Abstract
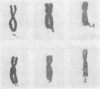
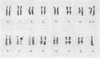
An X-linked pattern of transmission observed in four families with familial mental retardation in several generations was associated with a probable secondary constriction at the distal end of the q arms of the X chromosome. Twenty retarded males and no retarded females were observed. All available live retarded males and most of their normal mothers were found to have the abnormal X chromosome. The marker chromosome was shown to be the X chromosome in each case by Giemsa banding. In affected male and female carriers the marker chromosome varied in appearance and was not present in all metaphases. The significance of this study in relation to previously reported pedigrees showing non-specific X-linked mental retardation is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birner R., Wiener S. Letter: G-banding with heat treatment. Lancet. 1975 Dec 13;2(7946):1217–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY W. J., BARRAI I., MORTON N. E., MI M. P. RECESSIVE GENES IN SEVERE MENTAL DEFECT. Am J Hum Genet. 1965 May;17:237–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B. Nouveau système de marquage chromosomique: Les bandes. Chromosoma. 1973 Apr 27;41(4):395–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00396497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALZBERG B. Sex differences in the prevalence of mental deficiency. Am J Ment Defic. 1953 Oct;58(2):301–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENPENNING H., GERRARD J. W., ZALESKI W. A., TABATA T. Familial sex-linked mental retardation. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Nov 3;87:954–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. D., Robinson A. Recessive sex-linked mental retardation in the absence of other recognizable abnormalities. Report of a family. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1969 Nov;8(11):669–674. doi: 10.1177/000992286900801114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Turner B., Collins E. X-linked mental retardation without physical abnormality: Renpenning's syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1971 Feb;13(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1971.tb03033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Turner B. X-linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1974 Jun;11(2):109–113. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]