Abstract
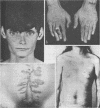
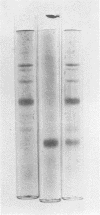
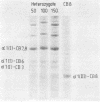
The Ehlers-Danlos type IV syndrome is a severe disease with premature death from catastrophic tearing of large arteries and a tendency to intestinal rupture. These patients lack the genetically distinct type III collagen. Here evidence is presented that obligate heterozygotes have lowered levels of type III collagen in their skin and that their cultured fibroblasts produce less than normal amounts of this protein. The inheritance is autosomal recessive.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barabas A. P. Heterogeneity of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: description of three clinical types and a hypothesis to explain the basic defect(s). Br Med J. 1967 Jun 3;2(5552):612–613. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5552.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beighton P., Price A., Lord J., Dickson E. Variants of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Clinical, biochemical, haematological, and chromosomal features of 100 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 May;28(3):228–245. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Miller E. J. Collagen polymorphism: characterization of molecules with the chain composition (alpha 1 (3)03 in human tissues. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Tanzer M. L., Lapiere C. M. Identification of two distinct species of procollagen synthesized by a clonal line of calf dermatosparactic cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):188–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio244188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Ferrante N., Leachman R. D., Angelini P., Donnelly P. V., Francis G., Almazan A. Lysyl oxidase deficiency in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type V. Connect Tissue Res. 1975;3(1):49–53. doi: 10.3109/03008207509152341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr (Alpha1(3))3 human skin collagen. Release by pepsin digestion and preponderance in fetal life. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3225–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Balleisen L., Remberger K., Fietzek P. P., Adelmann B. C., Kühn K. Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of collagen type III in human arterial walls, arterial thrombi, and in leukocytes, incubated with collagen in vitro. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Oct 1;53(19):899–902. doi: 10.1007/BF01468981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. The nature of the collagen synthesized by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Byers P. H., Smith B. D., Martin G. R. Identification of the collagenous proteins synthesized by cultured cells from human skin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1589–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., Kohn L. D., Byers P. H., McKusick V. A. Defect in conversion of procollagen to collagen in a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Epstein E. H., Jr, Piez K. A. Identification of three genetically distinct collagens by cyanogen bromide cleavage of insoluble human skin and cartilage collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell S. R., Krane S. M., Kenzora J. E., Glimcher M. J. A heritable disorder of connective tissue. Hydroxylysine-deficient collagen disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 11;286(19):1013–1020. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197205112861901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope F. M., Martin G. R., Lichtenstein J. R., Penttinen R., Gerson B., Rowe D. W., McKusick V. A. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV lack type III collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1314–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Byers P. H., Martin G. R. Production of procollagen by human fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3260–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L. Human aorta collagens: evidence for three distinct species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]