Abstract
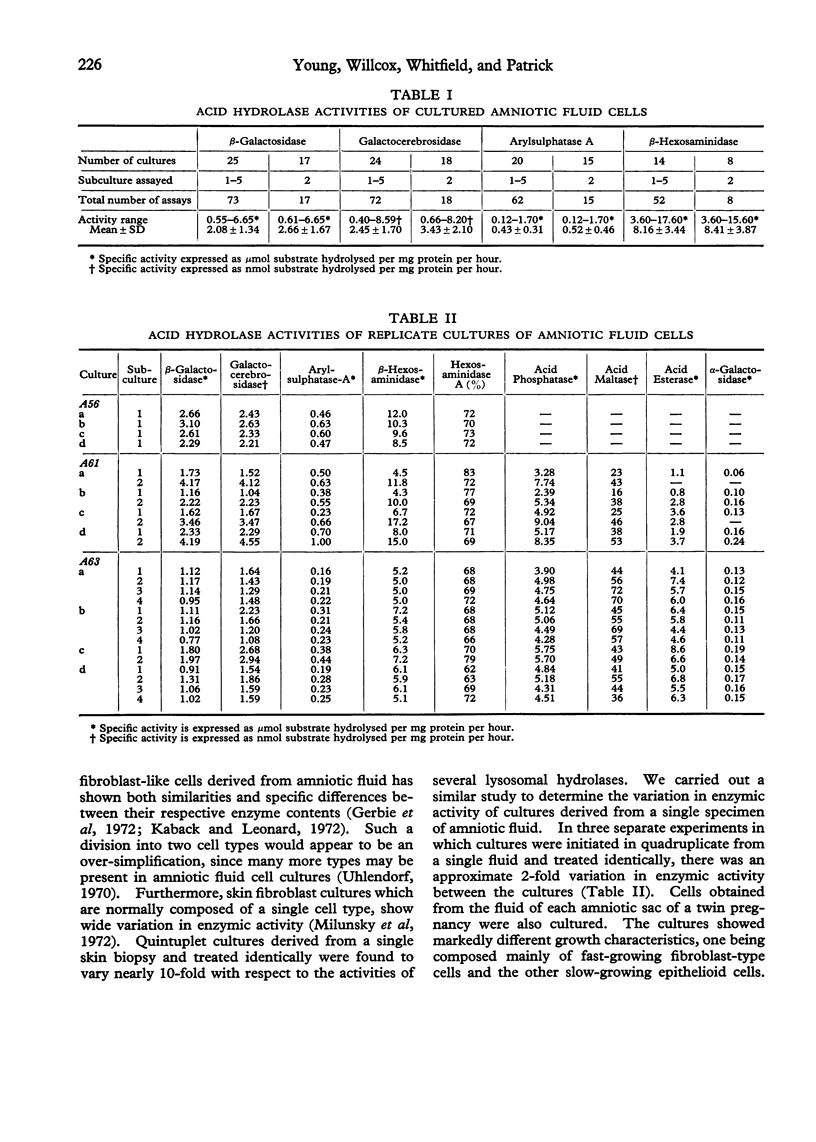
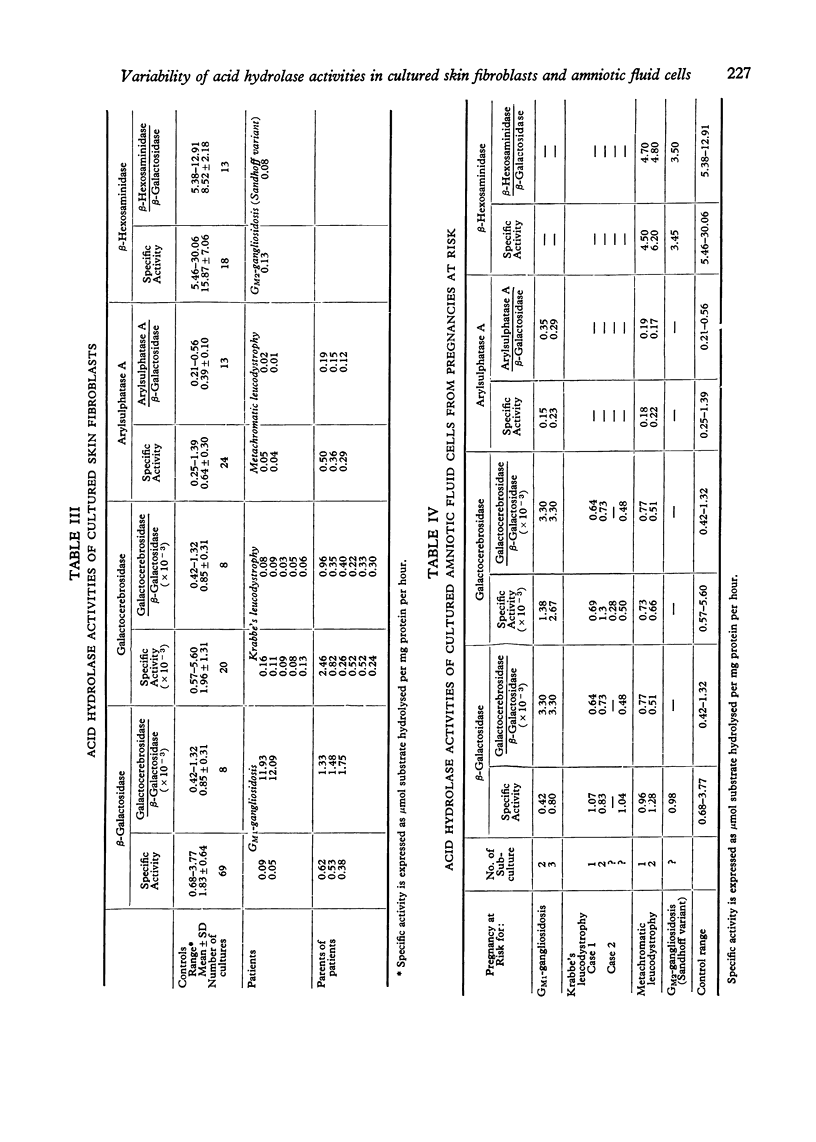
The specific activities of lysosomal hydrolases in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells showed wide and unpredictable variations between cultures, which may lead to difficulty in differentiating normal, heterozygous, and homozygous cells. However, the variability for a given culture was similar for all enzymes assayed, so that a clearer differentiation of a relative deficiency of a given enzyme could be obtained by expressing its activity in ratio to that of another enzyme. Activity ratios were particularly useful in the evaluation of enzyme levels in cultured amniotic fluid cells. Results of their application to tests of pregnancies at risk for metachromatic leucodystrophy, Krabbe's leucodystrophy, GM1-gangliosidosis, and GM2-gangliosidosis (Sandhoff variant) are presented.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Trinidad F., Teplitz R., Nadler H. Beta-glucosidase activity in fibroblasts from homozygotes and heterozygotes for Gaucher's disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jan;23(1):62–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. M., Radin N. S. Cerebroside galactosidase: a method for determination and a comparison with other lysosomal enzymes in developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):501–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett E. M., Ellis R. B., Haas L., Ikonne J. U., Lake B. D., Patrick A. D., Stephens R. Late onset GM2-gangliosidosis. Clinical, pathological, and biochemical studies on 8 patients. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):775–785. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristofalo V. J., Parris N., Kritchevsky D. Enzyme activity during the growth and aging of human cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Jun;69(3):263–271. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. B., Ikonne J. U., Patrick A. D., Stephens R., Willcox P. Letter: Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Lancet. 1973 Nov 17;2(7838):1144–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbie A. B., Melancon S. B., Ryan C., Nadler H. L. Cultivated epithelial-like cells and fibroblasts from amniotic fluid: their relationship to enzymatic and cytologic analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Oct 1;114(3):314–320. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90608-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. Alpha-L-iduronidase activity in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):817–821. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90577-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Ageing of human fibroblasts in culture: studies on enzymes and mutation. Humangenetik. 