Abstract
Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is a biologically active gut microbiome-derived dietary metabolite. Recent studies have shown that high circulating plasma TMAO levels are closely associated with diseases such as atherosclerosis and hypertension, and metabolic disorders such as diabetes and hyperlipidemia, contributing to endothelial dysfunction. There is a growing interest to understand the mechanisms underlying TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction in cardio-metabolic diseases. Endothelial dysfunction mediated by TMAO is mainly driven by inflammation and oxidative stress, which includes: (1) activation of foam cells; (2) upregulation of cytokines and adhesion molecules; (3) increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS); (4) platelet hyperreactivity; and (5) reduced vascular tone. In this review, we summarize the potential roles of TMAO in inducing endothelial dysfunction and the mechanisms leading to the pathogenesis and progression of associated disease conditions. We also discuss the potential therapeutic strategies for the treatment of TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction in cardio-metabolic diseases.
Keywords: TMAO, endothelial dysfunction, cardio-metabolic diseases, inflammation, oxidative stress
1. Introduction
The endothelium is a monolayer of cells that lines the interior surface of the blood vessel and forms a partially permeable barrier between endothelial tissues and blood circulation. Blood vessels, comprising endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), serve essential secretory, synthetic, metabolic, and immunological roles [1]. Normal physiological conditions of the endothelium regulate vascular homeostasis by modulating vascular tone, platelet adhesion, inflammation, plasmatic coagulation, fibrinolysis, and VSMC proliferation. The generation and release of vasoactive factors by endothelial cells, such as endothelium-derived relaxing factors (EDRFs) and contracting factors (EDCFs), are vital for the maintenance of normal physiological conditions, and disturbances to these factors are known to increase the incidence of endothelial dysfunction [2,3,4]. Endothelial dysfunction, a pathophysiological condition wherein the endothelial homeostasis is disrupted, enhances the risk of thrombosis, inflammation, angiospasm, and intraplaque hemorrhage, resulting in atherothrombosis, infraction, and ischemia [1], and contributes to cardio-metabolic diseases, such as atherosclerosis, acute coronary syndromes, hypertension, reproductive disorders, and diabetes [5,6]. Multiple factors trigger endothelial dysfunction, which includes high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, genetics, and lifestyle practices such as smoking, physical inactivity, and diet. According to the Global Burden of Disease, Injuries, and Risk Factor study 2013, dietary risks are one of the most significant factors that contribute to cardio-metabolic diseases [7].
In recent years, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) was found to be closely associated with cardio-metabolic diseases mediated through endothelial dysfunction. TMAO is a biologically active compound from a class of amine oxides, generated from dietary precursors highly enriched in red meat, fish, and egg yolk [8]. Studies have shown that plasma TMAO levels are elevated in individuals with type II diabetes [9], diastolic dysfunction [10], heart failure [10], atherosclerotic plaque deposition [11,12], and peripheral artery disease (PAD) [13]. Subsequent mechanistic studies revealed that TMAO treatment elevates inflammation and oxidative stress, which triggers cardio-metabolic diseases [14,15]. Given its well-established association with chronic inflammation and accelerated progression of cardio-metabolic diseases, TMAO has recently gained significant scientific interest as a potential circulating biomarker for predicting cardio-metabolic diseases and chronic kidney diseases (CKD) [16].
In this review, we discuss the currently available methods for TMAO detection and its known association with disease conditions. Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms of TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction in experimental and clinical studies, as well as potential treatment strategies to prevent the progression of diseases triggered by TMAO, are also summarized.
2. TMAO Metabolism, Biosynthesis, and Excretion
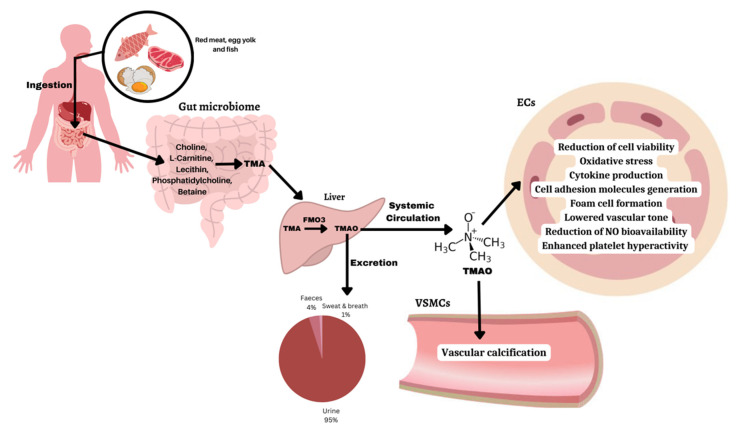
The biochemical pathways involved in TMAO biosynthesis, metabolism, excretion, and processes leading to endothelial dysfunction causing cardiovascular complications are summarized in Figure 1. Specifically, trimethylamine (TMA) is generated by gut microbes through dietary precursors such as choline, L-carnitine, lecithin, phosphatidylcholine, and betaine [15]. Bacterial strains involved in TMA generation include Anaerococcus hydrogenalis, Clostridium asparagiforme, Clostridium hathewayi, Clostridium sporogenes, Edwardsiella tarda, Escherichia fergusonii, Proteus penneri, and Providencia rettgeri [17]. Interestingly, individuals with cardio-metabolic diseases have an imbalance in the levels of bacteria in the gut. Elevated levels of pathogenic bacteria such as Firmicutes and Proteobacteria are found and are known to be associated with increased levels of inflammation and insulin resistance, resulting in poor metabolism [18]. In contrast, healthy individuals have a greater diversity of gut microbes that are found in stable amounts. Beneficial bacteria namely Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii are present in abundant levels and are associated with improved metabolism and lower levels of inflammation [19]. Most of the TMA formed is rapidly absorbed via portal circulation [20]. In the liver, a class of hepatic flavin monooxygenase (FMO) enzymes, predominantly FMO3, causes the oxidation of TMA to TMAO [21]. Homogenous distribution of TMAO takes place throughout the body through systemic circulation, but it may accumulate in higher amounts in certain tissues [22]. In most individuals, about half of the TMAO generated is excreted without any modifications within 24 h, through urine (95%), feces (4%), as well as by sweat and breath (less than 1%) [23]. Not excreted TMAO remains circulating in the plasma, and its levels are remarkably high in patients with type II diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, and coronary heart disease [8]. In summary, these findings indicate that the gut microbiome plays an essential role in the advancement and acceleration of cardio-metabolic diseases. Therefore, understanding the species involved in TMA formation could potentially result in novel therapeutic strategies to lower the risk of these diseases. Moreover, these observations suggest that plasma TMAO levels may serve as a pre-chronic disease biomarker to assess the health status of an individual.
Figure 1.
Biochemical pathways involved in the formation of TMAO. TMAO is synthesized from dietary precursors after the action of the gut microbiota and flavin-containing monooxygenases, mainly the FMO3 enzyme in the liver. Increased plasma TMAO levels are associated with biological pathways that trigger endothelial dysfunction and lead to cardiovascular complications.
3. TMAO Detection and Measurement Methods
With the conceptual understanding that TMAO can be considered a potential biomarker for chronic diseases, detection of TMAO in plasma becomes crucial in the preliminary prognosis of several disease conditions. TMAO levels in plasma, feces, and urine samples have been analyzed [24], and commonly used methods for TMAO detection include chromatography techniques such as selective solid-phase extraction, ion chromatography, UPLC-M/MS, flow injection gas diffusion-ion chromatography, and liquid chromatography-selective ion monitoring [25,26,27,28] (Table 1). These methods are advantageous due to their analytical precision and reproducibility, but they require the expertise of specialized technicians [29], and the process is time-consuming and expensive. Other techniques involve the use of electrochemical tools such as cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry, oxygen anti-interference membrane, and microbial electrochemical technology [30,31,32,33]. They are user-friendly and have long operational stability. However, they may be prone to environmental interferences in clinical applications. In summary, there is still a need to develop cheaper, more reliable, and more efficient testing tools to detect TMAO clinically, and identify patients with higher cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks. This will enable clinicians to intervene with the right treatment strategies and prevent the evolution of the condition.
Table 1.
Current TMAO detection and measurement methods.
| Experimental Method | Technique | Linear Range | Limit of Detection | Sensitivity | Response Time | Advantage | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromatography | FIGD-IC | 40–600 nmol/dm3 | 1.35 nmol/dm3 | - | 20 min | Non-hazardous, reliable, precise (3%), sensitive | Time-consuming, expensive equipment, requires specialized technicians | [34] |
| GC-MS | SPME | 14.9–956 μmol/L | 0.01 μmol/L | 14.9 μmol/L | - | Analysis of volatile and semi-volatile compounds | Complicated, laborious, time-consuming, incomplete TMAO transformation | [35] |
| Electrophoresis | Capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV-detection | 0.025–2.5 mmol/L | 2.5 mmol/L | - | - | Analytical precision, repeatability | Time-consuming, expensive equipment, specialized technicians, restrict point-of-care testing (PCOT) | [36] |
| Liquid chromatography | SPE | 5.0–50.0 μg/mL | 0.05 μg | - | - | Selective determination in presence of other primary and secondary short chain aliphatic amines | - | [25] |
| Chromatography | Ion chromatography | 1.0–20.0 mg/mL | 0.10 mg/L | - | 16 min | Inexpensive and stable | Time-consuming, requires specialized technicians | [26] |
| Chromatography | LC-SIMs | 15–944 pg/μL | 115 pg/mL | - | 5 min | Robust, highly sensitive, reproducible, no sample pre-treatment required, only small volume of sample needed | Expensive | [27] |
| Chromatography | UPLC-M/MS | 15–1500 μg/L | 0.12 μg/L | - | 6 min | Repeatable, rapid, and economic | Not a point-of-care testing | [28] |
| Fluorescence | IDA | 0–1.22 mmol/L | 8.98 μmol/L | - | - | Low cost, easy to operate, label free, sensitive | - | [37] |
| Electrochemical | CV | 2–110 µmol/L | 2.96 nmol/L | 14.16 nA/mM | 16 s | Sensor can operate over prolonged daily measurements, quite good short-term usage stability | Complex preparation process (enzyme purification and protein reconstruction) | [30] |
| Electrochemical | DPV | 1–15 ppm | 1.5 ppm | 2.47 µA mL/ppm/cm2 | 20 min | Easy to construct and operate, highly selective | - | [31] |
| Electrochemical | Oxygen anti-interference membrane | 2 µM–15 mmol/L | 10 µmol/L | 2.75 µA/mM | 33 s | Operational stability over 3 weeks | Vulnerable to environmental interferences in clinical applications | [32] |
| Electrochemical | Microbial electrochemical technology | 0–250 µmol/L | 5.96 µmol/L | 23.92 µA/mM | 600 s | 90% accuracy in real serum, high feasibility in clinical applications | - | [33] |
FIGD-IC: flow injection-ion chromatography; GC-MS: gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; SPME: solid-phase microextraction; SPE: solid-phase extraction; LC-SIMs: liquid chromatography-selective ion monitoring; UPLC-M/MS: ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; IDA: indicator displacement assay; CV: cyclic voltammetry; DPV: differential pulse voltammetry.
