Abstract
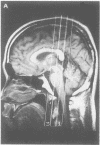
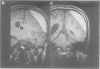
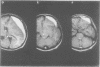
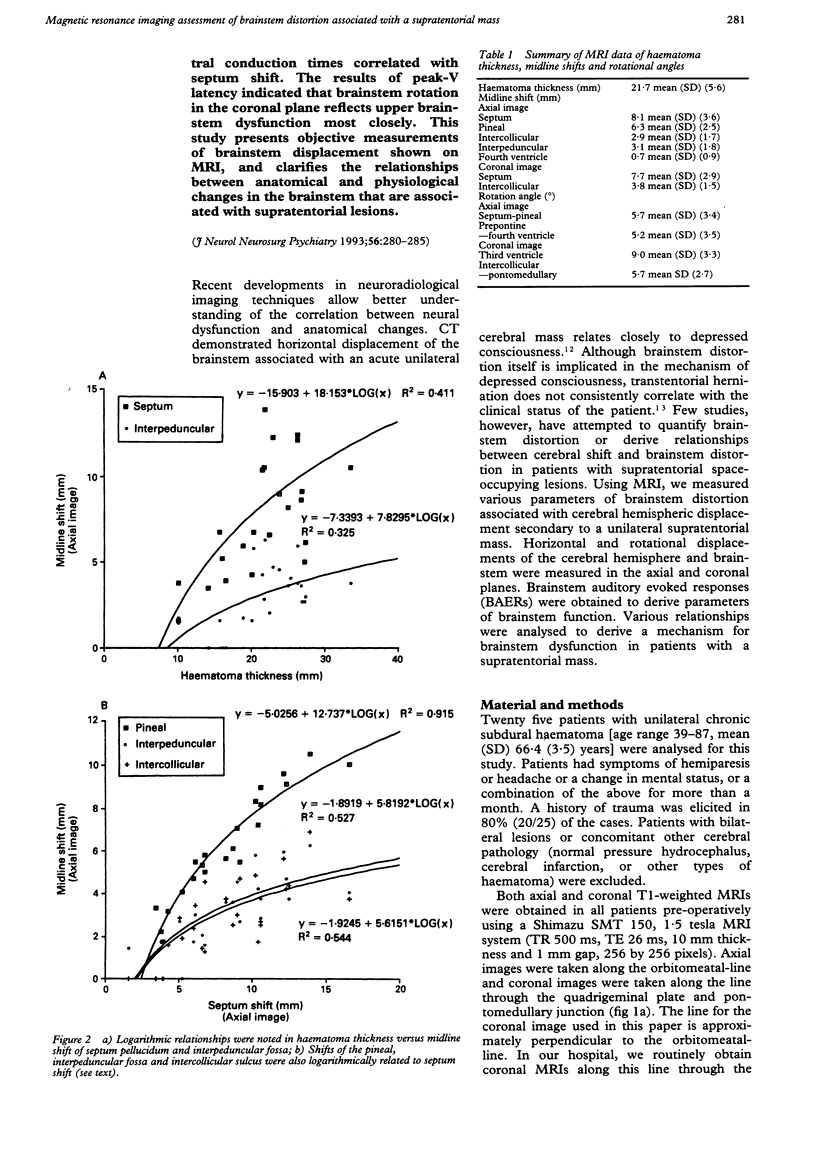
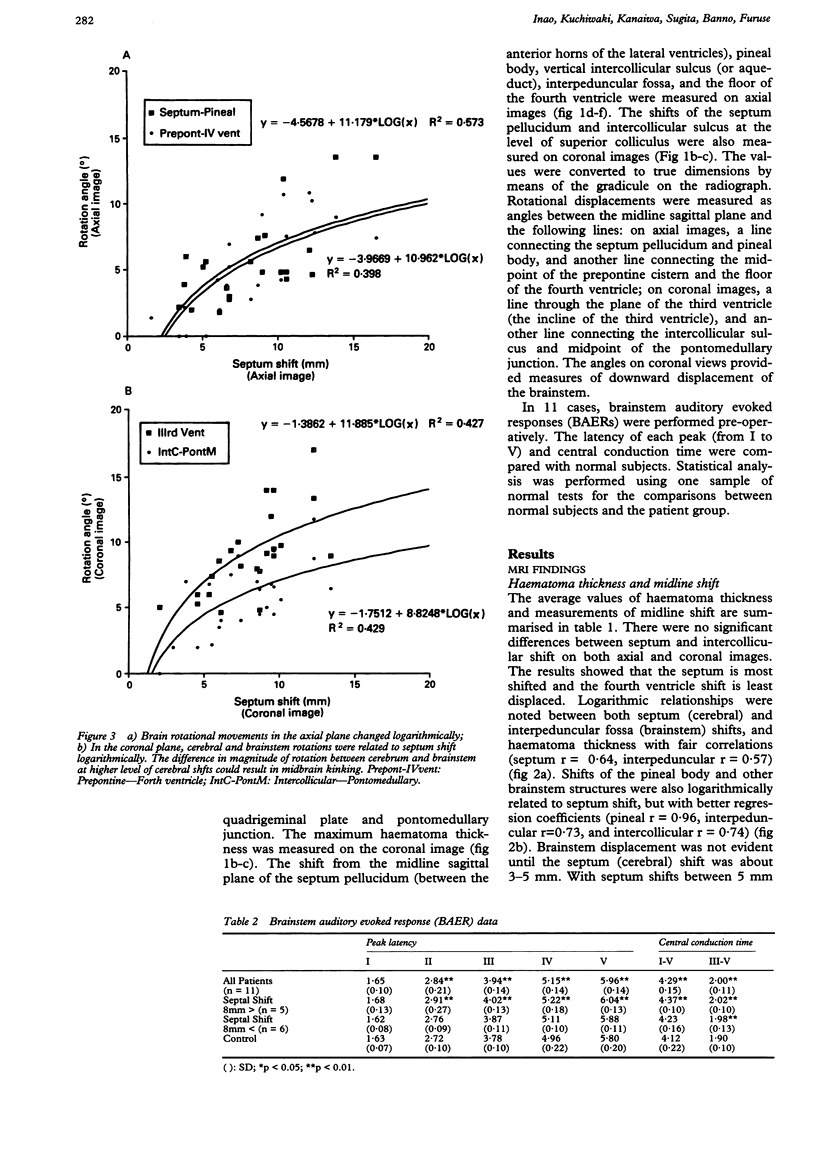
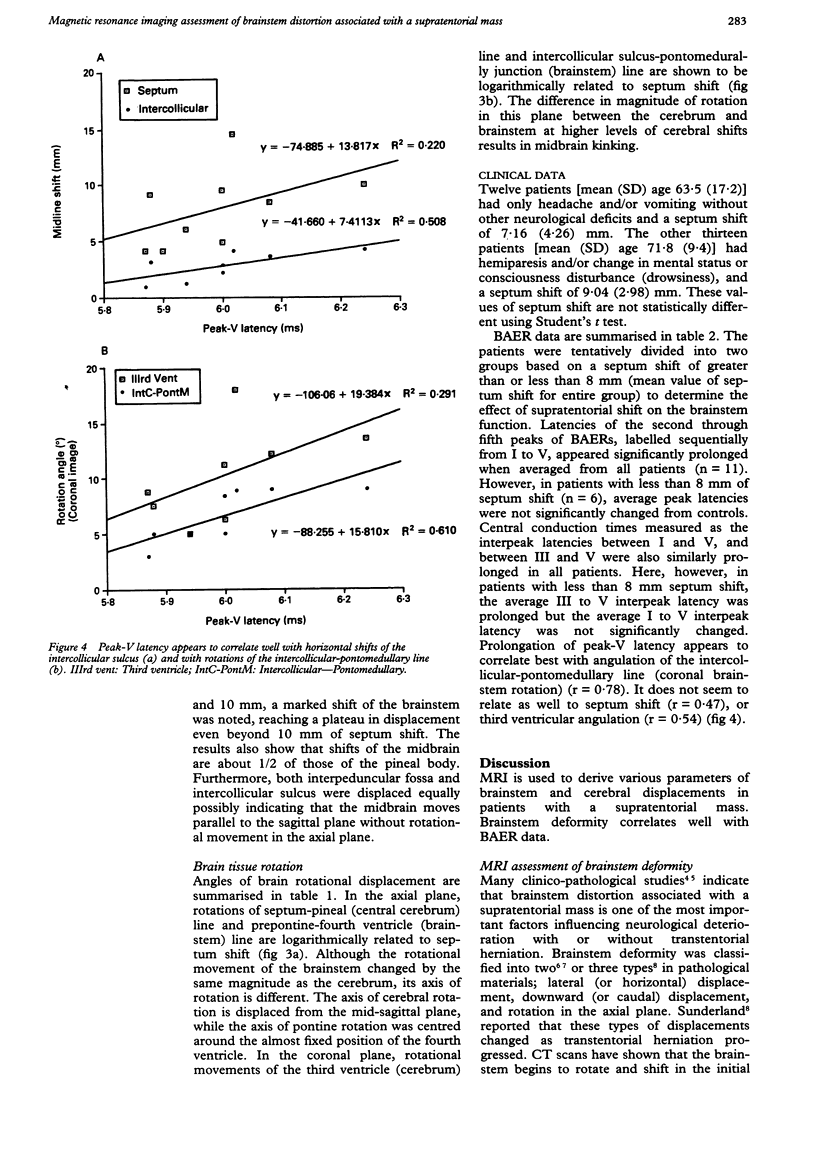
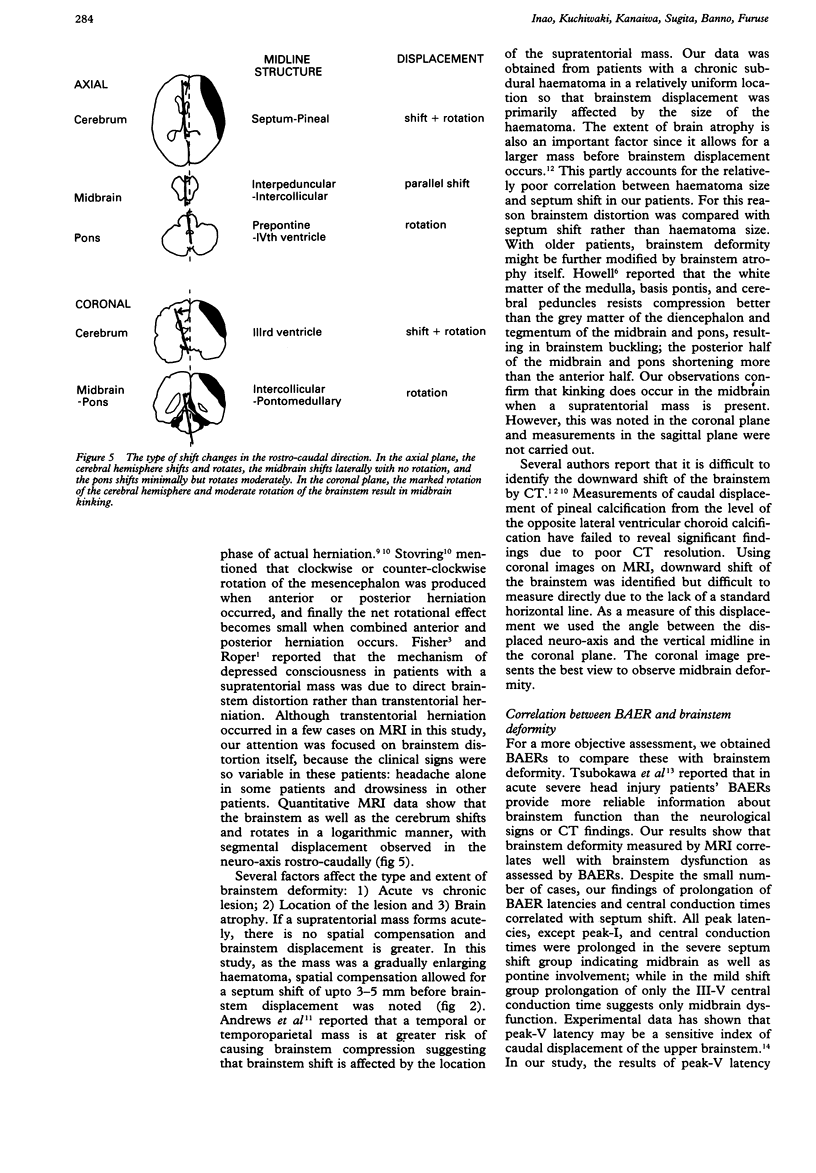
Quantitative measurements of brainstem distortion and neural dysfunction were obtained in 25 cases of chronic subdural haematoma. The horizontal and rotational brainstem displacements were measured on axial and coronal MRI in all patients pre-operatively, and brainstem auditory evoked responses (BAERs) were obtained in 11 cases. Logarithmic relationships were noted on both horizontal and rotational displacements of the brainstem and cerebrum. The type of shift changed in the rostro-caudal direction. In the axial plane, the cerebral hemisphere shifts and rotates, the midbrain shifts laterally with no rotation, and the pons shifts minimally but rotates moderately. In the coronal plane, the marked rotation of the cerebral hemisphere and moderate rotation of the brainstem result in midbrain kinking, suggesting a downward displacement of the midbrain. The prolongation of BAER latencies and central conduction times correlated with septum