Abstract
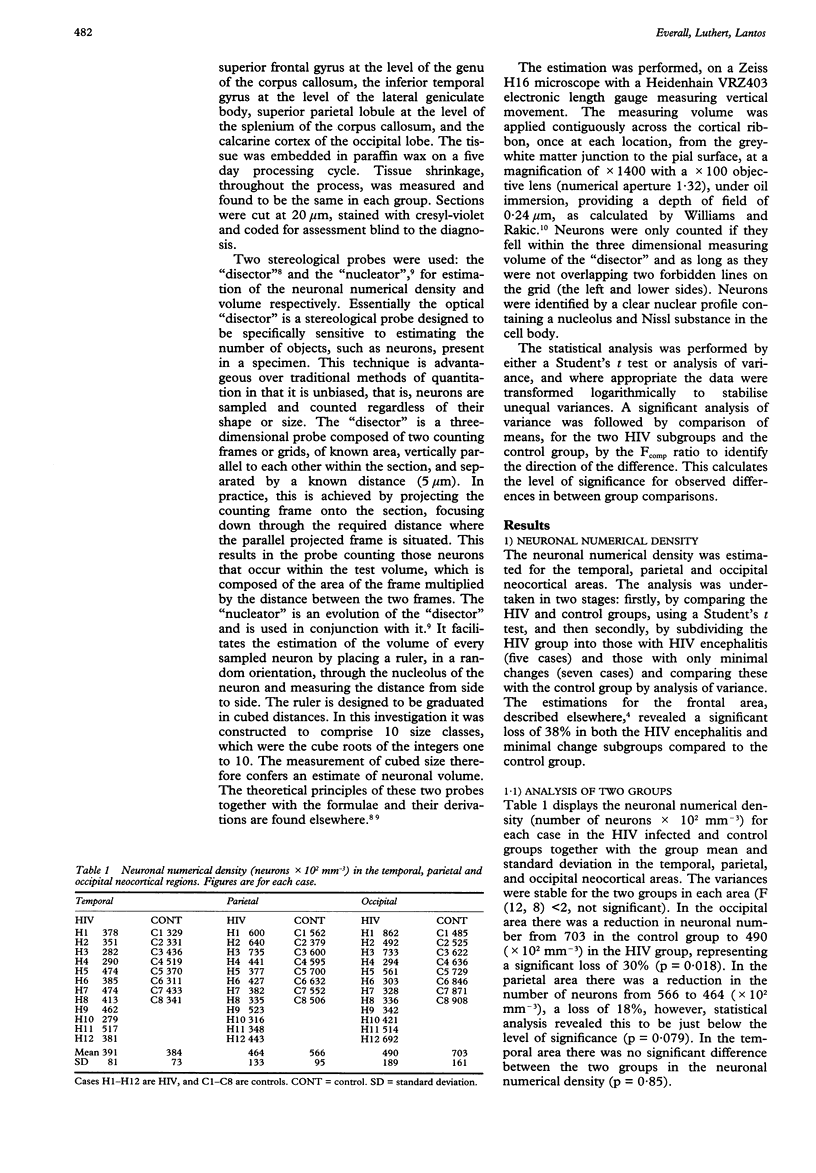
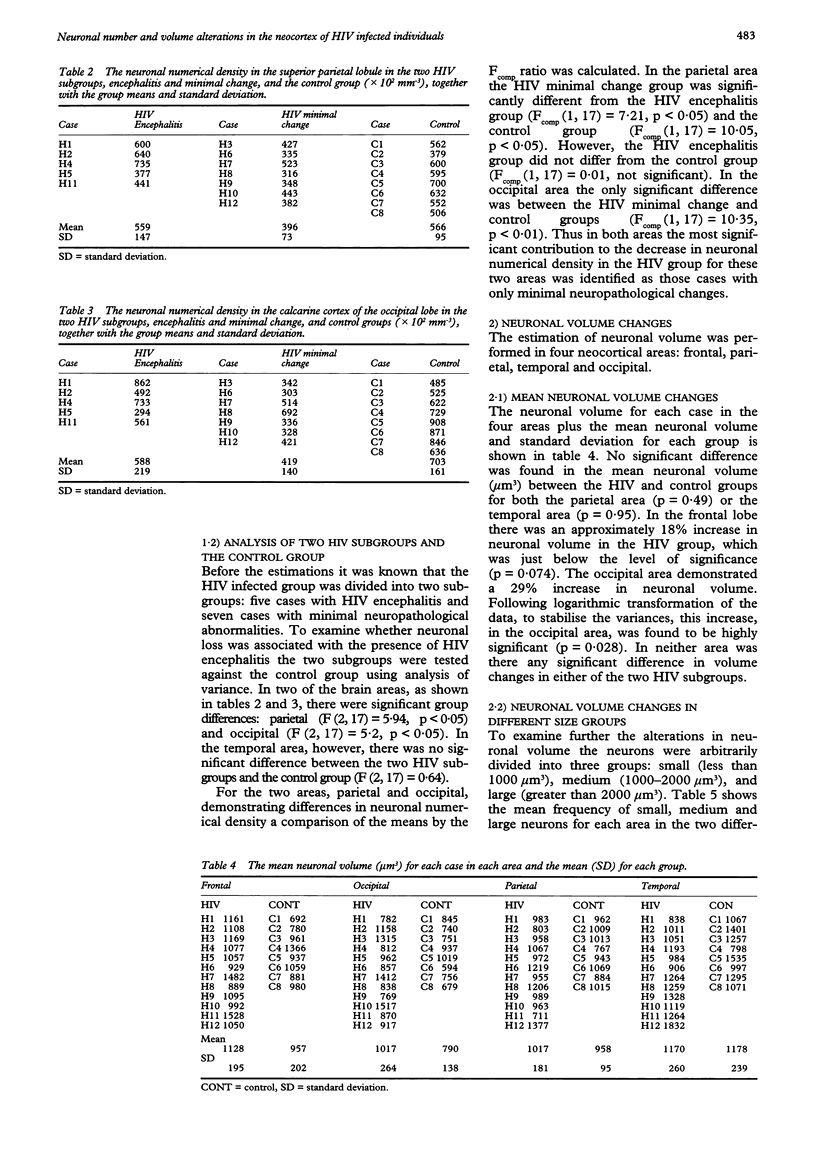
Substantial neuronal loss in the superior frontal gyrus in patients who have died of AIDS have been reported previously. This investigation examined the distribution of neuronal loss in three other neocortical areas and, alteration in neuronal volume in four neocortical areas. This was carried out using two stereological probes, the "disector" and the "nucleator". These recently developed methods provide estimations, regardless of size and shape, in real three-dimensional space, and are more efficient than conventional quantitation. The study was performed on 12 HIV infected individuals and nine controls. The HIV group had no neuropathological evidence of opportunistic infections or neoplasms, five had HIV encephalitis and the remaining seven had only minimal pathology. There was significant neuronal loss of 30% (p = 0.018) in the calcarine cortex (primary visual area), and loss of 18% in the superior parietal lobule which just failed to reach significance. This loss was not related to the presence of HIV encephalitis. The mean neuronal volume was increased in the occipital area by 29% (p = 0.028) and the frequency of large neurons (over 2000 microns 3) doubled in the frontal (p < 0.05) and parietal (p < 0.02) areas. The results confirm the hypothesis that HIV infection is associated with neuronal injury and death, and suggest that increase in neuronal size may be a feature of the cytopathology of this condition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODY H. Organization of the cerebral cortex. III. A study of aging in the human cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1955 Apr;102(2):511–516. doi: 10.1002/cne.901020206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braendgaard H., Evans S. M., Howard C. V., Gundersen H. J. The total number of neurons in the human neocortex unbiasedly estimated using optical disectors. J Microsc. 1990 Mar;157(Pt 3):285–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Wiley C. A., Kleihues P., Artigas J., Asbury A. K., Cho E. S., Cornblath D. R., Dal Canto M. C., DeGirolami U., Dickson D. HIV-associated disease of the nervous system: review of nomenclature and proposal for neuropathology-based terminology. Brain Pathol. 1991 Apr;1(3):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi A., Sinclair E., Scaravilli F., Harcourt-Webster N. J., Lucas S. The involvement of the cerebral cortex in human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00662637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer E. B., Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):364–367. doi: 10.1126/science.2326646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everall I. P., Luthert P. J., Lantos P. L. Neuronal loss in the frontal cortex in HIV infection. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1119–1121. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F., Kort J. J., Koch-Nolte F., Koch G. Similarities of viral proteins to toxins that interact with monovalent cation channels. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1381–1384. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J. Stereology of arbitrary particles. A review of unbiased number and size estimators and the presentation of some new ones, in memory of William R. Thompson. J Microsc. 1986 Jul;143(Pt 1):3–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J. The nucleator. J Microsc. 1988 Jul;151(Pt 1):3–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Tomlinson B. E., Gibson P. H. Cell counts in human cerebral cortex in normal adults throughout life using an image analysing computer. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Apr;46(1):113–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Tomlinson B. E., Weightman D. Cell counts in the human cerebral cortex using a traditional and an automatic method. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Jun;25(2):129–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes M. P., Brew B. J., Martin A., Price R. W., Salazar A. M., Sidtis J. J., Yergey J. A., Mouradian M. M., Sadler A. E., Keilp J. Quinolinic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in HIV-1 infection: relationship to clinical and neurological status. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):202–209. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerwin R. W., Pay S., Bhoola K. D., Pycock C. J. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat brain: regional distribution and localization on hypothalamic neurons. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;32(8):561–566. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. HIV-related neurotoxicity. Brain Pathol. 1991 Apr;1(3):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Sucher N. J., Kaiser P. K., Dreyer E. B. Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90079-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Crowe S., Sadick M. D., Heinzel F. P., Gardner K. D., Jr, McGrath M. S., Mills J. Release of interleukin 1 inhibitory activity (contra-IL-1) by human monocyte-derived macrophages infected with human immunodeficiency virus in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2097–2105. doi: 10.1172/JCI113831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon D. K., Baudouin C. J., Tomlinson D., Hoyle C. Proton MR spectroscopy and imaging of the brain in AIDS: evidence of neuronal loss in regions that appear normal with imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990 Nov-Dec;14(6):882–885. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199011000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels J., Sharer L. R., Epstein L. G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the nervous system: a review. Immunodefic Rev. 1988;1(1):71–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Cooper J. R. N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid content of human neural tumours and bovine peripheral nervous tissues. J Neurochem. 1972 Feb;19(2):313–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkenberg B., Gundersen H. J. Total number of neurons and glial cells in human brain nuclei estimated by the disector and the fractionator. J Microsc. 1988 Apr;150(Pt 1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam L., Herndier B. G., Tang N. M., McGrath M. S. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected macrophages produce soluble factors that cause histological and neurochemical alterations in cultured human brains. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):503–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI115024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staun-Olsen P., Ottesen B., Gammeltoft S., Fahrenkrug J. The regional distribution of receptors for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 25;330(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90691-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterio D. C. The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc. 1984 May;134(Pt 2):127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1984.tb02501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., DeTeresa R., Hansen L. A. Neocortical cell counts in normal human adult aging. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jun;21(6):530–539. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Peck A., DeTeresa R., Schechter R., Horoupian D. S. Some morphometric aspects of the brain in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1981 Aug;10(2):184–192. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Masliah E., Morey M., Lemere C., DeTeresa R., Grafe M., Hansen L., Terry R. Neocortical damage during HIV infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):651–657. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. W., Rakic P. Three-dimensional counting: an accurate and direct method to estimate numbers of cells in sectioned material. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Dec 15;278(3):344–352. doi: 10.1002/cne.902780305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Martin B., Chen H. C. Antimicrobial activity of synthetic magainin peptides and several analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):910–913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