4. TMAO Level Variations and Disease Conditions
Plasma TMAO levels are regulated by several factors such as age, genetics, gut microbiome, FMO3 activity, and diet [22]. For example, many studies have shown that an increase in age influences plasma TMAO levels [38,39]. Furthermore, links between various disease conditions, their progression, and plasma TMAO levels have also been established [8,40], which are summarized in Table 2. Hence, quantification and understanding of plasma TMAO levels in individuals may be essential in the pre-diagnosis of certain specific diseases. However, some findings have inherent limitations due to tight sample size, uneven gender distribution, and lack of control groups. In addition, a controversial study has shown that plasma TMAO levels may be an independent risk factor for disease conditions [41]. These different findings need to be validated by a large-scale analysis including a greater number of individuals with a balanced representation of both genders.
Table 2.
Association of plasma TMAO levels with various disease conditions.
| Experimental Model | Condition (If Any) | Plasma TMAO Level for Control | Plasma TMAO Level for Condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human and Rodents | - | 0.5–5 µmol/L | - | [11,42] |
| Human | Patients undergoing hemodialysis | 0.92–1.9 µmol/L | 28–67 µmol/L | [43] |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | - | 32.2–75.2 µmol/L | [44] | |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | - | 2.27 µmol/L | [45] | |
| Plaque rupture | 4.2 ± 2.4 μmol/L | 8.6 ± 4.8 µmol/L | [46] | |
| Calcified aortic valve disease | 1.4–2.8 µmol/L | 2.3–6.4 µmol/L | [47] | |
| Stage 1 hypertensive patients | - | 87.2 ng/mL | [48] | |
| Older age, BMI, lower eGFR, HDL-levels, higher choline and carnitine levels, higher TG | 2.83 ± 1.34 μmol/L | 8.43 ± 4.85 µmol/L | [49] | |
| Stroke | 1.4–3.7 µmol/L | 1.6–4.0 µmol/L | [50] | |
| First ever acute ischemic stroke and neurological deficit | 2.6–6.1 µmol/L | 0.5–18.3 µmol/L | [51] | |
| Stroke (LAA), transient ischemic attack, history of diabetes, CAD, HBP, HLP | 1.91 µmol/L | 2.70 µmol/L | [52] |
BMI: body mass index; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; TG: triglycerides; LAA: large-artery atherosclerosis; CAD: coronary artery disease; HBP: high blood pressure; HLP: hyperlipidemia.
5. Molecular Mechanisms of TMAO-Induced Diseases (Table 3)
5.1. Endothelial Dysfunction Mediated by TMAO
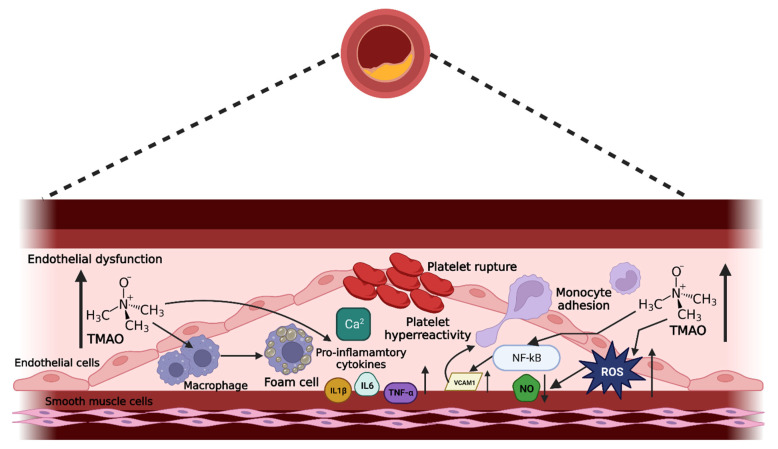
Endothelial dysfunction, often classified as the impairment of endothelium-dependent vasodilation, is associated with oxidative stress and exaggerated activation of inflammatory pathways, which are mediated through foam cell formation, expression of inflammatory cytokines, and generation of adhesion molecules [4,6]. Endothelial dysfunction is known to play key roles in blood clotting, immune response, and vascular tone [4] (modulated via the synthesis and release of various EDRFs and EDCFs by the endothelium [4,6]), reported to contribute to CVD, CKD, and cardio-metabolic diseases such as diabetes. The proposed mechanisms of action of TMAO-activating endothelial dysfunction and triggering cardio-metabolic complications are summarized in Figure 2. These include a reduction in endothelial cell viability, overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), enhanced vascular inflammation, vascular calcification leading to atherosclerotic plaques, and reduced vascular tone, which will be discussed in detail in the subsequent section. However, most studies associating TMAO and endothelial dysfunction were performed in rodents or in cell culture [53]. There is a need for clinical data to better understand the molecular mechanisms of TMAO-driven endothelial dysfunction in humans. This is crucial for the development of effective therapeutic interventions to overcome the complications of disease evolution.
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of action in TMAO-induced cardio-metabolic diseases. Increased circulating levels of TMAO cause various processes within the endothelial cells, contributing to the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis.
5.1.1. Effect of TMAO on Cell Viability
Cell viability assay is a common tool to evaluate the direct impact of TMAO exposure on endothelial cells. Despite numerous studies reporting TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction, the effects of TMAO on endothelial cell viability remain inconsistent. For instance, TMAO (125–1000 µM) treatment for 48 h was shown to increase apoptosis in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) [54]. Consistent with this observation, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) showed lower viability after 48 h of TMAO treatment (100 µM or higher) [55]. On the other hand, several studies reported that TMAO has no significant effect on endothelial cell viability. For example, HUVEC cells treated with 10–100 µM of TMAO for 24 h did not result in any changes in cell viability [56]. Similarly, TMAO did not induce any difference in cell viability in other endothelial cell types, such as human endothelial progenitor cells [53]. This observation was consistent with another recent study where TMAO did not influence cell viability at any time point or concentration in bovine aortic endothelial cells-1 (BAEC-1) treated with 1 µM–10 mM of TMAO for 24 h–72 h [57]. Collectively, there is controversial evidence regarding the impact of TMAO on cell viability. These contradicting results may be due to the usage of different endothelial cell types, the wide range of treatment durations, and varied TMAO doses, although the range of concentrations used in these in vitro experiments were usually physiologically relevant to the plasma serum levels of patients with disease conditions (Table 2).
5.1.2. TMAO Enhances Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is caused by the imbalance between the generation of ROS and the ability of the cells to neutralize these ROS through antioxidant activities [3,58]. Many studies have demonstrated that high TMAO concentrations induce endothelial dysfunction in cultured endothelial cells through oxidative stress [38,59]. Specifically, TMAO has been shown to trigger ROS production through thioredoxin-interacting protein- NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (TXNIP-NLRP3). It was demonstrated that the TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome complex production was activated in a time and dose-dependent manner by TMAO [60]. Another pathway responsible for oxidative stress is the Sirtuin 3 and superoxide dismutase 2 (SIRT3-SOD2) ROS signaling, which is activated by TMAO in vascular inflammation models [61]. Interestingly, TMAO lowered expression levels of SIRT1 and increased oxidative stress, both in vivo and in vitro by triggering the p53/p21/retinoblastoma tumor suppressor signaling pathways [62]. In addition, TMAO is correlated with an increase in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase activity resulting in vascular oxidative stress [63]. Finally, elevated circulating TMAO levels are associated with aging in mice and humans [64], which may deteriorate endothelial cell through senescence and increase ROS generation.
5.1.3. TMAO Induces Inflammation
Inflammation is a sequence of native and comprehensive immune responses that our body generates as feedbacks, upon exposure to harmful stimuli [65]. Inflammatory response, involving migration of immune cells to the damaged region, is the first step. It is followed by repair and regeneration (2nd step), involving the building of new collagen and restoration of skin homeostasis [66]. Lastly, remodeling and maturation occur to improve cellular organization where the injured tissue matures. Factors such as the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, enhanced adhesion, and activation of foam cell formation is part of the inflammatory response [67]. Simultaneously, blood vessels present at the inflammatory site narrow down, which slows down the blood flow and activates vascular modifications [68], a phenomenon that can cause endothelial dysfunction.
Enhanced Cytokine Production
TMAO triggers inflammation by increasing the generation of inflammatory cytokines. Inflammatory cytokines (or pro-inflammatory cytokines) are signaling molecules generated by activated macrophages and are important players of inflammation. Some of the significant pro-inflammatory cytokines include interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and IL-6 [69]. TMAO is known to initiate the production of TNF-α and IL-1β [61,70], and in vitro studies confirmed the elevated levels of TNF-α production in endothelial cells, through the activation of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which enhances leukocyte adhesion to endothelial walls [14]. This activates endothelial dysfunction, which may trigger CVD risks such as thrombosis and atherosclerosis [15]. In human trials, a positive relationship was also found between TMAO and IL-1β in patients with angina [53], and in a population of individuals at risk of CVD, a positive correlation was observed between TMAO levels and inflammation [71]. Collectively, data show that elevated plasma TMAO levels contribute to inflammatory and cardio-metabolic risks via the induction of inflammatory cytokines [72,73].
Activation of Adhesion Molecules
Relationships between TMAO and adhesion molecules have been established in the evolution of endothelial dysfunction. Expression of the vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM-1) is induced by TMAO in primary rats and human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) [74], while TMAO-induced VCAM-1 expression is triggered by the methylation of the NF-κB p65 subunit in HUVEC [56]. In fact, many studies demonstrated that TMAO-induced NF-κB activation is a significant downstream process that upregulates monocyte adhesion through upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules such as VCAM-1, but also intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and E-selectin, and enhances endothelial dysfunction [14,15]. Moreover, TMAO (10, 50 and 100 µM) is known to activate the protein kinase C (PKC) in a dose-dependent manner, which plays a crucial role in upregulating monocyte adhesion [20,75]. In summary, increased TMAO levels, in animal models and human endothelial cells, contribute to increased adhesion of monocytes and low endothelial self-repair by the activation of PKC, NF-κB, and VCAM-1 signaling pathways [56], resulting in endothelial dysfunction.
