Abstract
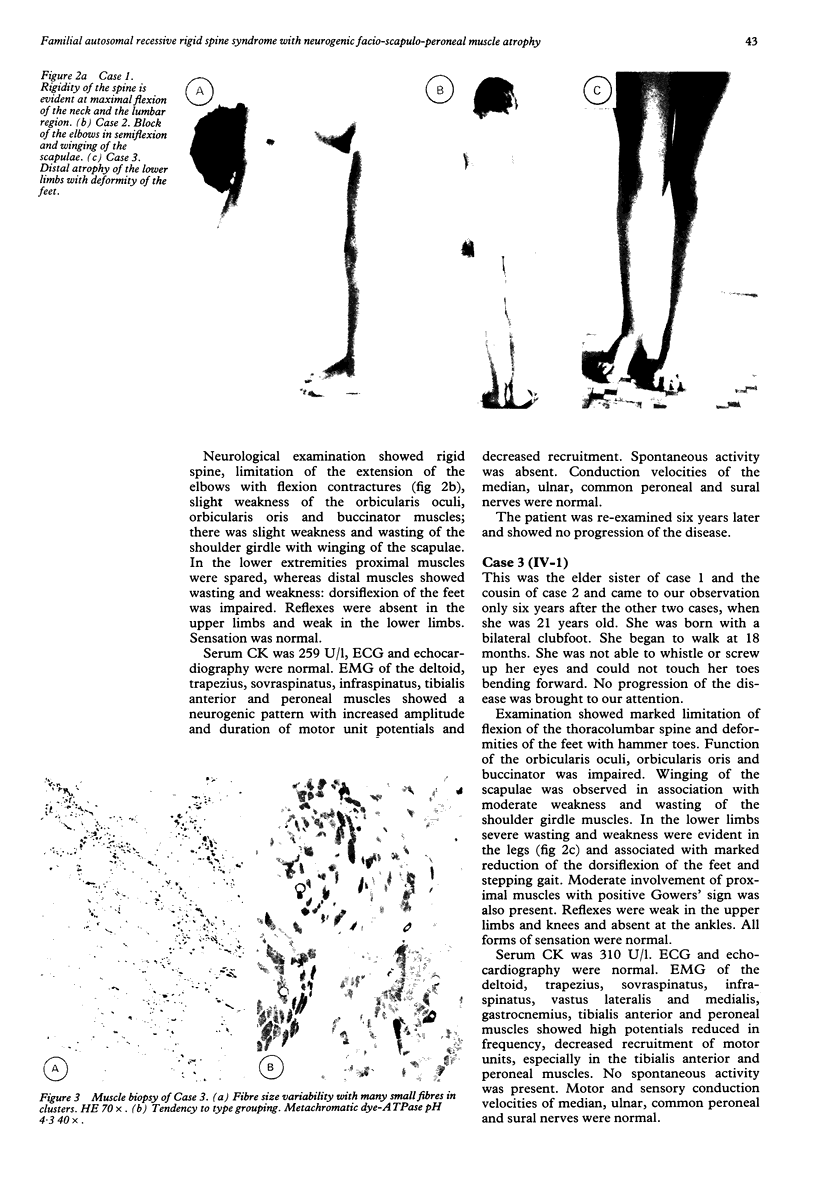
Two sisters and a first cousin presented with rigid spine and facio-scapulo-peroneal muscle atrophy. The patients belonged to a family with two first-cousin marriages. Electromyography, muscle and nerve biopsy showed neurogenic muscle atrophy without peripheral nerve involvement. Follow up did not show progression of the disease. This is the first observation of an association of neurogenic facio-scapulo-peroneal and rigid spine syndrome. The double first-cousin marriage suggests autosomal recessive inheritance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben Hamida M., Hentati F., Ben Hamida C. Maladie à multiminicores au cours d'un syndrome de la colonne raide. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1987;143(4):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertini E., Marini R., Sabetta G., Palmieri G. P., Spagnoli L. G., Vaccario M. L., de Barsy T. The spectrum of the so-called rigid spine syndrome: nosological considerations and report of three female cases. J Neurol. 1986 Aug;233(4):248–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00314029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti A., Pearce J. M. Scapuloperoneal syndrome with cardiomyopathy: report of a family with autosomal dominant inheritance and unusual features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Dec;44(12):1146–1152. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.12.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doriguzzi C., Mongini T., Palmucci L., Gagnor E., Schiffer D. Quantitative analysis of quadriceps muscle biopsy. Results in 30 healthy females. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Nov-Dec;66(2-3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doriguzzi C., Mongini T., Palmucci L., Schiffer D. A new method for myofibrillar Ca++-ATPase reaction based on the use of metachromatic dyes: its advantages in muscle fibre typing. Histochemistry. 1983;79(3):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00491766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echenne B., Astruc J., Brunel D., Pages M., Baldet P., Martinazzo G. Congenital muscular dystrophy and rigid spine syndrome. Neuropediatrics. 1983 May;14(2):97–101. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery E. S., Fenichel G. M., Eng G. A spinal muscular atrophy with scapuloperoneal distribution. Arch Neurol. 1968 Feb;18(2):129–133. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470320031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto I., Muraoka S., Fujii N., Ohta M., Kuroiwa Y. Rigid spine syndrome: clinical and histological problems. J Neurol. 1981;226(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00313443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyser C. L., Kissel J. T., Warmolts J. R., Mendell J. R. Scapuloperoneal neuropathy: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Oct;87(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeser H. E. Scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):407–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows J. C., Marsden C. D. Scapuloperoneal amytrophy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Jan;20(1):9–12. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480070019002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercelis R., Demeester J., Martin J. J. Neurogenic scapuloperoneal syndrome in childhood. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;43(10):888–896. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.10.