Abstract
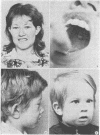
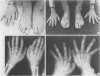
A new syndrome characterized by cleft palate, coloboma, hypospadias, deafness, short stature, and radial synostosis has been described. The family history suggests either an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance with limited expression in females or X-linkage. Other syndromes with similar phenotypes and modes of inheritance are discussed. The need for accurate and complete family histories in cases involving cleft palate and cleft lip/palate is discussed in relation to genetic counselling and recurrent risk estimates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fraser F. C. The genetics of cleft lip and cleft palate. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 May;22(3):336–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorlin R. J., Cervenka J., Anderson R. C., Sauk J. J., Bevis W. D. Robin's syndrome. A probably X-linked recessive subvariety exhibiting persistence of left superior vena cava and atrial septal defect. Am J Dis Child. 1970 Feb;119(2):176–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHTLEBEN P. ZUR PATHOGENESE UND THERAPIE DES PIERRE-ROBIN-SYNDROMS. Arch Kinderheilkd. 1964 Aug;171:55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein E. D., Cohen M. M. Sex-linked cleft palate. Report of a family and review of 77 kindreds. J Med Genet. 1966 Mar;3(1):17–22. doi: 10.1136/jmg.3.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]