Elevated Foam Cell Formation
Foam cell formation is an indicative feature in the introductory phase of atherosclerosis progression, which characterizes CVD. Indeed, CVD is distinguished by inflammation-induced atherosclerotic complications, resulting from an increase in lipid particle transport to endothelial cells causing foam cell formation [76]. Foam cells (also called lipid-laden macrophages) are a key source of pro-inflammatory phenotypes as they generate inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, chemokines, and ROS, and play a significant role in activating inflammation at different stages of the atherosclerotic progression. Foam cells are formed when immune cells such as macrophages take up large amounts of cholesterol through absorption of lipoproteins via different transporters, mostly mediated by CD36, SR-A, and LOX-1. They then become overloaded with cholesterol and are unable to process it effectively. This causes these macrophages to transform into foam cells (which store esterified cholesterol and are characterized by their large and frothy appearance), which accumulate in the walls of blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerosis [77,78,79]. Studies have shown that in mice models, TMAO stimulates macrophage recruitment by promoting their migration and expression of TNF-α, IL-6 (considered promoters of foam cell formation [79]), as well ICAM1 [80]. Moreover, TMAO plays a critical role in the accumulation of ox-LDL in macrophages through upregulation of multiple scavenger receptors, CD36, lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1), and class A1 scavenger receptors (SR-A1) [77], that contribute to the formation of atherosclerosis by enhancing cholesterol uptake with lipoprotein modifications [11]. This process triggers the transformation of more macrophages into foam cells within the vascular membrane [81]. Other studies demonstrated that dietary choline, a precursor of TMAO, increases foam cell production in ApoE knockout mice [11], extensively used as a model of atherosclerosis. Finally, TMAO promotes the development of foam cells by upregulating macrophage scavenger receptors [11,12,82]. Eventually, foam cell formation modulates lipoprotein metabolism and causes lesions [83]. Plaques with abundant foam cells can rupture, leading to thrombosis and CVD-related events [78]. In summary, there is a mechanistic link between TMAO and elevated foam cell generation resulting in atherosclerosis.
5.1.4. TMAO Reduces Vascular Tone
Endothelial dysfunction is associated with abnormal changes in the vascular tone, which is regulated by the production of at least three vasoactive factors, nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin I2 (PGI2), and endothelium-derived hyperpolarization (EDH) [3,58,84,85,86]. PGI2, one of the prostanoids of arachidonic acid metabolism, is a potent vasodilator that inhibits platelet aggregation, leukocyte adhesion, and VSMC cell proliferation [87]. NO is produced through the enzymatic conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline by endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) [86,88]. The vasodilator actions of NO are mediated via the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase, leading to the accumulation of cGMP and the relaxation of smooth muscle cells [89,90]. Lastly, EDH is generated by contact-mediated (myoendothelial gap junctions) and non-contact-mediated mechanisms, which involve the opening of small- and intermediate calcium-activated potassium channels (SKCa and IKCa) and subsequent hyperpolarization and relaxation of VSMC. Collectively, the endothelium functions normally through the production of NO, PGI2, and EDH to maintain vascular tone and an imbalance in these vasoactive factors result in endothelial dysfunction [91,92,93].
Effects of TMAO on NO Bioavailability
Studies have shown a link between elevated circulating TMAO levels and reduced eNOS, and therefore reduced NO bioavailability in the aorta of Fischer-344 rats [38]. This reduced eNOS seems to result from the upregulation of vascular oxidative stress and inflammation [94]. These data were consistent with another study where TMAO pre-treatment for 24 h significantly reduced NO production after ATP stimulation in BAEC-1, indicating the potential involvement of TMAO in damaging the endothelial-dependent vasodilatory mechanism [57]. Conversely, in the same study, TMAO pre-treatment for 1 h did not influence the intracellular NO release and eNOS phosphorylation in BAEC-1. Other findings demonstrate that eNOS activity remains unchanged in the aorta of rats treated with TMAO and in HAEC pre-incubated with 1 µM of TMAO [57]. These last findings suggest that increased plasma TMAO levels in the near-physiological range are neutral to vascular function. In summary, from these experimental results, the effects of TMAO on NO bioavailability are inconsistent, and it appears that only pharmacological concentrations of TMAO could have a negative effect in normal metabolic conditions. However, underlying metabolic diseases may interfere with TMAO effects, explaining the contradictory data from the different studies.
Association between TMAO and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
H2S and other vasoactive factors are key signaling molecules associated with vasorelaxation, cardio-protection, neuroprotection, and anti-inflammation. Hence, TMAO-induced NO bioavailability may potentially have a stronger effect in altering the vasculature in patients with underlying metabolic disorders, increasing their risk of endothelial dysfunction-driven diseases. H2S is produced in various tissues and plays a significant role in the circulatory system homeostasis, including the heart, blood vessels, and kidneys [95]. H2S also protects against ROS, and its proangiogenic effects can lower blood pressure and heart rate. Studies revealed that a diet enriched in choline reduces the plasma H2S levels, which activates cardiac dysfunction through the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase -stimulator of interferon genes-NOD-like receptor protein 3 (cGAS-STING-NLRP3) inflammasome-mediated pathway in mice [96]. However, the study did not directly measure the association between TMAO and H2S, hence, the direct impact of TMAO on H2S production and its vascular effects warrants further investigation.
Role of Prostanoids in Vasoconstriction
Prostanoids, metabolites of arachidonic acid, are dominant lipid mediators that modulate inflammatory responses. They include PGD2, PGE2, PGF2 alpha, PGI2, thromboxane A2 (TXA2) [88]. PGI2 is the most potent vasodilator prostanoid in the cardiovascular system and lowers the risk of atherosclerosis plaque formation. In mice models, choline reduces serum PGI2 levels and increases TXA2 production [97]. This causes a vasoconstrictor response and a proatherogenic phenotype, resulting in endothelial cell damage. However, there is a very limited number of studies showing the relationship between prostanoids and TMAO in causing endothelial dysfunction.
EDH in Endothelial Dysfunction
EDH is an essential component in small arteries, and it impacts vascular resistance, blood pressure, and the distribution flow [3]. In rats, acute treatment with TMAO specifically impairs acetylcholine-evoked EDH-mediated relaxation in the femoral arteries, indicating that TMAO contributes to the progression of peripheral arterial disease [98]. This observation is consistent with another study in rats where EDH-type relaxations were selectively disrupted without interference with NO-induced vasodilation in isolated mesenteric arteries. Taken together, these data suggest that a reduction in EDH elevates the process of endothelial dysfunction in various diseases that could be influenced by TMAO levels.
5.1.5. TMAO-Enhanced Platelet Hyperreactivity
Platelet hyperreactivity is a significant factor in the activation of thrombotic environments resulting in heart attack, ischemic stroke, and severe diabetes complications [99]. High blood pressure, oxidative stress, and upregulated levels of vascular shear stress are conditions that often contribute to platelet hyperreactivity [100]. Under resting periods, platelets show a low intracellular [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]i) as they circulate through the healthy vessels [101]. However, at the site of vessel injury, platelets are activated by increased [Ca2+]i, a precursor to thrombus formation [102]. Physiological levels of TMAO enhance submaximal thrombin-induced augmentation of platelet [Ca2+]i in a dose-dependent manner [103]. In addition, the MAPK signaling pathway is a well-established driving factor of platelet aggregation by collagen [104], and TMAO causes platelet hyper-responsiveness to collagen by promoting the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) [105], triggering thrombotic phenotypes [103].
5.2. TMAO Triggers Heart Failure
As discussed, TMAO increases the risk of atherosclerosis and CVD by different mechanisms. The terminal stage of a variety of CVD complications is heart failure (HF), a well-known cause of disability and death. The pathological mechanisms of HF are very complex, and they initiate cardiac remodeling and inflammatory responses. These processes include apoptosis and extracellular matrix accumulation, consequently causing fibrosis [106]. Animal models, such as rats and mice, have been used to study the effects of TMAO on HF. NLRP3 inflammasome activation by TMAO triggers cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through the suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic 3 (Smad 3) signaling pathway [107]. In addition, TMAO triggers oxidative damage, promotes glycogen synthesis, and reduces pyruvate dehydrogenase activity as well as fatty acid β oxidation in mitochondria. This results in mitochondrial dysfunction and lower cardiac energy production [108].
5.3. TMAO Promotes Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome corresponds to simultaneous disorders including hypertension, obesity, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia, which increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type II diabetes, as well as the risk of CVD. Some of the major causes of these metabolic disorders are genetics, organ dysfunction, and mitochondrial dysfunction. A high-fat diet with TMAO precursors activates impaired glucose tolerance and inhibits the hepatic insulin signaling pathway [109]. Indeed, studies have shown that TMAO directly binds to and activates the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), causing hyperglycemia [110,111]. In addition, obesity traits are increased in mice treated with TMAO resulting in a high risk of type II diabetes, mediated by the intestinal reverse cholesterol transport and the TMA/FMO3/TMAO pathways [112]. TMAO also activates metabolic dysfunction through bile acid metabolism. It positively correlates with plasma levels of bile acids and hepatic mRNA expression of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) in mice, which trigger hepatic lipogenesis and hepatic steatosis via the bile acid-mediated hepatic farnesoid X receptor (FXR) signaling pathway [113].
Table 3.
In vitro and in vivo models studying TMAO-linked molecular mechanisms and diseases.