1972;16(1):83–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00393991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hors-Cayla M. C., Maroteaux P., de Grouchy J. Fibroblastes en culture au cours de mucopolysaccharidoses: influence du sérum sur la métachromasie. Ann Genet. 1968 Dec;11(4):265–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback M. M., Howell R. R. Infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 11;282(24):1336–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006112822403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittlick P. D., Neupert G., Lümkemann U. Die Wirkung verschiedener Seren auf die Mucopolysaccharidsynthese in Fibroblastenkulturen. Exp Pathol (Jena) 1973;8(3):194–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Dumon J., Radermecker J. Deficiency of arylsulphatase A in leucocytes and skin fibroblasts in juvenile machromatic leucodystrophy. Nature. 1970 May 9;226(5245):553–554. doi: 10.1038/226553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Spielvogel C., Kanfer J. N. Lysosomal enzyme variations in cultured normal skin fibroblasts. Life Sci II. 1972 Nov 22;11(22):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeijer M. F., Halley D., Sachs E., Tichelaar-Klepper C., Garver K. L. Transport and storage of amniotic fluid samples for prenatal diagnosis of metabolic diseases. Humangenetik. 1973;20(2):175–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00284856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., Veath M. L., Leroy J., O'Brien J. S. Ganglioside GM2 storage diseases: hexosaminidase deficiencies in cultured fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jan;23(1):55–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. L., Krooth R. S. The influence of progressive growth on the specific catalase activity of human diploid cell strains. I. Effect of cellular genotype: homozygous strains. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Apr;71(2):151–159. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040710205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin N. S., Arora R. C. A simplified assay method for galactosyl ceramide beta-galactosidase. J Lipid Res. 1971 Mar;12(2):256–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A., Lee S. Y., Nadler H. L. Effect of culture conditions on enzyme activities in cultivated human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1972;71(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. P., Patrick A. D. Deficiency of acid esterase activity in Wolman's disease. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Oct;45(243):664–668. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.243.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E., Ellis R. B., Patrick A. D., Singer H. S., Schafer I. A. Leukocyte -galactosidase activity in GM 1 -gangliosidosis. Pediatrics. 1972 Sep;50(3):502–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



