Abstract
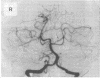
Localised neuronal heterotopias are an increasingly recognised cause of intractable focal epilepsies. The aetiology of these circumscribed disorders of neuronal migration is often unknown although in some instances proximity to areas of prenatal infarction suggests that severe ischaemia was responsible. A patient is described with intractable complex partial seizures associated with heterotopic grey matter and cerebral hypoplasia confined to the territory of the left posterior cerebral artery; the left hippocampus was spared. Angiography showed a normal left anterior choroidal artery but a hypoplastic left posterior cerebral artery, implicating prenatal ischaemia without frank infarction as the aetiology of the malformation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. G. Disorders of neuronal migration. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Feb;14(1):1–16. doi: 10.1017/s031716710002610x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. G., van der Harten J. J. Parabiotic twin syndrome with topical isocortical disruption and gastroschisis. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;67(3-4):345–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00687825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard P., Caviness V. S., Jr, Prats-Vinas J., Lyon G. The mechanism of arrest of neuronal migration in the Zellweger malformation: an hypothesis bases upon cytoarchitectonic analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Feb 20;41(2):109–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00689761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I. A Golgi analysis of unlayered polymicrogyria. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;65(1):69–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00689830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. Cytogenesis and pathology of neuroglia and microglia. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;168(4):271–278. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(80)80269-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzniecky R., Berkovic S., Andermann F., Melanson D., Olivier A., Robitaille Y. Focal cortical myoclonus and rolandic cortical dysplasia: clarification by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):317–325. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. N., Fisher M. A., Caviness V. S., Jr Porencephaly with microgyria: a pathologic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;29(2):99–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00684769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman M. G. Bilateral encephaloclastic lesions in a 26 week gestation fetus: effect on neuroblast migration. Can J Neurol Sci. 1980 Aug;7(3):191–194. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100023180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn R. E., Byrd S. E., Naidich T. P., Bohan T. P., Friedman H. MR imaging of neuronal migrational disorders. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;9(6):1101–1106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):170–176. doi: 10.1126/science.3291116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. P., Stewart R. M., Caviness V. S., Jr Cerebral microgyria in a 27-week fetus: an architectonic and topographic analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Jul;33(3):374–384. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197407000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe C. C., Berkovic S. F., Sia S. T., Austin M., McKay W. J., Kalnins R. M., Bladin P. F. Localization of epileptic foci with postictal single photon emission computed tomography. Ann Neurol. 1989 Nov;26(5):660–668. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman R. L., Rakic P. Neuronal migration, with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 9;62(1):1–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90617-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]