| Disease | Species/Cells | Molecular Mechanisms | Potential Pathways Triggered | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis and CVD | THP-1y HUVECs (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells) | ↑ adhesion of monocytes, ↓ endothelial self-repair, endothelial dysfunction |
Activation of PKC, NF-κB and VCAM-1 pathways | [56] |
| LDLR-/- mice fed a choline diet (aorta), HAECs (Human Aortic Endothelial Cells), VSMECs (Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells) | ↑ pro-inflammatory cytokines, ↑ leukocyte adhesion to endothelial wall |
MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway | [14] | |
| HUVECs and ApoE-/- mice (aorta) | Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, ↑ vascular inflammation |
Inhibition of SIRT3-SOD2-mitochondrial ROS signaling pathway | [61] | |
| Human and C57BL/6J ApoE-/- mice | ↓ bile acid synthetic enzyme, ↓ reverse cholesterol transport, ↓ lipid metabolism and transport |
Unknown pathway, likely to be linked to Niemann Pick Cl-like1 (Npc1L1) | [11,12,114] | |
| ApoE-/- mice and ApoE-/- mice with a high-fat diet | ↑ macrophage scavenger receptors CD36 and SR-A1, ↑ lipid accumulation, ↑ foam cell formation |
CD36-dependent MAPK/JNK pathway | [11,80,115] | |
| Fischer-344 rats | ↑ oxidative stress, ↑ pro-inflammatory cytokines, ↑ endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation |
Unknown | [38] | |
| Heart failure | Male C57BL/6 mice and adult male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats | Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, triggers cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis |
Smad 3 signaling pathway | [116] |
| Male C57BL/6 mice and cultured cardiac fibroblasts | ↑ pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-1β, ↑ interstitial fibrosis in heart, ↑ myocardial inflammation, activation of NLRP3 inflammasome |
NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway | [107] | |
| ICR mice and male Wistar rats | ↓ cardiac energy production, ↓ pyruvate dehydrogenase activity & fatty acid β-oxidation, ↑ glycogen synthesis, ↑ oxidative damage to proteins, mitochondrial dysfunction |
Cardiac energy metabolism | [108] | |
| Kidney disease | Human and high-fat diet/low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes rats | ↑ pro-fibrotic factors TGF-β1, IL-1β and Smad3, ↑ phosphorylation and Smad3 activation, ↑ kidney injury molecule-1, activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, renal inflammation, renal fibrosis and renal dysfunction |
NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway, transforming growth factor β, SMAD signaling pathway | [117,118] |
| Metabolic dysfunction | Male C57BL/6 mice with high-fat diet (HFD)-fed | ↑ insulin signaling pathway, ↑ glycogen synthesis, ↑ gluconeogenesis and glucose transport in liver, impaired glucose tolerance, ↑ insulin resistance |
Hepatic insulin signaling pathway | [119] |
| Human and Male ob/ob mice and wild-type C57BL/6 | ↑ insulin resistance, ↑ FMO3, ↑ FOX01, hyperglycemia |
FMO3/TMAO pathway | [111] | |
| Male wild-type C57BL/6 mice | ↑ hepatic FMO3 expression, TMAO activates PERK, ↑ FOX01 |
Stress- and PERK-related pathways | [110] | |
| Human and ASO-treated mice | ↑ obesity traits and Type II diabetes, negative regulatory role for FMO3 in beiging of white adipose tissue | TMA/FMO3/TMAO pathway and transintestinal cholesterol excretion (TICE)/intestinal pathway of reverse cholesterol transport | [112] | |
| Human and cholesterol 7 alpha hydroxylase (CYP7A1) mice | ↑ Cyp7a1 in mice, ↑ hepatic lipogenesis, ↑ hepatic steatosis through bile acid metabolism |
Bile acid-mediated hepatic FXR signaling pathway | [113] |
THP-1y: the human monocyte cell line; PKC: protein kinase C; NF-Kb: NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; LDLR -/-: low-density lipoprotein receptor; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinases; SIRT3-SOD2: sirtuin 3-superoxide dismutase 2; CD36: cluster of differentiation 36; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta; NLRP3: nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich–containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3; ICR: institute of cancer research; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor- beta 1; SMAD3: mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3; FMO3: flavin-containing monooxygenase 3; FOX01: forkhead box protein O1; PERK: orotein kinase R-like ER kinase; TMA: trimethylamine; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; FXR: farnesoid X receptor.
6. Potential Treatment Strategies
Understanding the involvement of TMAO in various disease conditions has resulted in active research and analyses to identify potential therapeutic strategies to reduce TMAO levels in the serum. As no specific compound directed against TMAO was found yet, a direct scavenger targeting TMAO is not available [23,120,121]. Hence, commonly proposed potential treatment strategies target the process of TMA generation, the activity of gut microbes to lower TMAO production, and the ingestion of natural products to reduce the concentration of TMAO. These therapeutic approaches are outlined in Table 4.
Table 4.
Proposed therapeutic approaches to target TMAO formation.
| Intervention | Therapy | Model | Intervention/Dosage | Duration | Route of Administration | Effects | Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targeting the gut microbiome | Prebiotics | Human | Whole grains, traditional Chinese medicinal foods, and prebiotics (WTP diet) | 30–90 days | Oral | Improves composition of gut microbiota to reduce TMAO formation | Gut microbiome is influenced by multiple components | [122] |
| Probiotics | Female germ-free mouse (C3H strain) | Basal mixed diet and probiotics supplementation in saline water |
14 days | Oral | Lowers TMAO formation in the gut | Unclear safety and effects in humans | [123] | |
| Antibiotics | Mouse | Drinking water with a cocktail of broad-spectrum antibiotics | 21 days | Oral | Suppression and inhibition of plasma TMAO levels | Inhibition of useful bacteria and induction of resistant bacteria. Not feasible in the long run |
[11] | |
| Antibiotics | Human | Metronidazole (500 mg twice daily) plus ciprofloxacin (500 mg once daily) for 1 week | 7 days | Oral | Suppression and inhibition of plasma TMAO levels | Inhibition of useful bacteria and induction of resistant bacteria. Not feasible in the long run |
[124] | |
| Oral non-absorbent binders | Human and rat | 10 mL solution of 800 mg of polymyxin B and 320 mg of tobramycin (selective decontamination of the digestive tract [SDD]) | 56 days | Oral | Removal of TMAO and its precursors from gut | Uncertain approach. Compound specific to TMAO has not yet been found |
[121] | |
| Targeting TMA formation | Inhibition of FMO3 | Wild-type C57BL/6J, male Sprague–Dawley rat (Harlan) and human | 50 mg/kg body weight of antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) | 7 weeks or 16 weeks | Intraperitoneal injection | Inhibition of TMAO formation from TMA | Accumulation of TMA in plasma may cause other diseases. Metabolism of other compounds is also mediated by FMO3 |
[111] |
| 3,3-Dimethyldimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) | Mouse | 1% DMB in drinking water | 56 days | Oral | Inhibition of TMA formation from dietary precursors choline, carnitine, corotonobetaine by inhibiting microbial TMA lyase | Complete TMAO formation cannot be avoided by DMB. Study not performed in humans. Unable to inhibit formation of TMA from γ-butyrobetaine |
[125] |
|
| 3,3-Dimethyldimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) | Mouse | 1%, v/v in drinking water | 16 weeks | Oral | Reorganization of gut microbial community and inhibition of TMA production | Only partial TMAO formation inhibition | [115] |
|
| Meldonium | Human and rat | Single dose of 13C-GBB (100 mg/kg) or 13C-GBB in combination with meldonium (GBB + M, 100 mg/kg each) |
14 days | Oral | Lowers TMAO formation from L-carnitine and increases TMAO excretion via urine | Unable to reduce TMAO formation from choline | [126,127] | |
| Therapeutic alternatives to lower TMAO concentration | Resveratrol | Female C57BL/6J mouse and ApoE-/- mouse with a C57BL/6 genetic background | 0.4% RSV | 30 days | Oral | Alters gut microbiome composition, hence reducing bacteria that forms TMA and increasing useful bacteria | Study performed only in mice. No changes when antibiotics are used |
[128] |
| Capsanthin | High-fat-diet induced obese C57BL/6J mice |
Capsanthin at 200 mg kg−1 body weight | 12 weeks | Oral | Lowers body weight, effectively reduces TMAO levels, and increases microbial diversity | Study performed in mice | [129] | |
| Lycopene (Lycopersicon esculentum [M.]), amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor), and sorghum red (Sorghum bicolor (L.)) pigments | High-fat diet fed C57BL/6 mice | 200 mg/kg body of lycopene or amaranth or sorghum red administration | 12 weeks | Oral | Ameliorates lipid metabolism, and lowers TMAO levels | Study performed in mice | [130] | |
| Gynostemma pentaphyllum | Rat | 120 mg/kg/day | 28 days | Oral gavage | Lowers plasma TMAO levels and rises in lecithin levels | Study performed only in rats | [131] |
|
| Gancao (root of glycyrrhiza uralensis) | Male Wistar rat | Single dose of Gancao (35.6 g kg−1 body weight) | - | Intragastric administration | Prevents increase in TMAO when administered with Fuzi (processed lateral root of Aconitum carmichaelii) | Does not lower TMAO levels when administered alone. Study performed in rats | [132] | |
| Oolong tea extract and citrus peel polymethoxyflavones | Mouse | 1 μg | Injection every 10 days for a period of 16 weeks | Intravenous injection | Lowers TMAO formation and vascular inflammation | Study performed only in mice | [133] | |
| Berberine (BBR) | ApoE-/- mouse on a C57BL/6 background | BBR treatment (50 mg/kg) twice weekly | 84 days | Intragastric administration | Lowers expression of hepatic FMO3 and serum TMAO levels | Study performed only in mice | [134] | |
| Trigonelline | C57BL/6 J mouse | Trigonelline (50 to 100 mg/kg) per day | 14 days | Oral | Inhibits conversion of TMA to TMAO by inhibiting FMO3 | Study performed only in mice | [135] | |
| Enalapril | Rat | 5.3 or 12.6 mg/kg | 14 days | Oral | Increases TMAO excretion in urine | Unclear mechanism. Does not affect TMA formation or composition of gut microbiota |
[21,136] | |
| Metformin | db/db mice | 250 mg/kg/day | 8 weeks | Oral | 2-fold reduction in TMAO levels and bacteria linked to TMAO production | Study performed in only mice | [137] |
6.1. Targeting TMA and TMAO Formation Process through Enzymatic Inhibition
6.1.1. Targeting TMAO
Some potential therapeutics involve the inhibition of TMAO-forming enzymes. In mice models, knockdown of FMO3 (the enzyme which converts TMA to TMAO) has been reported to suppress the expression of FoxO1 (a key protein regulating metabolism), and to prevent the occurrence and progression of metabolic dysfunction such as hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis. Consistent with this finding, FMO3 overexpression in mice upregulates the levels of lipids in the plasma and liver, suggesting that FMO3 may be linked to gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis, and may play a major role in glucose and lipid homeostasis regulation [138]. The drawback of FMO3 inhibition is an accumulation of TMA, which can lead to trimethylaminuria characterized by a fishy odor, and which induces inflammation. In addition, if FMO3 overexpression is closely associated with the upregulation of TMAO formation [23,82,138,139], TMAO is not the only substrate of FMO3. Hence, the inhibition of this enzyme will also lower the metabolism of other substrates such as morphine, propranolol, and tyramine [23], potentially leading to co-lateral metabolism modifications that may not be beneficial.
6.1.2. Targeting TMA
Studies performed in mouse models showed that the 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB), found in balsamic vinegar, olive oil, grape seed oil, and red wines [21], and which inhibits the choline TMA lyase enzyme [21], reduces macrophage foam cell formation and aortic root atherosclerotic lesion development in Apo E knockout mice [22,115]. In obese mice fed with a high-fat western diet, the DMB treatment does not have any effects on body weight and dyslipidemia, but significantly lowers plasma TMAO levels and prevents cardiac dysfunction. Moreover, DMB successfully prevents the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-10) and TNFα. However, it is unable to completely prevent TMAO formation and does not inhibit the formation of TMA from γ-butyrobetaine [115,125]. Prevention of bacterial TMAO formation through competitive inhibition of the bacterial carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT-1) has also been observed to be possible with meldonium. Meldonium, known for its anti-atherosclerotic and anti-ischemic properties, is an analogue of carnitine that lowers the generation of TMA from L-carnitine, but not choline, and improves endothelial function [22,127,140]. Finally, plant sterol esters can reduce the gut microbiota generation of TMA as well as cholesterol accumulation, and eliminate atherogenesis in mice [141]. However, the effects remain unclear in humans.
