Abstract
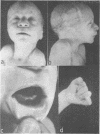
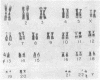
A newborn infant with clinical and pathological findings typical trisomy 13 and 22 syndromes had an extra chromosome which was a derivative chromosome from maternal balanced translocation affecting Nos. 13 and 22; 47,XY,+der(22),t(13:22)(q22:q12)Mat. The presence of extra specific euchromatic regions of No. 13(13q22 and/or 13q34) and No. 22 (22q11) seem to be responsible for the trisomy 13 and 22 syndromes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bove K. E., Koffler H., McAdams A. J. Nodular renal blastema. Definition and possible significance. Cancer. 1969 Aug;24(2):323–332. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196908)24:2<323::aid-cncr2820240215>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg W. R. Quinacrine fluorescence for identifying metaphase chromosomes, with special reference to photomicrography. Stain Technol. 1972 Mar;47(2):87–93. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. J., Reiss H. E., France N. E., Briddon S. Antenatal diagnosis of Patau's syndrome (trisomy 13) including a detailed pathological study of the fetus. J Med Genet. 1973 Dec;10(4):367–370. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. The structure and function of chromatin. Adv Hum Genet. 1972;3:237–431. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4429-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar J. I., Sanchez O., Yunis J. J. Trisomy for the distal segment of chromosome 13: a new syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Aug;128(2):217–220. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110270091019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Eggermont E., Verresen H., van den Berghe H. Partial trisomy 13: karyotype 46,XY,-6, plus t(13q,6q). Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):47–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00278564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn K., Lucas M., Wallace I. Precise identification of various chromosomal abnormalities. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Apr;36(4):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn H., Wolf U., Schumacher H., Wehinger H. A chromosome 13q+ in a patient with characteristics of the trisomy 13 syndrome. Humangenetik. 1971;13(1):34–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00446411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Shapiro L. R., Gertner M., Lieber E., Hirschhorn K. Trisomy 22: a clinical entity. J Pediatr. 1971 Jul;79(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence K. M., Gregory P. J., Sharp F. Prenatal detection of D trisomy. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):398–400. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATAU K., SMITH D. W., THERMAN E., INHORN S. L., WAGNER H. P. Multiple congenital anomaly caused by an extra autosome. Lancet. 1960 Apr 9;1(7128):790–793. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90676-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penchaszadeh V. B., Coco R. Trisomy 22. Two new cases and delineation of the phenotype. J Med Genet. 1975 Jun;12(2):193–199. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poissonnier M., Saint-Paul B., Dutrillaux B., Chassaigne M., Gruyer P., de Blignières-Strouk G. Trisomie 21 partielle (21q21 leads to 21q22.2) Ann Genet. 1976 Mar;19(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. W. AUTOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1964 Dec 1;90:SUPPL–SUPPL:1077. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(64)90835-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. I. Autosomal trisomy syndromes: a detailed study of 27 cases of Edwards' syndrome and 27 cases of Patau's syndrome. J Med Genet. 1968 Sep;5(3):227–252. doi: 10.1136/jmg.5.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida I. A., Ray M., McRae K. N., Besant D. F. Familial occurrence of trisomy 22. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Mar;20(2):107–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warkany J., Passarge E., Smith L. B. Congenital malformations in autosomal trisomy syndromes. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Dec;112(6):502–517. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090150046002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Summitt R. L., Martens P. R., Kimbrell R. A. Familial Down syndrome due to t(10;21) translocation: evidence that the Down phenotype is related to trisomy of a specific segment of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;27(4):478–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]