll W., Mostafawy A. Caudales Hypoplasiesyndrom mit zusätzlichen Missbildungen bei unbalancierter Translokation 13-15-16. Z Kinderheilkd. 1969;107(3):246–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent C., Robert J. M. Translocation t(2q-; 21q+) sur trois générations. Ann Genet. 1968 Mar;11(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisti J., Leisti S., Perheentupa J., Savilahti E., Aula P. Absence of IgA and growth hormone deficiency associated with short arm deletion of chromosome 18. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Apr;48(4):320–322. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.4.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J., Rethore M. O., Dutrillaux B., Martin G. Translocation 8-22 sans changement de longueur et trisomie partielle 8q. Detection par denaturation ménagée. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Sep;74(1):293–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D., Penrose L. S. Diagnosis with dermatoglyphic discriminants. J Ment Defic Res. 1971 Sep;15(3):185–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1971.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Meredith R. Autosomal translocations causing male sterility and viable aneuploidy in the mouse. Cytogenetics. 1966;5(5):335–354. doi: 10.1159/000129909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERCER R. D., DARAKJIAN G. Apparent translocation between chromosome 2 and an acrocentric in group 13-15. Lancet. 1962 Oct 13;2(7259):784–784. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90612-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macintyre M. N., Walden D. B., Hempel J. M. Tertiary trisomy in a human kindred containing an E/G translocation. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Sep;23(5):431–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpuech G., Raynaud E. J., Belin J., Godeneche P., de Grouchy J. Délétion du bras court du 18 par translocation t(G-;18p+). Une étude en fluorescence par la moutarde de quinacrine. Ann Genet. 1971 Sep;14(3):213–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M. Down's syndrome. Current stage of cytogenetic research. Humangenetik. 1971;12(1):1–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00291028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Dill F. J., Corey M. J., Rigg J. M. A rare translocation (47,XY,t(2p-;21q+),21+) associated with Down's syndrome. J Med Genet. 1970 Dec;7(4):389–393. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteleone P. L., Monteleone J. A., Grzegocki J. An unusual balanced reciprocal translocation in several members of a family. J Med Genet. 1969 Dec;6(4):394–398. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.4.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. K., Engel E. Clinical, cytogeneti and autoradiographic studies in 0 cases with rare chromosome disorders. IV. Cases 9 and 10. Ann Genet. 1970 Dec;13(4):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagome Y., Inuma K., Matsui I. Three translocations involving C- or G-group chromosomes. J Med Genet. 1973 Jun;10(2):174–176. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M. S., Cunningham C., Jacobs P. A., Price W. H., Fraser I. A. Chromosome survey of a hospital for the mentally subnormal. 2. Autosome abnormalities. Clin Genet. 1972;3(4):226–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb04271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orye E., Van Nevel C. Familial D-E translocation. Humangenetik. 1968;6(3):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00291862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENROSE L. S. A NOTE ON THE MEAN MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN CHROMOSOMES. Ann Hum Genet. 1964 Nov;28:195–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1964.tb00477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEIFFER R. A. CHROMOSOMENANOMALIE BEI EINEM NEUGEBORENEN MIT RENOFAZIALER DYSPLASIE. REZIPROKE TRANSLOKATION ZWISCHEN AKROZENTRISCHEN CHROMOSOMEN DER GRUPPE D (13-15) Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1964 Nov 13;89:2192–2195. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1113259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUESCHEL E., SCHADE H., SCHOELLER L. MULTIPLE MISSBILDUNGEN BEI HETEROZYGOTER TRANSLOKATION MIT 45 CHROMOSOMEN. Med Welt. 1965 Jan 2;34:67–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali F., Zuffardi O., Severi F., Colombo A., Burgio G. R. Tandem translocation 15-13. Ann Genet. 1973 Mar;16(1):47–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Bachmann K. D., Bartel K. Missbildungssyndrom bei autosomaler Defizienz (D2-G1) Z Kinderheilkd. 1967;100(4):279–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Laermann J., Heidtmann H. L. Reziproke Translokation zwischen einem Chromosom Nr. 21 (G1) und einem Chromosom der Gruppe C(C6) Helv Paediatr Acta. 1967 Dec;22(6):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieur M., Dutrillaux B., Rethoré M. O., Lejeune J. Analyse d'une translocation t (18p+;21q-) par dénaturation ménagée. Ann Genet. 1971 Dec;14(4):305–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss J. A., Wyandt H. E., Magenis R. E., Lovrien E. W., Hecht F. Mosaicism with translocation: autoradiographic and fluorescent studies of an inherited reciprocal translocation t(2q+;14q-). J Med Genet. 1972 Sep;9(3):280–286. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.3.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethoré M. O., Hoehn H., Rott H. D., Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Analyse de la trisomie 9p par dénaturation ménagée. A propos d'un nouveau cas. Humangenetik. 