6.2. Reduction in TMAO Generation by Modifying the Gut Microbiota
6.2.1. Prebiotics and Probiotics
Both prebiotics and probiotics can be used to improve the composition of the gut microbiota and regulate the level of TMAO formation [122]. Prebiotics are inclusive of all kinds of non-digestible food and are known to trigger the growth and development of useful bacteria [142], while probiotics involve the administration of living microbes that can yield beneficial effects on human health when administered in sufficient amounts, as defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations [143]. Conversely, some bioactive food can reduce the generation of bacteria that convert dietary precursors in TMA. As such, the administration of Lactobacillus paracasei in germ-free mice colonized with human infant microbiota results in reduced TMA formation, and the use of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium lowers the risk of atherosclerosis [123,144]. Other studies have reported the possibility of using methanogenic bacteria (e.g., the large group of Methanobacteriales), such as Methanomassiliicoccus luminyensis B10, to metabolize TMA and deplete it [145,146]. In addition, probiotics lower inflammation by triggering anti-inflammatory cytokines and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines that regulate the NF-κB pathway [147], which is linked to MAPK, pathogen recognition, and inflammatory signaling pathways [148]. The toll-like receptor expression has been shown to be downregulated by probiotics, hence also lowering intestinal inflammation [149]. However, a common limitation of probiotics used to lower TMAO levels and potentially reduce the risk of atherosclerosis is that the effect of treatment may change according to the gut microbiota composition of each specific individual.
6.2.2. Antibiotics
Another strategy to lower or eliminate the conversion of dietary precursors into TMA is to target the gut microbiome composition via antibiotics. Antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin and metronidazole effectively suppress TMAO levels in clinical trials [150,151]. However, after one month of antibiotics withdrawal, TMAO levels are detected again [21,124]. Furthermore, the use of antibiotics may incur bacterial resistance or kill beneficial bacteria in addition to harmful ones [124].
6.3. Other Therapeutic Alternatives to Lower TMAO Concentration
Oral non-absorbent binders have been used to eliminate TMAO and its precursors. Clinically used, oral charcoal adsorbent AST-120 eliminates uremic contaminants such as indoxyl sulfate from end-stage renal disease patients [152]. However, this remains an uncertain approach as none of these absorbents specifically target TMAO [23,120,121].
Consumption of natural products may also reduce TMAO levels. Specifically, studies showed that Resveratrol (a polyphenol with antioxidant activities) modifies the composition of the gut microbiome, reducing the bacteria that promote TMA formation and increasing the useful bacteria [128,153]. Gynostemma pentaphyllum (an herbaceous climbing vine) lowers plasma TMAO levels and increases lecithin levels in rat models [131]. Gancao (the root of Glycyrrhiza uralensis) prevents the rise of TMAO levels when administered with Fuzi (the processed lateral root of Aconitum carmichaelii). However, it does not lower plasma TMAO levels when administered alone [60]. Oolong tea extract and citrus peel polymethoxyflavones target the TMAO formation process and lower vascular inflammation [154]. Other compounds such as berberine (BBR) [134] and trigonelline [135] are also natural products known to inhibit the formation of TMAO from TMA by lowering the expression of the FMO3 enzyme.
Anti-diabetic medications also have the potential to modify the gut microbiome. Similarly, the gut microbiota can modify the effectiveness of diabetic medications. The majority of data indicate that metformin is the most effective drug as compared to all the other anti-diabetic medications [155]. Interestingly, in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus, treatment with metformin results in a twofold reduction in TMAO concentration and the generation of bacteria associated to TMAO precursors production [137]. In this study, it was suggested that a reduction in TMAO concentration with the use of metformin is an effective therapeutic strategy to exert cardiovascular benefits.
In addition, some potential anti-obesity drugs such as capsanthin, as well as the lycopene, amaranth, and sorghum red pigments obtained from Lycopersicon esculentum (M.), Amaranthus tricolor, and Sorghum bicolor, respectively, also reduce serum levels of TMAO and increase microbial diversity in mouse fed with high-fat diet [129,130].
Another drug, Enalapril (ACE [angiotensin converting enzyme] inhibitor), tested in rats, increases the excretion of TMAO in the urine. However, the mechanism remains unclear, as it does not target TMAO formation or modification of the gut microbiota [21].
Despite the promising effects of these products to reduce TMAO levels, studies were only performed in mouse models. Hence, there is insufficient evidence to confirm their impact in humans.
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspective
In conclusion, the gut microbial metabolite TMAO is a significant biomarker of cardio-metabolic diseases. The molecular mechanisms underlying TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction and subsequent development of cardio-metabolic diseases are multi-factorial, and primarily involve vascular inflammation and oxidative stress via the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Through oxidative stress and inflammation, TMAO triggers other effects such as platelet hyperreactivity and reduction in vascular tone through the impairment of EDH-mediated relaxation and PGI2 production. While other reported factors, such as cell viability and NO bioavailability remain controversial, the differences observed may be attributed to distinct metabolic backgrounds of models, as well as study design (cell types, TMAO concentrations, and treatment durations). Future studies should explore the molecular signatures and pathways that contribute to endothelial dysfunction and/or other cardio-metabolic diseases. While most of the current treatment strategies focus on preventing the formation of TMAO, other plausible treatment strategies could focus on targeting key mechanistic pathways that contribute to disease pathology in the various organs. Hence, a better understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms will lead to the development of new therapeutic agents such as small molecules [156], peptides [157,158] or natural products [159,160,161] that have potent vasoprotective effects (e.g., anti-inflammatory properties) to effectively prevent or reverse TMAO-induced endothelial dysfunction and/or other cardio-metabolic diseases.
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 and Figure 2 were created using elements from Canva and BioRender. MS was a recipient of the SUTD Ph.D. Scholarship. The sponsors have no role in the study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, or writing of the report and in the decision to submit the article for publication. The authors thank Xiaogang Liu for his feedback and guidance in this study.
Author Contributions
M.S.: Conceptualization, writing, revision. S.B.: Supervision, revision. C.H.L.: Conceptualization, supervision, revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential competing interest.
Funding Statement
The research was partially funded by SUTD Start-up Research Grant (SRG-SMT-2020–156), SUTD-ZJU Grant (ZJUVP2000102), and SUTD Kickstarter Initiative (SKI_2021_02_05).
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Baselet B., Sonveaux P., Baatout S., Aerts A. Pathological effects of ionizing radiation: Endothelial activation and dysfunc-tion. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019;76:699–728. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2956-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nappi F., Fiore A., Masiglat J., Cavuoti T., Romandini M., Nappi P., Singh S.S.A., Couetil J.-P. Endothelium-Derived Relaxing Factors and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines. 2022;10:2884. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leo C.H., Jelinic M., Ng H.H., Tare M., Parry L.J. Serelaxin: A Novel Therapeutic for Vascular Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016;37:498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marshall S.A., Leo C.H., Girling J.E., Tare M., Beard S., Hannan N.J., Parry L.J. Relaxin treatment reduces angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction in pregnancy and protects against endothelial dysfunctiondagger. Biol. Reprod. 2017;96:895–906. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Woodman O.L., Leo C.H. Flavonols in the Prevention of Diabetes-induced Vascular Dysfunction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015;65:532–544. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ng H.H., Leo C.H., Prakoso D., Qin C., Ritchie R.H., Parry L.J. Serelaxin treatment reverses vascular dysfunction and left ventricular hypertrophy in a mouse model of Type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:39604. doi: 10.1038/srep39604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Subramaniam S., Fletcher C. Trimethylamine N-oxide: Breathe new life. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018;175:1344–1353. doi: 10.1111/bph.13959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kalagi N.A., Thota R.N., Stojanovski E., Alburikan K.A., Garg M.L. Association between Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels and Type 2 Diabetes: A Case Control Study. Nutrients. 2022;14:2093. doi: 10.3390/nu14102093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tang W.H., Wang Z., Kennedy D.J., Wu Y., Buffa J.A., Agatisa-Boyle B., Li X.S., Levison B.S., Hazen S.L. Gut micro-biota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mor-tality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res. 2015;116:448–455. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang Z., Klipfell E., Bennett B.J., Koeth R., Levison B.S., Dugar B., Feldstein A.E., Britt E.B., Fu X., Chung Y.M., et al. Gut flora metabolism of phos-phatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2011;472:57–63. doi: 10.1038/nature09922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koeth R.A., Wang Z., Levison B.S., Buffa J.A., Org E., Sheehy B.T., Britt E.B., Fu X., Wu Y., Li L., et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of l-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013;19:576–585. doi: 10.1038/nm.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Senthong V., Li X.S., Hudec T., Coughlin J., Wu Y., Levison B., Wang Z., Hazen S.L., Tang W.H. Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide, a Gut Microbe-Generated Phosphatidylcholine Metabolite, Is Associated with Atherosclerotic Burden. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016;67:2620–2628. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Seldin M.M., Meng Y., Qi H., Zhu W., Wang Z., Hazen S.L., Lusis A.J., Shih D.M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-kappaB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e002767. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang S., Li X., Yang F., Zhao R., Pan X., Liang J., Tian L., Li X., Liu L., Xing Y., et al. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Marker TMAO in Promoting Cardiovascular Disease: Inflammation Mechanism, Clinical Prognostic, and Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Pharmacol. 2019;10:1360. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dehghan P., Farhangi M.A., Nikniaz L., Nikniaz Z., Asghari-Jafarabadi M. Gut microbiota-derived metabolite trime-thylamine N-oxide (TMAO) potentially increases the risk of obesity in adults: An exploratory systematic review and dose-response meta- analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020;21:e12993. doi: 10.1111/obr.12993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Romano K.A., Vivas E.I., Amador-Noguez D., Rey F.E. Intestinal Microbiota Composition Modulates Choline Bioavailability from Diet and Accumulation of the Proatherogenic Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide. Mbio. 2015;6:e02481. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02481-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tang W.W., Kitai T., Hazen S.L. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2017;120:1183–1196. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hansen T.H., Gobel R.J., Hansen T., Pedersen O. The gut microbiome in cardio-metabolic health. Genome. Med. 2015;7:33. doi: 10.1186/s13073-015-0157-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu Y., Dai M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Generated by the Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Vascular Inflammation: New Insights into Atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020;2020:4634172. doi: 10.1155/2020/4634172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Janeiro M.H., Ramírez M.J., Milagro F.I., Martínez J.A., Solas M. Implication of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) in Disease: Potential Biomarker or New Therapeutic Target. Nutrients. 2018;10:1398. doi: 10.3390/nu10101398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Velasquez M.T., Ramezani A., Manal A., Raj D.S. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Toxins. 2016;8:326. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zeisel S.H., Warrier M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide, the Microbiome, and Heart and Kidney Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017;37:157–181. