Abstract
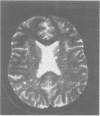
Three tourists developed eosinophilic meningitis after visiting the Fijian Islands. Two had a severe and long lasting illness with chronic intractable pain. In one patient electrophysiological studies and MRI scan of the brain were abnormal and provided evidence of both radicular and cerebral parenchymal involvement by the most likely causative agent, Angiostrongylus cantonensis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck M. J., Cardina T. M., Alicata J. E. Eosinophilic meningitis due to angiostrongyliasis cantonesis in American Samoa. Hawaii Med J. 1980 Oct;39(10):254–2-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. N. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of antibodies to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(3):398–405. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaroonvesama N., Charoenlarp K., Buranasin P., Zaraspe G. G., Cross J. H. ELISA testing in cases of clinical angiostrongyliasis in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1985 Mar;16(1):110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaroonvesama N. Differential diagnosis of eosinophilic meningitis. Parasitol Today. 1988 Sep;4(9):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(88)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliks M. M., Kroenke K., Hardman J. M. Eosinophilic radiculomyeloencephalitis: an angiostrongyliasis outbreak in American Samoa related to ingestion of Achatina fulica snails. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Nov;31(6):1114–1122. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko R. C., Chan S. W., Chan K. W., Lam K., Farrington M., Wong H. W., Yuen P. Four documented cases of eosinophilic meningoencephalitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Hong Kong. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(5):807–810. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko R. C., Chiu M. C., Kum W., Chan S. H. First report of human angiostrongyliasis in Hong Kong diagnosed by computerized axial topography (CAT) and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(3):354–355. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuberski T., Wallace G. D. Clinical manifestations of eosinophilic memingitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Neurology. 1979 Dec;29(12):1566–1570. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.12.1566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punyagupta S., Juttijudata P., Bunnag T. Eosinophilic meningitis in Thailand. Clinical studies of 484 typical cases probably caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Nov;24(6 Pt 1):921–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Wallis W. E. The chronic and severe forms of eosinophilic meningitis. Aust N Z J Med. 1984 Apr;14(2):163–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1984.tb04283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimgeour E. M. Angiostrongyliasis in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. Aust N Z J Med. 1983 Dec;13(6):644–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1983.tb02627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangchai P., Nye S. W., Beaver P. C. Eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by angiostrongyliasis in Thailand. Autopsy report. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jul;16(4):454–461. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE G. D., ROSEN L. STUDIES ON EOSINOPHILIC MENINGITIS. I. OBSERVATIONS ON THE GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION OF ANGIOSTRONGYLUS CANTONENSIS IN THE PACIFIC AREA AND ITS PREVALENCE IN WILD RATS. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Jan;81:52–62. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J. S., Dobson C., Campbell G. R. Immunodiagnosis and seroepidemiology of Angiostrongylus cantonensis zoonoses in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(5):614–623. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yii C. Y. Clinical observations on eosinophilic meningitis and meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis on Taiwan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Mar;25(2):233–249. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]