shift. The results of peak-V latency indicated that brainstem rotation in the coronal plane reflects upper brainstem dysfunction most closely. This study presents objective measurements of brainstem displacement shown on MRI, and clarifies the relationships between anatomical and physiological changes in the brainstem that are associated with supratentorial lesions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. T., Chiles B. W., 3rd, Olsen W. L., Pitts L. H. The effect of intracerebral hematoma location on the risk of brain-stem compression and on clinical outcome. J Neurosurg. 1988 Oct;69(4):518–522. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.69.4.0518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelholm R., Heiskanen O., Waltimo O. Chronic subdural hematoma in adults. Influence of patient's age on symptoms, signs, and thickness of hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1975 Jan;42(1):43–46. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.42.1.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL D. A. Upper brain-stem compression and foraminal impaction with intracranial space-occupying lesions and brain swelling. Brain. 1959 Dec;82:525–550. doi: 10.1093/brain/82.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T., YATES P. O. Brain stem haemorrhages in expanding supratentorial conditions. Acta radiol. 1956 Jul-Aug;46(1-2):250–256. doi: 10.3109/00016925609170834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNRO D., SISSON W. R., Jr Hernia through the incisura of the tentorium cerebelli in connection with craniocerebral trauma. N Engl J Med. 1952 Nov 6;247(19):699–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195211062471901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Roccaforte P., Moody R. A. Acute intracranial hypertension and auditory brain-stem responses. Part 2: The effects of brain-stem movement on the auditory brain-stem responses due to transtentorial herniation. J Neurosurg. 1979 Dec;51(6):846–851. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.6.0846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn A. G. Diagnosis of descending transtentorial herniation by cranial computed tomography. Radiology. 1977 Apr;123(1):93–96. doi: 10.1148/123.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropper A. H. Lateral displacement of the brain and level of consciousness in patients with an acute hemispheral mass. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):953–958. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D. A., Olsen W. L., Ross A. M., Andrews B. T., Pitts L. H. Brain shift, level of consciousness, and restoration of consciousness in patients with acute intracranial hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1989 Oct;71(4):498–502. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.4.0498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERLAND S. The tentorial notch and complications produced by herniations of the brain through that aperture. Br J Surg. 1958 Mar 18;45(193):422–438. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004519306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stovring J. Descending tentorial herniation: findings on computed tomography. Neuroradiology. 1977 Dec 14;14(3):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00333050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubokawa T., Nishimoto H., Yamamoto T., Kitamura M., Katayama Y., Moriyasu N. Assessment of brainstem damage by the auditory brainstem response in acute severe head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Nov;43(11):1005–1011. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.11.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]