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zixin Y., Lulu C., Xiangchang Z., Qing F., Binjie Z., Chunyang L., Tai R., Dongsheng O. TMAO as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for chronic kidney disease: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022;13:929262. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.929262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cháfer-Pericás C., Herráez-Hernández R., Campıns-Falcó P. Liquid chromatographic determination of trimethylamine in water. J. Chromatogr. 2004;1023:27–31. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li F., Liu H.Y., Xue C.H., Xin X.Q., Xu J., Chang Y.G., Xue Y., Yin L.A. Simultaneous determination of dimethylamine, trimethylamine and trimethylamine-n-oxide in aquatic products extracts by ion chromatography with non-suppressed con-ductivity detection. J. Chromatogr. 2009;1216:5924–5926. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.06.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Veeravalli S., Karu K., Phillips I.R., Shephard E.A. A highly sensitive liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry method for quantification of TMA, TMAO and creatinine in mouse urine. Methodsx. 2017;4:310–319. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2017.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu Q., Zhao Y., Zhang X., Yang X. A faster and simpler UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of tri-methylamine N-oxide, trimethylamine and dimethylamine in different types of biological samples. Food Funct. 2019;10:6484–6491. doi: 10.1039/C9FO00954J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chang Y.-C., Chu Y.-H., Wang C.-C., Wang C.-H., Tain Y.-L., Yang H.-W. Rapid Detection of Gut Microbial Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide for Chronic Kidney Disease Prevention. Biosensors. 2021;11:339. doi: 10.3390/bios11090339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mitrova B., Waffo A.F.T., Kaufmann P., Iobbi-Nivol C., Leimkühler S., Wollenberger U. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Elec-trochemical Biosensor with a Chimeric Enzyme. ChemElectroChem. 2018;6:1732–1737. doi: 10.1002/celc.201801422. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lakshmi G.B.V.S., Yadav A.K., Mehlawat N., Jalandra R., Solanki P.R., Kumar A. Gut microbiota derived trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) detection through molecularly imprinted polymer based sensor. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:1338. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80122-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Waffo A., Mitrova B., Tiedemann K., Iobbi-Nivol C., Leimkühler S., Wollenberger U. Electrochemical Trimethylamine N-Oxide Biosensor with Enzyme-Based Oxygen-Scavenging Membrane for Long-Term Operation under Ambient Air. Biosensors. 2021;11:98. doi: 10.3390/bios11040098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yi Y., Liang A., Luo L., Zang Y., Zhao H., Luo A. A novel real-time TMAO detection method based on microbial electro-chemical technology. Bioelectrochemistry. 2022;144:108038. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.108038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hatton A.D., Gibb S.W. A Technique for the Determination of Trimethylamine-N-oxide in Natural Waters and Biological Media. Anal. Chem. 1999;71:4886–4891. doi: 10.1021/ac990366y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mills G.A., Walker V., Mughal H. Quantitative determination of trimethylamine in urine by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999;723:281–285. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4347(98)00542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Timm M., Jørgensen B.M. Simultaneous determination of ammonia, dimethylamine, trimethylamine and trimethylamine-n-oxide in fish extracts by capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV-detection. Food Chem. 2002;76:509–518. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00289-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yu H., Geng W.-C., Zheng Z., Gao J., Guo D.-S., Wang Y. Facile Fluorescence Monitoring of Gut Microbial Metabolite Trimethylamine N-oxide via Molecular Recognition of Guanidinium-Modified Calixarene. Theranostics. 2019;9:4624–4632. doi: 10.7150/thno.33459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li T., Chen Y., Gua C., Li X. Elevated Circulating Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels Contribute to Endothelial Dysfunction in Aged Rats through Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Front. Physiol. 2017;8:350. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang Z., Tang W.H.W., Buffa J.A., Fu X., Britt E.B., Koeth R.A., Levison B.S., Fan Y., Wu Y., Hazen S.L. Prognostic value of choline and betaine depends on intestinal microbiota-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide. Eur. Heart J. 2014;35:904–910. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roy S., Yuzefpolskaya M., Nandakumar R., Colombo P.C., Demmer R. Plasma Trimethylamine-N-oxide and impaired glucose regulation: Results from The Oral Infections, Glucose Intolerance and Insulin Resistance Study (ORIGINS) PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0227482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dong Z., Liang Z., Guo M., Hu S., Shen Z., Hai X. The Association between Plasma Levels of Trimethylamine N-Oxide and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Chinese Patients with or without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Dis. Markers. 2018;2018:1578320. doi: 10.1155/2018/1578320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ufnal M., Zadlo A., Ostaszewski R. TMAO: A small molecule of great expectations. Nutrition. 2015;31:1317–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kaysen G.A., Johansen K.L., Chertow G.M., Dalrymple L.S., Kornak J., Grimes B., Dwyer T., Chassy A.W., Fiehn O. Associations of Trimethylamine N-Oxide With Nutritional and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients New to Dialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015;25:351–356. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2015.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Missailidis C., Hällqvist J., Qureshi A.R., Barany P., Heimbürger O., Lindholm B., Stenvinkel P., Bergman P. Serum Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Is Strongly Related to Renal Function and Predicts Outcome in Chronic Kidney Disease. PLOS ONE. 2016;11:e0141738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wilson A., Teft W.A., Morse B.L., Choi Y.-H., Woolsey S., DeGorter M.K., Hegele R.A., Tirona R.G., Kim R.B. Trimethylamine-N-oxide: A Novel Biomarker for the Identification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015;60:3620–3630. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3797-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fu Q., Zhao M., Wang D., Hu H., Guo C., Chen W., Li Q., Zheng L., Chen B. Coronary Plaque Characterization Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography and Plasma Trimethylamine-N-oxide Levels in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016;118:1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.07.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li J., Zeng Q., Xiong Z., Xian G., Liu Z., Zhan Q., Lai W., Ao L., Meng X., Ren H., et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces osteogenic responses in human aortic valve interstitial cells in vitro and aggravates aortic valve lesions in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021;118:2018–2030. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang J.-M., Yang M.-X., Wu Q.-F., Chen J., Deng S.-F., Chen L., Wei D.-N., Liang F.-R. Improvement of intestinal flora: Accompany with the antihypertensive effect of electroacupuncture on stage 1 hypertension. Chin. Med. 2021;16:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00417-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Xiong X., Zhou J., Fu Q., Xu X., Wei S., Yang S., Chen B. The associations between TMAO-related metabolites and blood lipids and the potential impact of rosuvastatin therapy. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2022;21:60. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01673-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nieuwdorp M., Xie L., Zhao B.-X., Li X.S., Qiu B., Zhu F., Li G.-F., He M., Wang Y., Wang B., et al. Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide Concentration Is Positively Associated With First Stroke in Hypertensive Patients. Stroke. 2018;49:2021–2028. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.118.021997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rexidamu M., Li H., Jin H., Huang J. Serum levels of Trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with ischemic stroke. Biosci. Rep. 2019;39 doi: 10.1042/BSR20190515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yin J., Liao S.X., He Y., Wang S., Xia G.H., Liu F.T., Zhu J.J., You C., Chen Q., Zhou L., et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota With Reduced Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Level in Patients With Large-Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2015;4:e002699. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chou R.-H., Chen C.-Y., Chen I.-C., Huang H.-L., Lu Y.-W., Kuo C.-S., Chang C.-C., Huang P.-H., Chen J.-W., Lin S.-J. Trimethylamine N-Oxide, Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells, and Endothelial Function in Patients with Stable Angina. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:4249. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40638-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wang Z., Wu F., Zhou Q., Qiu Y., Zhang J., Tu Q., Zhou Z., Shao Y., Xu S., Wang Y., et al. Berberine Improves Vascular Dysfunction by Inhibiting Trimethylamine-N-oxide via Regulating the Gut Microbiota in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertensive Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022;13:691. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.814855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chen L., Jin Y., Wang N., Yuan M., Lin T., Lu W., Wang T. Trimethylamine N-oxide impairs perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020;530:95–99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ma G., Pan B., Chen Y., Guo C., Zhao M., Zheng L., Chen B. Trimethylamine N-oxide in atherogenesis: Impairing endo-thelial self-repair capacity and enhancing monocyte adhesion. Biosci. Rep. 2017;37:BSR20160244. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Querio G., Antoniotti S., Geddo F., Levi R., Gallo M.P. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Impairs Purinergic Induced In-tracellular Calcium Increase and Nitric Oxide Release in Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:3982. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Leo C.H., Fernando D.T., Tran L., Ng H.H., Marshall S.A., Parry L.J. Serelaxin Treatment Reduces Oxidative Stress and Increases Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 to Attenuate Nitrate Tolerance. Front. Pharmacol. 2017;8:141. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Singh G.B., Zhang Y., Boini K.M., Koka S. High Mobility Group Box 1 Mediates TMAO-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3570. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sun X., Jiao X., Ma Y., Liu Y., Zhang L., He Y., Chen Y. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016;481:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen M.L., Zhu X.H., Ran L., Lang H.D., Yi L., Mi M.T. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Induces Vascular Inflammation by Activating the NLRP3 Inflammasome Through the SIRT3-SOD2-mtROS Signaling Pathway. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e006347. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ke Y., Li D., Zhao M., Liu C., Liu J., Zeng A., Shi X., Cheng S., Pan B., Zheng L., et al. Gut flora-dependent metabolite Trimethylamine-N-oxide accelerates endothelial cell senescence and vascular aging through oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018;116:88–100. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.007. Erratum in Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 608–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.González-Loyola A., Petrova T.V. Development and aging of the lymphatic vascular system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021;169:63–78. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Brunt V.E., LaRocca T.J., Bazzoni A.E., Sapinsley Z.J., Miyamoto-Ditmon J., Gioscia-Ryan R.A., Neilson A.P., Link C.D., Seals D.R. The gut microbiome–derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide modulates neuroinflammation and cognitive function with aging. Geroscience. 2020;43:377–394. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00257-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Turner M.D., Nedjai B., Hurst T., Pennington D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and in-flammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1843:2563–2582. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Theofilis P., Sagris M., Oikonomou E., Antonopoulos A., Siasos G., Tsioufis C., Tousoulis D. Inflammatory Mechanisms Contributing to Endothelial Dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2021;9:781. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Angelovich T.A., Hearps A.C., Jaworowski A. Inflammation-induced foam cell formation in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015;93:683–693. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Pober J.S., Sessa W.C. Inflammation and the blood microvascular system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2014;7:a016345. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhang J.M., An J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007;45:27–37. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Boutagy N.E., Neilson A.P., Osterberg K.L., Smithson A.T., Englund T.R., Davy B.M., Hulver M.W., Davy K.P. Pro-biotic supplementation and trimethylamine-N-oxide production following a high-fat diet. Obesity. 2015;23:2357–2363. doi: 10.1002/oby.21212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Meyer K.A. Population studies of TMAO and its precursors may help elucidate mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020;111:1115–1116. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fu B.C., Hullar M.A.J., Randolph T.W., Franke A.A., Monroe K.R., Cheng I., Wilkens L.R., Shepherd J.A., Madeleine M.M., Le Marchand L., et al. Associations of plasma trimethylamine N-oxide, choline, carnitine, and betaine with inflammatory and cardiometabolic risk biomarkers and the fecal microbiome in the Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phe-notype Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020;111:1226–1234. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Papandreou C., More M., Bellamine A. Trimethylamine N-Oxide in Relation to Cardiometabolic Health-Cause or Effect? Nutrients. 2020;12:1330. doi: 10.3390/nu12051330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Liu H., Jia K., Ren Z., Sun J., Pan L.-L. PRMT5 critically mediates TMAO-induced inflammatory response in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:299. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04719-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Durpes M.C., Morin C., Paquin-Veillet J., Beland R., Pare M., Guimond M.O., Rekhter M., King G.L., Geraldes P. PKC-beta activation inhibits IL-18-binding protein causing endothelial dysfunction and diabetic atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015;106:303–313. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kong P., Cui Z.-Y., Huang X.-F., Zhang D.-D., Guo R.-J., Han M. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: Signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022;7:131. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00955-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gui Y., Zheng H., Cao R.Y. Foam Cells in Atherosclerosis: Novel Insights into Its Origins, Consequences, and Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022;9:842. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.845942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bentzon J.F., Otsuka F., Virmani R., Falk E. Mechanisms of Plaque Formation and Rupture. Circ. Res. 2014;114:1852–1866. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Zheng Y., Li Y., Rimm E.B., Hu F.B., Albert C.M., Rexrode K.M., Manson J.E., Qi L. Dietary phosphatidylcholine and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular-specific mortality among US women and men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016;104:173–180. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.131771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Geng J., Yang C., Wang B., Zhang X., Hu T., Gu Y., Li J. Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes atherosclerosis via CD36-dependent MAPK/JNK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018;97:941–947. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Herrema H., Niess J.H. Intestinal microbial metabolites in human metabolism and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2020;63:2533–2547. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05268-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Shih D.M., Zhu W., Schugar R.C., Meng Y., Jia X., Miikeda A., Wang Z., Zieger M., Lee R., Graham M., et al. Genetic Deficiency of Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 (Fmo3) Protects Against Thrombosis but Has Only a Minor Effect on Plasma Lipid Levels—Brief Report. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019;39:1045–1054. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhou S., Xue J., Shan J., Hong Y., Zhu W., Nie Z., Zhang Y., Ji N., Luo X., Zhang T., et al. Gut-Flora-Dependent Me-tabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Atherosclerosis-Associated Inflammation Responses by Indirect ROS Stimulation and Signaling Involving AMPK and SIRT1. Nutrients. 2022;14:3338. doi: 10.3390/nu14163338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Matsumoto T., Kojima M., Takayanagi K., Taguchi K., Kobayashi T. Role of S-Equol, Indoxyl Sulfate, and Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Vascular Function. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020;33:793–803. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Leo C.H., Jelinic M., Ng H.H., Tare M., Parry L.J. Time-dependent activation of prostacyclin and nitric oxide pathways during continuous i.v. infusion of serelaxin (recombinant human H2 relaxin) Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016;173:1005–1017. doi: 10.1111/bph.13404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Leo C., Hart J., Woodman O. Impairment of both nitric oxide-mediated and EDHF-type relaxation in small mesenteric arteries from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011;162:365–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Leo C.H., Jelinic M., Parkington H.C., Tare M., Parry L.J. Acute Intravenous Injection of Serelaxin (Recombinant Human Relaxin-2) Causes Rapid and Sustained Bradykinin-Mediated Vasorelaxation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014;3:e000493. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Leo C.H., Jelinic M., Ng H.H., Marshall S.A., Novak J., Tare M., Conrad K.P., Parry L.J. Vascular actions of relaxin: Nitric oxide and beyond. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017;174:1002–1014. doi: 10.1111/bph.13614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ng H.H., Jelinic M., Parry L.J., Leo C.-H. Increased superoxide production and altered nitric oxide-mediated relaxation in the aorta of young but not old male relaxin-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2015;309:H285–H296. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00786.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Leo C.-H., Hart J.L., Woodman O.L. 3′,4′-Dihydroxyflavonol Reduces Superoxide and Improves Nitric Oxide Function in Diabetic Rat Mesenteric Arteries. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e20813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Jelinic M., Kahlberg N., Leo C.H., Ng H.H., Rosli S., Deo M., Li M., Finlayson S., Walsh J., Parry L.J., et al. Annexin-A1 deficiency exacerabates pathological remodelling of the mesenteric vasculature in insulin-resistance but not insulin-deficiency. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020;177:1677–1691. doi: 10.1111/bph.14927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kahlberg N., Qin C.X., Anthonisz J., Jap E., Ng H.H., Jelinic M., Parry L.J., Kemp-Harper B.K., Ritchie R.H., Leo C.H. Adverse vascular remodelling is more sensitive than endothelial dysfunction to hyperglycaemia in diabetic rat mesenteric ar-teries. Pharmacol. Res. 2016;111:325–335. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Jelinic M., Jackson K.L., O’Sullivan K., Singh J., Giddy T., Deo M., Parry L.J., Ritchie R.H., Woodman O.L., Head G.A., et al. Endothelium-dependent relaxation is impaired in Schlager hypertensive (BPH/2J) mice by region-specific mechanisms in conductance and resistance arteries. Life Sci. 2023;320:121542. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Li T., Gua C., Wu B., Chen Y. Increased circulating trimethylamine N-oxide contributes to endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;495:2071–2077. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Pan L.-L., Qin M., Liu X.-H., Zhu Y.-Z. The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide on Cardiovascular Homeostasis: An Overview with Update on Immunomodulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017;8:686. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bai L., Dai J., Xia Y., He K., Xue H., Guo Q., Tian D., Xiao L., Zhang X., Teng X., et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Ame-liorated High Choline-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting cGAS-STING-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022;2022:1392896. doi: 10.1155/2022/1392896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yang C., Zhao Y., Ren D., Yang X. Protective Effect of Saponins-Enriched Fraction of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against High Choline-Induced Vas-cular Endothelial Dysfunction and Hepatic Damage in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020;43:463–473. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Matsumoto T., Kojima M., Takayanagi K., Taguchi K., Kobayashi T. Trimethylamine-N-oxide Specifically Impairs Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factor-Type Relaxation in Rat Femoral Artery. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020;43:569–573. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Marquardt L., Ruf A., Mansmann U., Winter R., Schuler M., Buggle F., Mayer H., Grau A.J. Course of Platelet Activation Markers After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2002;33:2570–2574. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000034398.34938.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kaur R., Kaur M., Singh J. Endothelial dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Molecular insights and therapeutic strategies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018;17:121. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0763-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Varga-Szabo D., Braun A., Nieswandt B. Calcium signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009;7:1057–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Dean W.L. Role of platelet plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in health and disease. World J. Biol. Chem. 2010;1:265–270. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i9.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhu W., Gregory J.C., Org E., Buffa J.A., Gupta N., Wang Z., Li L., Fu X., Wu Y., Mehrabian M., et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell. 2016;165:111–124. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Adam F., Kauskot A., Rosa J., Bryckaert M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008;6:2007–2016. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Xie Z., Liu X., Huang X., Liu Q., Yang M., Huang D., Zhao P., Tian J., Wang X., Hou J. Remodelling of gut microbiota by Berberine attenuates trimethylamine N-oxide-induced platelet hyperreaction and thrombus formation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021;911:174526. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Herrera J., Henke C.A., Bitterman P. Extracellular matrix as a driver of progressive fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018;128:45–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI93557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Li X., Geng J., Zhao J., Ni Q., Zhao C., Zheng Y., Chen X., Wang L. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Exacerbates Cardiac Fibrosis via Activating the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Physiol. 2019;10:866. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Makrecka-Kuka M., Volska K., Antone U., Vilskersts R., Grinberga S., Bandere D., Liepinsh E., Dambrova M. Trime-thylamine N-oxide impairs pyruvate and fatty acid oxidation in cardiac mitochondria. Toxicol. Lett. 2017;267:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Guo S. Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2014;220:T1–T23. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Chen P.Y., Qin L., Li G., Wang Z., Dahlman J.E., Malagon-Lopez J., Gujja S., Cilfone N.A., Kauffman K.J., Sun L., et al. Endothelial TGF-beta signalling drives vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Nat. Metab. 2019;1:912–926. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0102-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Miao J., Ling A.V., Manthena P.V., Gearing M.E., Graham M.J., Crooke R.M., Croce K.J., Esquejo R.M., Clish C.B., Morbid Obesity Study G., et al. Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 as a potential player in diabe-tes-associated atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:6498. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Schugar R.C., Shih D.M., Warrier M., Helsley R.N., Burrows A., Ferguson D., Brown A.L., Gromovsky A.D., Heine M., Chatterjee A., et al. The TMAO-Producing Enzyme Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 Regulates Obesity and the Beiging of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2017;19:2451–2461. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Tan X., Liu Y., Long J., Chen S., Liao G., Wu S., Li C., Wang L., Ling W., Zhu H. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Aggravates Liver Steatosis through Modulation of Bile Acid Metabolism and Inhibition of Farnesoid X Receptor Signaling in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019;63:e1900257. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Koeth R.A., Levison B.S., Culley M.K., Buffa J.A., Wang Z., Gregory J.C., Org E., Wu Y., Li L., Smith J.D., et al. γ-Butyrobetaine Is a Proatherogenic Intermediate in Gut Microbial Metabolism of L-Carnitine to TMAO. Cell Metab. 2014;20:799–812. