Abstract
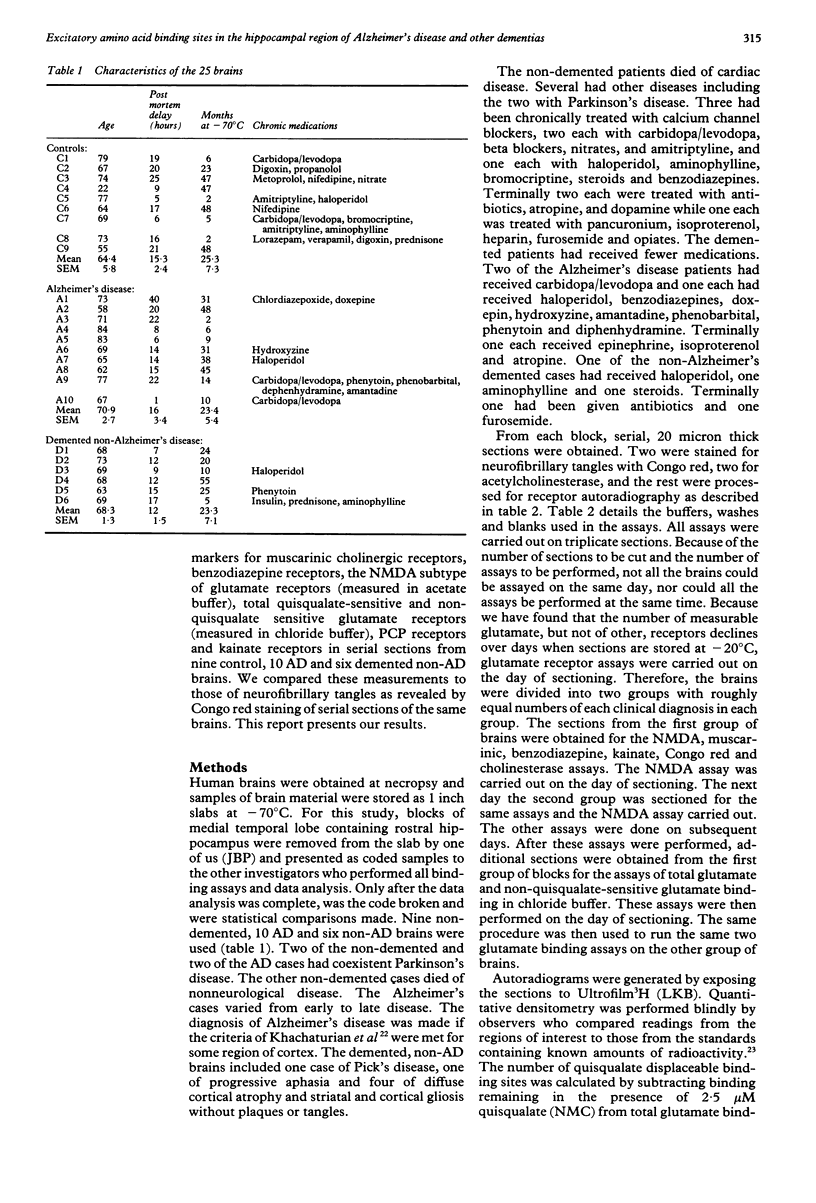
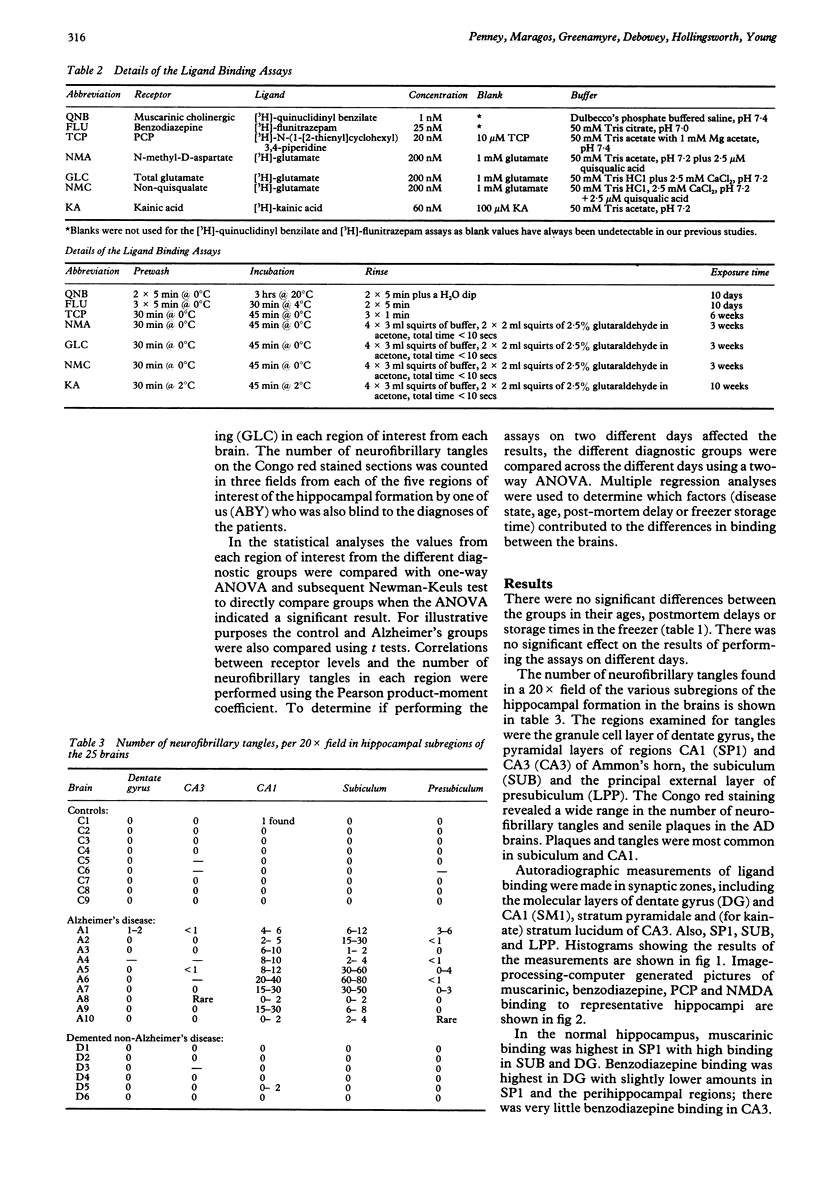
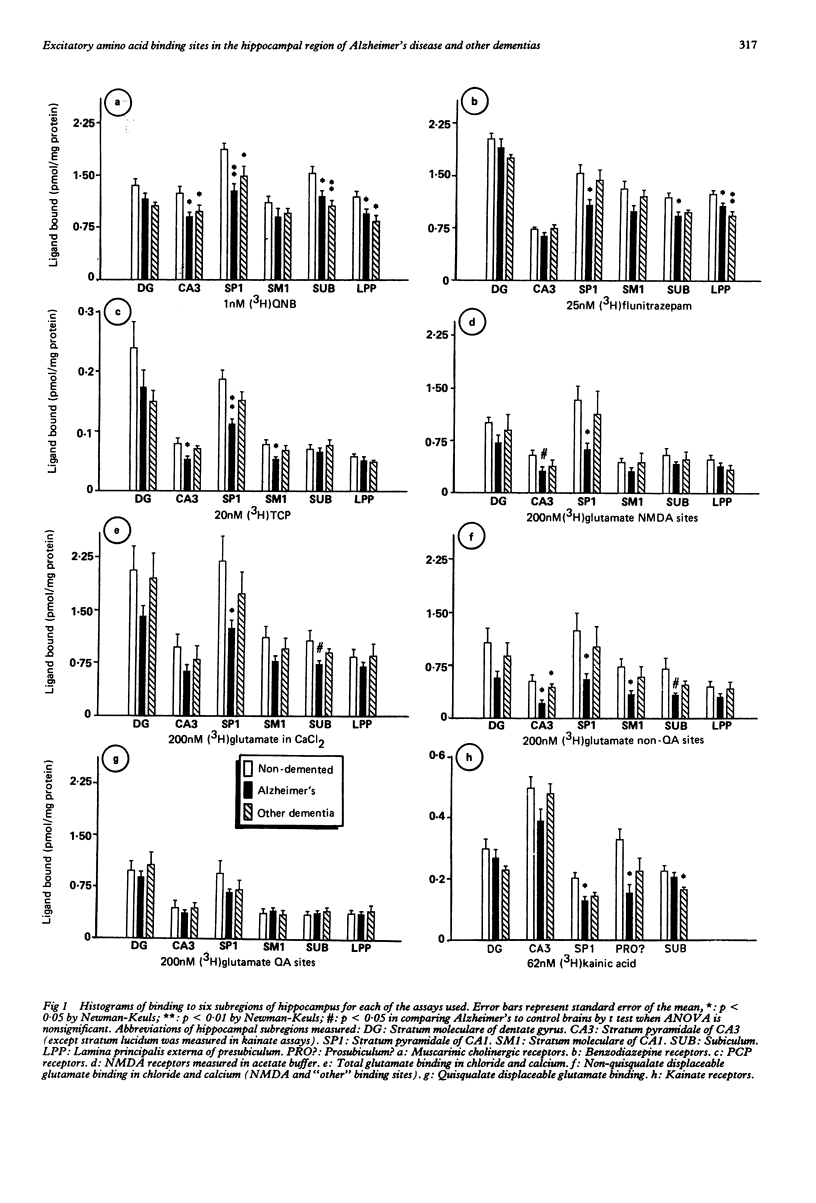
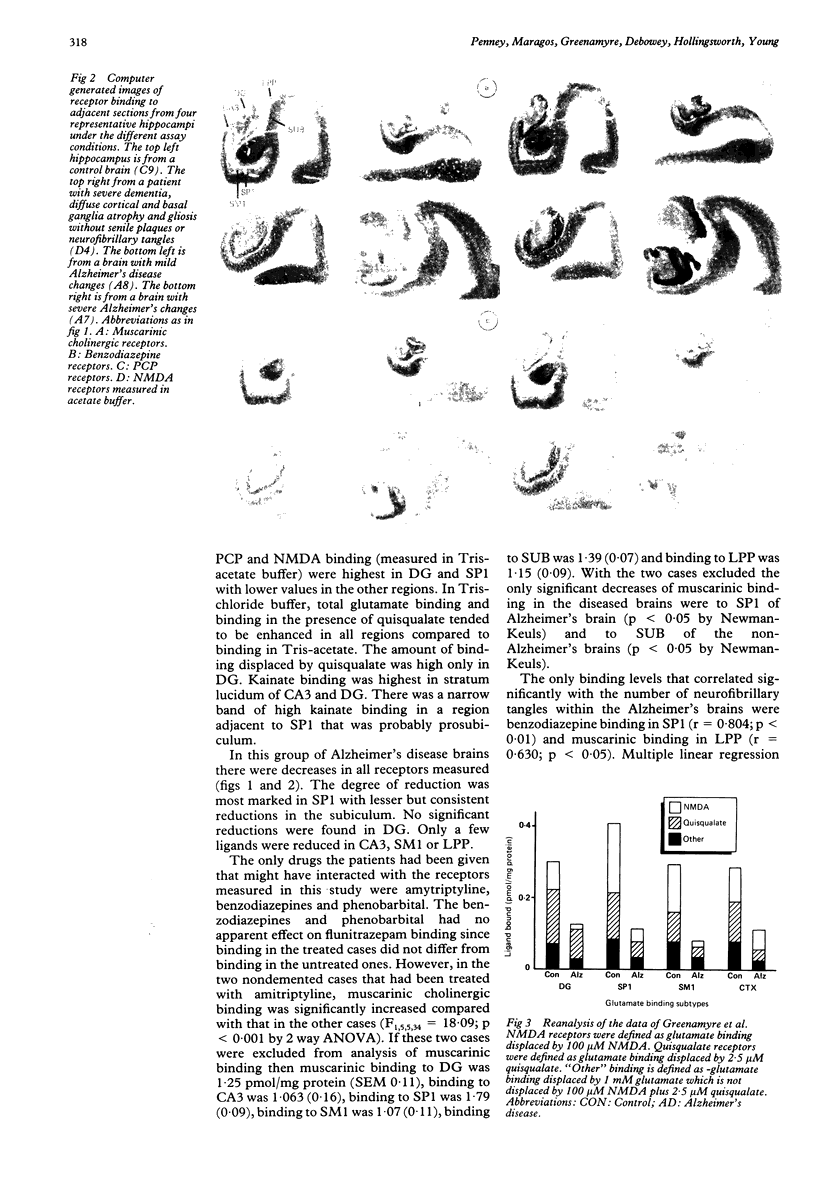
Quantitative receptor autoradiography was used to measure muscarinic cholinergic, benzodiazepine, kainate, phencyclidine (PCP), N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) (measured in Tris acetate), quisqualate-sensitive, non-quisqualate-sensitive and total glutamate (measured in Tris chloride buffer) binding sites in adjacent sections of the hippocampal region of 10 Alzheimer's disease, nine control, and six demented, non-Alzheimer's disease postmortem human brains. The measurements were compared to the number of neurofibrillary tangles as revealed by Congo red staining of adjacent sections. All assays and measurements were done by observers blinded to the clinical diagnoses. Binding was decreased significantly for all ligands except quisqualate in stratum pyramidale of CA1 of the Alzheimer's disease brains. The binding loss was significantly greater for the non-quisqualate and NMDA sites than for the muscarinic, benzodiazepine and kainate sites with the total glutamate and PCP site losses being intermediate. Only the loss of benzodiazepine binding was significantly correlated with the number of neurofibrillary tangles. Lesser binding losses were seen in adjacent areas. This difference in the degree of binding decrease is consistent with the hypothesis that NMDA receptors are located on more distal dendrites of hippocampal neurons. There they may be relatively more vulnerable than the other receptors to the pathological process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catalá I., Ferrer I., Galofré E., Fábregues I. Decreased numbers of dendritic spines on cortical pyramidal neurons in dementia. A quantitative Golgi study on biopsy samples. Hum Neurobiol. 