Abstract
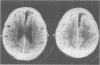
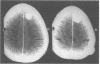
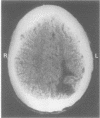
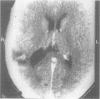
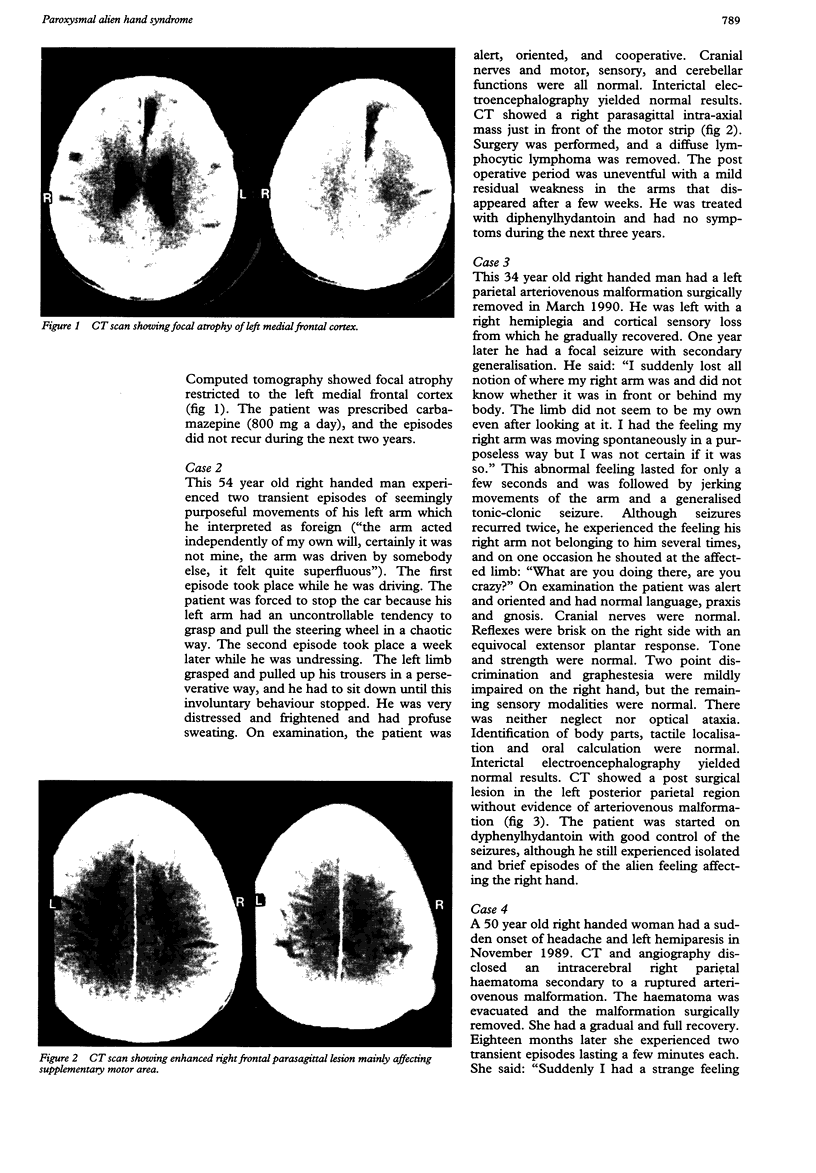
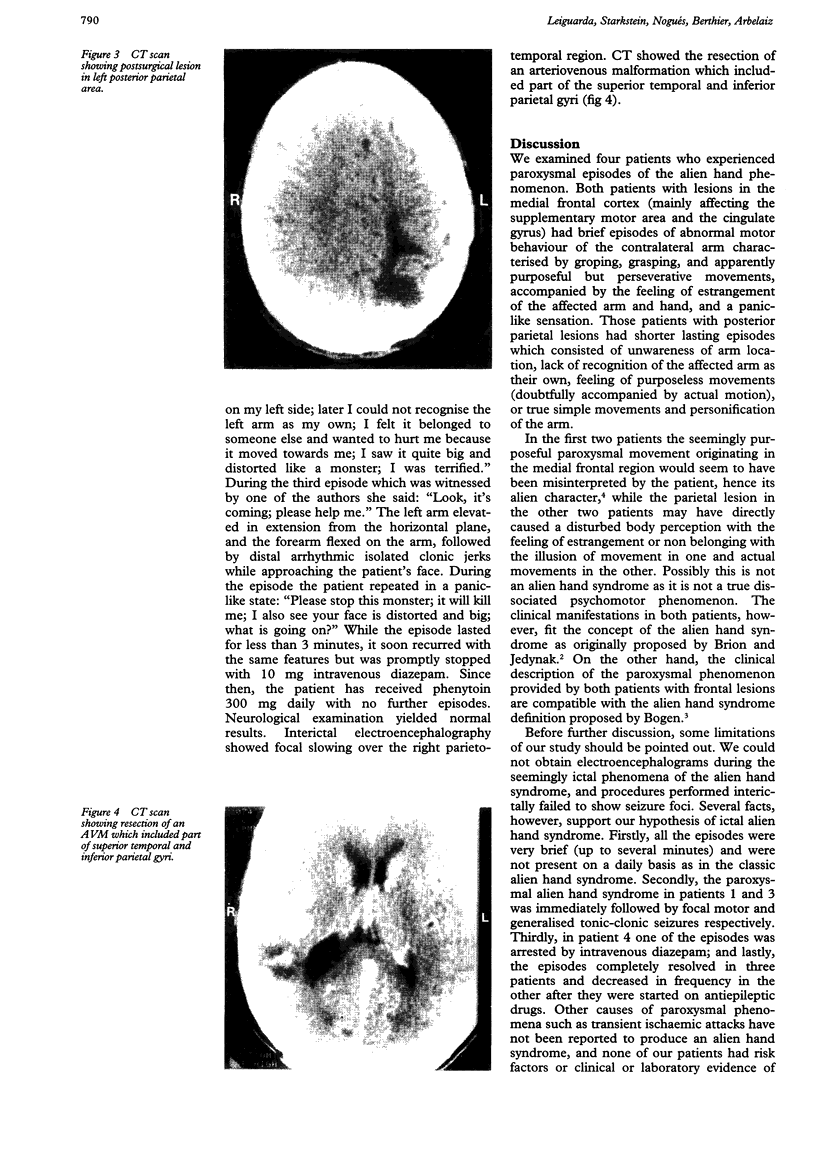
Four patients are described who presented with a paroxysmal form of the alien hand syndrome. Two patients with damage to one frontomedial cortex had brief episodes of abnormal motor behaviour of the contralateral arm that featured groping, grasping, and apparently purposeful but perseverative movements, which both patients interpreted as alien or foreign. The other two patients, with posterior parietal damage, reported a paroxysmal feeling of unawareness of the location of the contralateral arm, lack of recognition of the arm as their own, purposeless movements, and personification of the arm. These cases represent a new form of the alien hand syndrome manifested by brief, paroxysmal episodes, which may be due to ictal mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks G., Short P., Martinez J., Latchaw R., Ratcliff G., Boller F. The alien hand syndrome. Clinical and postmortem findings. Arch Neurol. 1989 Apr;46(4):456–459. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520400116030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion S., Jedynak C. P. Troubles du transfert interhémisphérique (callosal disconnection). A propos de trois observations de tumeurs du corps calleux. Le signe de la main étrangére. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1972 Apr;126(4):257–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNY-BROWN D., MEYER J. S., HORENSTEIN S. The significance of perceptual rivalry resulting from parietal lesion. Brain. 1952 Dec;75(4):433–471. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING J. F. R., CROSBY E. C. The parietal lobe as an additional motor area; the motor effects of electrical stimulation and ablation of cortical areas 5 and 7 in monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1955 Dec;103(3):485–512. doi: 10.1002/cne.901030306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier S., Bancaud J., Talairach J., Bonis A., Enjelvin M., Hossard-Bouchaud H. Automatisms during frontal lobe epileptic seizures. Brain. 1976 Sep;99(3):447–458. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier S., Bancaud J., Talairach J., Bonis A., Hossard-Bouchaud H., Enjelvin M. Ictal tonic postural changes and automatisms of the upper limb during epileptic parietal lobe discharges. Epilepsia. 1977 Dec;18(4):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1977.tb04999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelmers H. J. Non-paralytic motor disturbances and speech disorders: the role of the supplementary motor area. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;46(11):1052–1054. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.11.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G., Mayer N. H., Toglia J. U. Medial frontal cortex infarction and the alien hand sign. Arch Neurol. 1981 Nov;38(11):683–686. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510110043004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyvärinen J., Poranen A. Function of the parietal associative area 7 as revealed from cellular discharges in alert monkeys. Brain. 1974 Dec;97(4):673–692. doi: 10.1093/brain/97.1.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Powell T. P. An anatomical study of converging sensory pathways within the cerebral cortex of the monkey. Brain. 1970;93(4):793–820. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiguarda R., Starkstein S., Berthier M. Anterior callosal haemorrhage. A partial interhemispheric disconnection syndrome. Brain. 1989 Aug;112(Pt 4):1019–1037. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.4.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. N., Rinn W. E. Opticosensory ataxia and alien hand syndrome after posterior cerebral artery territory infarction. Neurology. 1986 Aug;36(8):1094–1097. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.8.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. C., Mountcastle V. B., Talbot W. H., Yin T. C. Parietal lobe mechanisms for directed visual attention. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;40(2):362–389. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.2.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNabb A. W., Carroll W. M., Mastaglia F. L. "Alien hand" and loss of bimanual coordination after dominant anterior cerebral artery territory infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;51(2):218–222. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. H., 3rd, Dinner D. S., Lüders H., Wyllie E., Kramer R. Supplementary motor seizures: clinical and electroencephalographic findings. Neurology. 1988 Jul;38(7):1075–1082. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.7.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle V. B., Lynch J. C., Georgopoulos A., Sakata H., Acuna C. Posterior parietal association cortex of the monkey: command functions for operations within extrapersonal space. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Jul;38(4):871–908. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.4.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Shibutani H., Kawano K. Functional properties of visual tracking neurons in posterior parietal association cortex of the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jun;49(6):1364–1380. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.6.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Takaoka Y., Kawarasaki A., Shibutani H. Somatosensory properties of neurons in the superior parietal cortex (area 5) of the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 21;64:85–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talairach J., Bancaud J., Geier S., Bordas-Ferrer M., Bonis A., Szikla G., Rusu M. The cingulate gyrus and human behaviour. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1973 Jan;34(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(73)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Iwasa H., Yoshida M. Diagonistic dyspraxia: case report and movement-related potentials. Neurology. 1990 Apr;40(4):657–661. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman K., Purves S. J., Kosaka B., Strauss E., Wada J. A. An epileptic syndrome caused by mesial frontal lobe seizure foci. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):577–582. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. T., Heilman K. M. Callosal apraxia. Brain. 1983 Jun;106(Pt 2):391–403. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P. D., Spencer D. D., Spencer S. S., Novelly R. A., Mattson R. H. Complex partial seizures of frontal lobe origin. Ann Neurol. 1985 Oct;18(4):497–504. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. H., Reeves A., Gazzaniga M., Culver C. Cerebral commissurotomy for control of intractable seizures. Neurology. 1977 Aug;27(8):708–715. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.8.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]