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L. Infantile scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1968 Mar;18(3):285–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murken J. D., Salzer G., Kunze D. Ringchromosom Nr. 18 und fehlendes IgA bei einem 6jährigen Mädchen (46,XX,18r) Z Kinderheilkd. 1970;109(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negri S., Caraceni T., Cornelio F. A case of scapulo-tibio-peroneal syndrome. Electromyographic and histoenzymologic considerations. Eur Neurol. 1973;10(1):31–40. doi: 10.1159/000114259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Mertens H. G., Schimrigk K. The neurogenic scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1968;1(5):257–274. doi: 10.1159/000113668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Mertens H. G. The differential diagnosis of the myogenic (facio)-scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1968;1(5):275–307. doi: 10.1159/000113669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. S., Swash M. Scapuloperoneal atrophy with sensory involvement: Davidenkow's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Nov;38(11):1063–1067. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.11.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Cros D., Pellissier J. F., Gastaut J. L., Pouget J. Dystrophie musculaire congénitale. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1980;136(6-7):445–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalke G., Hökendorf H., von Roques P. The differential diagnosis of scapuloperoneal amyotrophy. J Neurol. 1976 Jun 14;212(3):253–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00314527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Nakamura H., Nakashima R. Scapuloperoneal dystrophy associated with neurogenic changes. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Dec;23(4):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Muratani H., Kira J., Itoyama Y., Goto I. Familial myopathy with scapulohumeral distribution, rigid spine, cardiopathy and mitochondrial abnormality. J Neurol. 1989 Jan;236(1):52–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00314219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Schott G. D., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Adult onset scapuloperoneal myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;38(10):1008–1015. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.10.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanneste J. A., Augustijn P. B., Stam F. C. The rigid spine syndrome in two sisters. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jan;51(1):131–135. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee W. C., Hahn A. F., Gilbert J. J. Adult onset scapuloperoneal myopathy: diagnostic value of nerve morphometry and multiple muscle biopsies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;51(6):808–813. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.6.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., McCormick W. F. Scapuloperoneal dystrophy and scapuloperoneal atrophy. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1968 Dec;23(6):643–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Munster E. T., Joosten E. M., van Munster-Uijtdehaage M. A., Kruls H. J., ter Laak H. J. The rigid spine syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Nov;49(11):1292–1297. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.11.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




