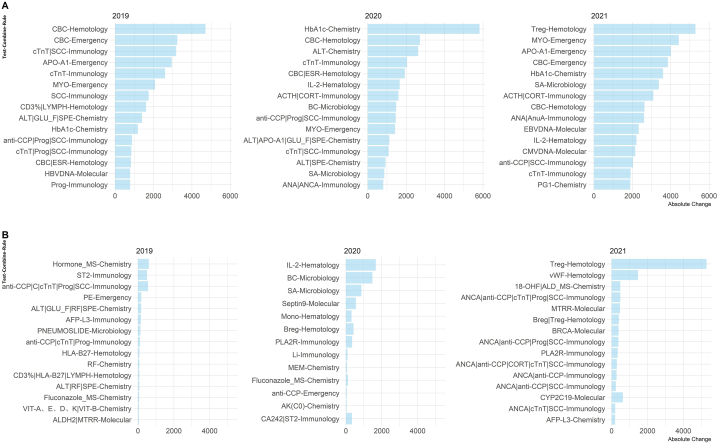
Fig. 3.
Test-combine-rules with the highest absolute and percentage increase from 2018 to 2021. (A) The test-combine-rules with the highest absolute increase. (B) The test-combine-rules with the highest percentage increase, but the bar shows the absolute increase for easier interpretation. CBC: complete blood count; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; cTNT: Cardiac Troponin T; SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; APO-A1: Apolipoprotein A1; MYO: myoglobin; LYMPH: lymphocyte count; GLU_F: fasting glucose; SPE: serum protein electrophoresis; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; anti-CPP: cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody; progesterone; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HBVDNA: hepatitis B virus DNA; MS: mass spectrometry; ST2: soluble interleukin 1 receptor-like 1; HLA-B27: human leukocyte antigen B27; RF: rheumatoid factors; AFP-L3: alpha-fetoprotein L3; IL-2: interleukin-2; ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone; CORT: cortisol; BC: bacteria culture; SA: antibiotic sensitivity; ANA: antinuclear antibodies; ANCA: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; Mono: mononucleosis; Breg: regulatory B cells; Treg: regulatory T cells; PLA2R: Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor; Li: lithium; MEM: membrane permeability; AK(C0): amikacin concentration; CA242: carbohydrate antigen 24–2; CMVDNA: Cytomegalovirus DNA; PG1: pepsinogen 1; vWF: on Willebrand factor antigen; 18-OHF: 18-hydroxycortisol; ALD: aldosterone.