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Wang Z., Roberts A.B., Buffa J.A., Levison B.S., Zhu W., Org E., Gu X., Huang Y., Zamanian-Daryoush M., Culley M.K., et al. Non-lethal Inhibition of Gut Microbial Trimethylamine Production for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Cell. 2015;163:1585–1595. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Li Z., Wu Z., Yan J., Liu H., Liu Q., Deng Y., Ou C., Chen M. Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2019;99:346–357. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0091-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Fang Q., Zheng B., Liu N., Liu J., Liu W., Huang X., Zeng X., Chen L., Li Z., Ouyang D. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Exacerbates Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rats With Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.682482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.El-Deeb O.S., Atef M.M., Hafez Y.M. The interplay between microbiota-dependent metabolite trimethylamine N -oxide, Transforming growth factor β /SMAD signaling and inflammasome activation in chronic kidney disease patients: A new mechanistic perspective. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019;120:14476–14485. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Gao X., Liu X., Xu J., Xue C., Xue Y., Wang Y. Dietary trimethylamine N-oxide exacerbates impaired glucose tolerance in mice fed a high fat diet. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014;118:476–481. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Nagatomo Y., Tang W.H.W. Intersections Between Microbiome and Heart Failure: Revisiting the Gut Hypothesis. J. Card. Fail. 2015;21:973–980. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Conraads V.M., Jorens P.G., De Clerck L.S., Van Saene H.K., Ieven M.M., Bosmans J.M., Schuerwegh A., Bridts C.H., Wuyts F., Stevens W.J., et al. Selective intestinal decontamination in advanced chronic heart failure: A pilot trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004;6:483–491. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2003.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Zhang C., Yin A., Li H., Wang R., Wu G., Shen J., Zhang M., Wang L., Hou Y., Ouyang H., et al. Dietary Modulation of Gut Microbiota Contributes to Alleviation of Both Genetic and Simple Obesity in Children. Ebiomedicine. 2015;2:968–984. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Martin F.P., Wang Y., Sprenger N., Yap I.K., Lundstedt T., Lek P., Rezzi S., Ramadan Z., van Bladeren P., Fay L.B., et al. Probiotic modulation of symbiotic gut microbial-host metabolic inter-actions in a humanized microbiome mouse model. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008;4:157. doi: 10.1038/msb4100190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Tang W.H.W., Wang Z., Levison B.S., Koeth R.A., Britt E.B., Fu X., Wu Y., Hazen S.L. Intestinal Microbial Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine and Cardiovascular Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:1575–1584. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Chen K., Zheng X., Feng M., Li D., Zhang H. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction in Western Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Physiol. 2017;8:139. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Dambrova M., Skapare-Makarova E., Konrade I., Pugovics O., Grinberga S., Tirzite D., Petrovska R., Kalvins I., Liepins E. Meldonium decreases the diet-increased plasma levels of trimethylamine N-oxide, a metabolite associated with atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013;53:1095–1098. doi: 10.1002/jcph.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kuka J., Liepinsh E., Makrecka-Kuka M., Liepins J., Cirule H., Gustina D., Loza E., Zharkova-Malkova O., Grinberga S., Pugovics O., et al. Suppression of intestinal microbiota-dependent production of pro-atherogenic trimethylamine N-oxide by shifting L-carnitine microbial degradation. Life Sci. 2014;117:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Chen M.-l., Yi L., Zhang Y., Zhou X., Ran L., Yang J., Zhu J.-D., Zhang Q.-Y., Mi M.-T., Rey F., et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced Atherosclerosis by Regulating TMAO Synthesis and Bile Acid Metabo-lism via Remodeling of the Gut Microbiota. MBio. 2016;7:e02210-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02210-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wu T., Gao Y., Hao J., Geng J., Zhang J., Yin J., Liu R., Sui W., Gong L., Zhang M. Capsanthin extract prevents obesity, reduces serum TMAO levels and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat-diet induced obese C57BL/6J mice. Food Res. Int. 2020;128:108774. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Wu T., Gao Y., Hao J., Yin J., Li W., Geng J., Liu R., Sui W., Zhang M. Lycopene, amaranth, and sorghum red pigments counteract obesity and modulate the gut microbiota in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6 mice. J. Func. Foods. 2019;60:103437. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103437. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Wang M., Wang F., Wang Y., Ma X., Zhao M., Zhao C. Metabonomics Study of the Therapeutic Mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum and Atorvastatin for Hyperlipidemia in Rats. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e78731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Sun B., Wang X., Cao R., Zhang Q., Liu Q., Xu M., Zhang M., Du X., Dong F., Yan X. NMR-based metabonomics study on the effect of Gancao in the attenuation of toxicity in rats induced by Fuzi. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;193:617–626. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Chen P.-Y., Li S., Koh Y.-C., Wu J.-C., Yang M.-J., Ho C.-T., Pan M.-H. Oolong Tea Extract and Citrus Peel Polymethoxyflavones Reduce Transformation of l-Carnitine to Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Decrease Vascular Inflammation in l-Carnitine Feeding Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019;67:7869–7879. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Shi Y., Hu J., Geng J., Hu T., Wang B., Yan W., Jiang Y., Li J., Liu S. Berberine treatment reduces atherosclerosis by me-diating gut microbiota in apoE-/- mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018;107:1556–1563. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Anwar S., Bhandari U., Panda B.P., Dubey K., Khan W., Ahmad S. Trigonelline inhibits intestinal microbial metabolism of choline and its associated cardiovascular risk. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018;159:100–112. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Konop M., Radkowski M., Grochowska M., Perlejewski K., Samborowska E., Ufnal M. Enalapril decreases rat plasma concentration of TMAO, a gut bacteria-derived cardiovascular marker. Biomarkers. 2018;23:380–385. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2018.1432689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Kuka J., Videja M., Makrecka-Kuka M., Liepins J., Grinberga S., Sevostjanovs E., Vilks K., Liepinsh E., Dambrova M. Metformin decreases bacterial trimethylamine production and trimethylamine N-oxide levels in db/db mice. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:14555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71470-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Shih D.M., Wang Z., Lee R., Meng Y., Che N., Charugundla S., Qi H., Wu J., Pan C., Brown J.M., et al. Flavin containing monooxygenase 3 exerts broad effects on glucose and lipid metab-olism and atherosclerosis. J. Lipid. Res. 2015;56:22–37. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M051680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Warrier M., Shih D.M., Burrows A.C., Ferguson D., Gromovsky A.D., Brown A.L., Marshall S., McDaniel A., Schugar R.C., Wang Z., et al. The TMAO-Generating Enzyme Flavin Monooxygenase 3 Is a Central Regulator of Cholesterol Balance. Cell Rep. 2015;10:326–338. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Vilskersts R., Zharkova-Malkova O., Mezhapuke R., Grinberga S., Cirule H., Dambrova M. Elevated vascular gam-ma-butyrobetaine levels attenuate the development of high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013;40:518–524. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Ryan P.M., Stanton C., Caplice N.M. Bile acids at the cross-roads of gut microbiome–host cardiometabolic interactions. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017;9:102. doi: 10.1186/s13098-017-0299-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Davani-Davari D., Negahdaripour M., Karimzadeh I., Seifan M., Mohkam M., Masoumi S.J., Berenjian A., Ghasemi Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods. 2019;8:92. doi: 10.3390/foods8030092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Hill C., Guarner F., Reid G., Gibson G.R., Merenstein D.J., Pot B., Morelli L., Canani R.B., Flint H.J., Salminen S., et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics con-sensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Ma J., Li H. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Atherosclerosis and Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:1082. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Brugere J.F., Borrel G., Gaci N., Tottey W., O’Toole P.W., Malpuech-Brugere C. Archaebiotics: Proposed therapeutic use of archaea to prevent trimethylaminuria and cardiovascular disease. Gut Microbes. 2014;5:5–10. doi: 10.4161/gmic.26749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Dridi B. Laboratory tools for detection of archaea in humans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012;18:825–833. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Pourrajab B., Fatahi S., Dehnad A., Kord Varkaneh H., Shidfar F. The impact of probiotic yogurt consumption on lipid profiles in subjects with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized con-trolled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;30:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Yousefi B., Eslami M., Ghasemian A., Kokhaei P., Salek Farrokhi A., Darabi N. Probiotics importance and their immuno-modulatory properties. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019;234:8008–8018. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Plaza-Diaz J., Ruiz-Ojeda F.J., Gil-Campos M., Gil A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019;10:S49–S66. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Li X., Hong J., Wang Y., Pei M., Wang L., Gong Z. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Pathway: A Potential Target for the Treatment of MAFLD. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021;8:733507. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.733507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Zhu Y., Li Q., Jiang H. Gut microbiota in atherosclerosis: Focus on trimethylamine N-oxide. Apmis. 2020;128:353–366. doi: 10.1111/apm.13038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hatakeyama S., Yamamoto H., Okamoto A., Imanishi K., Tokui N., Okamoto T., Suzuki Y., Sugiyama N., Imai A., Kudo S., et al. Effect of an Oral Adsorbent, AST-120, on Dialysis Initiation and Survival in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012;2012:376128. doi: 10.1155/2012/376128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Bird J.K., Raederstorff D., Weber P., Steinert R.E. Cardiovascular and Antiobesity Effects of Resveratrol Mediated through the Gut Microbiota. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2017;8:839–849. doi: 10.3945/an.117.016568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Chen L., He W., Peng B., Yuan M., Wang N., Wang J., Lu W., Wang T. Sodium Tanshinone IIA sulfonate improves post-ischemic angiogenesis in hyperglycemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019;520:580–585. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Kant R., Chandra L., Verma V., Nain P., Bello D., Patel S., Ala S., Chandra R., Antony M.A. Gut microbiota interactions with anti-diabetic medications and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Methodol. 2022;12:246–257. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Marshall S.A., Qin C.X., Jelinic M., O’Sullivan K., Deo M., Walsh J., Li M., Parry L.J., Ritchie R.H., Leo C.H. The Novel Small-molecule Annexin-A1 Mimetic, Compound 17b, Elicits Vasoprotective Actions in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:1384. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Leo C.H., Jelinic M., Ng H.H., Parry L.J., Tare M. Recent developments in relaxin mimetics as therapeutics for cardio-vascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019;45:42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2019.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Ng H.H., Leo C.H., Parry L.J., Ritchie R.H. Relaxin as a Therapeutic Target for the Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Ong E.S., Low J., Tan J.C.W., Foo S.Y., Leo C.H. Valorization of avocado seeds with antioxidant capacity using pressurized hot water extraction. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:13036. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17326-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Leo C.H., Foo S.Y., Tan J.C.W., Tan U.-X., Chua C.K., Ong E.S. Green Extraction of Orange Peel Waste Reduces TNFα-Induced Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. Antioxidants. 2022;11:1768. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ong E., Oh C., Tan J., Foo S., Leo C. Pressurized Hot Water Extraction of Okra Seeds Reveals Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Vasoprotective Activities. Plants. 2021;10:1645. doi: 10.3390/plants10081645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.