1988;6(4):255–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. C., Penney J. B., Jr, Young A. B. Quantitative autoradiography of hippocampal GABAB and GABAA receptor changes in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 4;82(3):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. D., Flood D. G. Neuron numbers and dendritic extent in normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):521–545. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(87)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowburn R., Hardy J., Roberts P., Briggs R. Regional distribution of pre- and postsynaptic glutamatergic function in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 14;452(1-2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Crow T. J., Ferrier I. N., Johnson J. A., Bloom S. R., Corsellis J. A. Serotonin receptor changes in dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1574–1581. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. W., Chang-Chui H., Cooper S. M., Lott I. T., Cotman C. W. Density and distribution of NMDA receptors in the human hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 3;399(1):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90611-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. W., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Lott I. T., Kim R. C., Chui H. C. Plasticity of hippocampal circuitry in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.4071042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Olson J. M., Penney J. B., Jr, Young A. B. Autoradiographic characterization of N-methyl-D-aspartate-, quisqualate- and kainate-sensitive glutamate binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):254–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Penney J. B., D'Amato C. J., Young A. B. Dementia of the Alzheimer's type: changes in hippocampal L-[3H]glutamate binding. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):543–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Ganong A. H., Cotman C. W. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus involves activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 3;323(1):132–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Kromer L. J., Damasio A. R. Perforant pathway changes and the memory impairment of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1986 Oct;20(4):472–481. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi Y., Miyakawa H., Ito K., Kato H. Quisqualate and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in induction of hippocampal long-term facilitation using conditioning solution. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 16;83(1-2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragos W. F., Chu D. C., Young A. B., D'Amato C. J., Penney J. B., Jr Loss of hippocampal [3H]TCP binding in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 9;74(3):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragos W. F., Penney J. B., Young A. B. Anatomic correlation of NMDA and 3H-TCP-labeled receptors in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):493–501. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00493.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehraein P., Yamada M., Tarnowska-Dziduszko E. Quantitative study on dendrites and dendritic spines in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. Adv Neurol. 1975;12:453–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Geddes J. W., Yao D., Chung C., Cotman C. W. [3H]TCP binding sites in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Cotman C. W. L-[3H]Glutamate binds to kainate-, NMDA- and AMPA-sensitive binding sites: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 12;340(2):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90936-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouradian M. M., Contreras P. C., Monahan J. B., Chase T. N. [3H]MK-801 binding in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman R., Cherubini E., Ben-Ari Y. Is activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor gated channels sufficient to induce long term potentiation? Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 5;80(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Meek J. L., Iadarola M. J., Chuang D. M., Roth B. L., Costa E. Coupling of inositol phospholipid metabolism with excitatory amino acid recognition sites in rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli A., Reilly J. A., Lysko P. G., Henneberry R. C. Glutamate becomes neurotoxic via the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor when intracellular energy levels are reduced. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90765-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M. Autoradiographic localization of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in the hippocampus of patients with senile dementia. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 8;243(1):173–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H. S., Frey K. A., Young A. B., Penney J. B., Jr Changes in [3H]muscimol binding in substantia nigra, entopeduncular nucleus, globus pallidus, and thalamus after striatal lesions as demonstrated by quantitative receptor autoradiography. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1189–1198. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01189.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimohama S., Taniguchi T., Fujiwara M., Kameyama M. Changes in nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in Alzheimer-type dementia. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):288–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. B., Ball M. J., Reynolds M. A., London E. D. Muscarinic binding and choline acetyltransferase in postmortem brains of demented patients. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):528–532. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ruiter J. P., Uylings H. B. Morphometric and dendritic analysis of fascia dentata granule cells in human aging and senile dementia. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 3;402(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