1973 Apr 16;18(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00291480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethoré M. O., Larget-Piet L., Abonyi D., Boeswillwald M., Berger R., Carpentier S., Cruveiller J., Dutrillau B., Lafourcade J., Penneau M. Sur quatre cas de trisomie pour le bras court du chromosome 9. Individualisation d'une nouvelle entite morbide. Ann Genet. 1970 Dec;13(4):217–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C. S., Bobrow M. The sites of radiation induced-breakage in human lymphocyte chromosomes, determined by quinacrine fluorescence. Mutat Res. 1973 Jun;18(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott H. D., Schwanitz G., Grosse K. P. Partielle Trisomie C9 bei balancierter B4-C9-Translokation bei der Mutter. Z Kinderheilkd. 1971;109(4):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Mundel G., Rosenblatt M., Katznelson M. B. Apparent G-monosomy, G-deletion, and incomplete Down's syndrome in a single family. J Med Genet. 1972 Dec;9(4):457–461. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.4.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. High resolution studies on the pattern of induced exchanges in the human karyotype. Chromosoma. 1973;40(4):333–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00399426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short E. M., Solitare G. B., Breg W. R. A case of partial 14 trisomy 47,XY,(14q-)+ and translocation t(9p+;14q-) in mother and brother. J Med Genet. 1972 Sep;9(3):367–373. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., Berg J. M., Ridler M. A., Faunch J. A., Farnham F. N., Pendrey M. J. Familial transmission of an aberrant submetacentric chromosome. J Ment Defic Res. 1967 Mar;11(1):58–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1967.tb00205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., Shear C. S., Jalowayski I., Akesson H. O. An unbalanced karyotype in a translocation (Cq-,Aq+) pedigree. J Ment Defic Res. 1969 Jun;13(2):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soudek D., Brunecký Z., Laxová R. A case of translocation D--,t(1p+). Humangenetik. 1969;7(1):5–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00278687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soukup S. W., Passarge E., Becroft D. M., Shaw R. L., Young L. G. Familial translocation (3?--;G?- q+) and nondisjunction of chromosome in group G in two unrelated families. Cytogenetics. 1969;8(5):315–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder G. R., Bühler E. M., Bühler U. K. Nachkommen von balancierten fusions- und translokationsheterozygoten Menschen. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1965 Jun;20(2):169–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stene J. Analysis of segregation patterns between sibships within families ascertained in different ways. Ann Hum Genet. 1970 Jan;33(3):261–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1970.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stene J. Statistical inference on segregation ratios for D-G-translocations, when the families are ascertained in different ways. Ann Hum Genet. 1970 Jul;34(1):93–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1970.tb00224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes P. L., Ziegler N. A. D-E (13-15/17-18) translocation: occurrence in an infant with 45 chromosomes. Am J Dis Child. 1965 Dec;110(6):686–688. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1965.02090030714019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdmanis A., Wilson J. R., Mann J. D., Pearson G., Shaw M. W. Subglottic pseudotumor, laryngeal dysplasia, and chondrodysplasia calcificans congenita with a t(D;B) chromosomal translocation. Ann Genet. 1967 Jun;10(2):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Löning B. Identification of a familial 19-21 translocation by Q and G band patterns. Humangenetik. 1973 May 25;18(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00290600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE C., ANDERSON I. F. GROUP B/D TRANSLOCATION CHROMOSOME IN A CASE WITH STIGMATA OF THE D TRISOMY. S Afr Med J. 1964 May 16;38:352–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbaum R., Samaille G., Scharfman W., Maillard E. Le problème de la trisomie 22. Pediatrie. 1970 Mar;25(2):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Wolf C. B. Familial C-G translocation causing mitotic nondisjunction. A cause of familial mosaic Down's syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1968 Dec;116(6):609–614. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1968.02100020613007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf U., Reinwein H., Gey W., Klose J. Cri-du-chat-syndrom mit translokation 5/D 2. Humangenetik. 1966;2(1):63–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00285911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyandt H. E., Hecht F., Lovrien E. W., Stewart R. E. Study of a patient with apparent monosomy 21 owing to translocation: 45,XX,21-,t(18q+). Cytogenetics. 1971;10(6):413–426. doi: 10.1159/000130162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying K. L. Sporadic (GqGq) translocations in Down's syndrome. Can J Genet Cytol. 1973 Jun;15(2):309–311. doi: 10.1139/g73-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELLWEGER H., MIKAMO K. Autosomal cytogenetics. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1961 Dec;16:670–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]