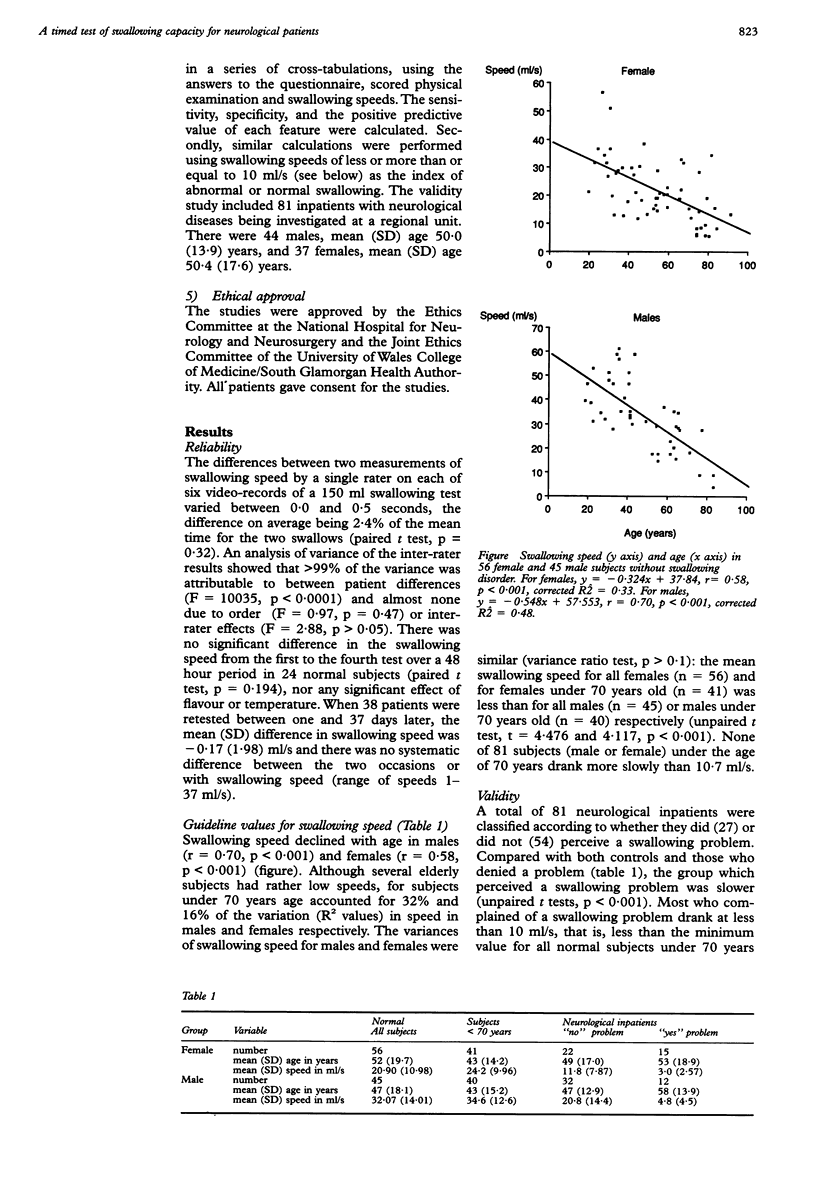
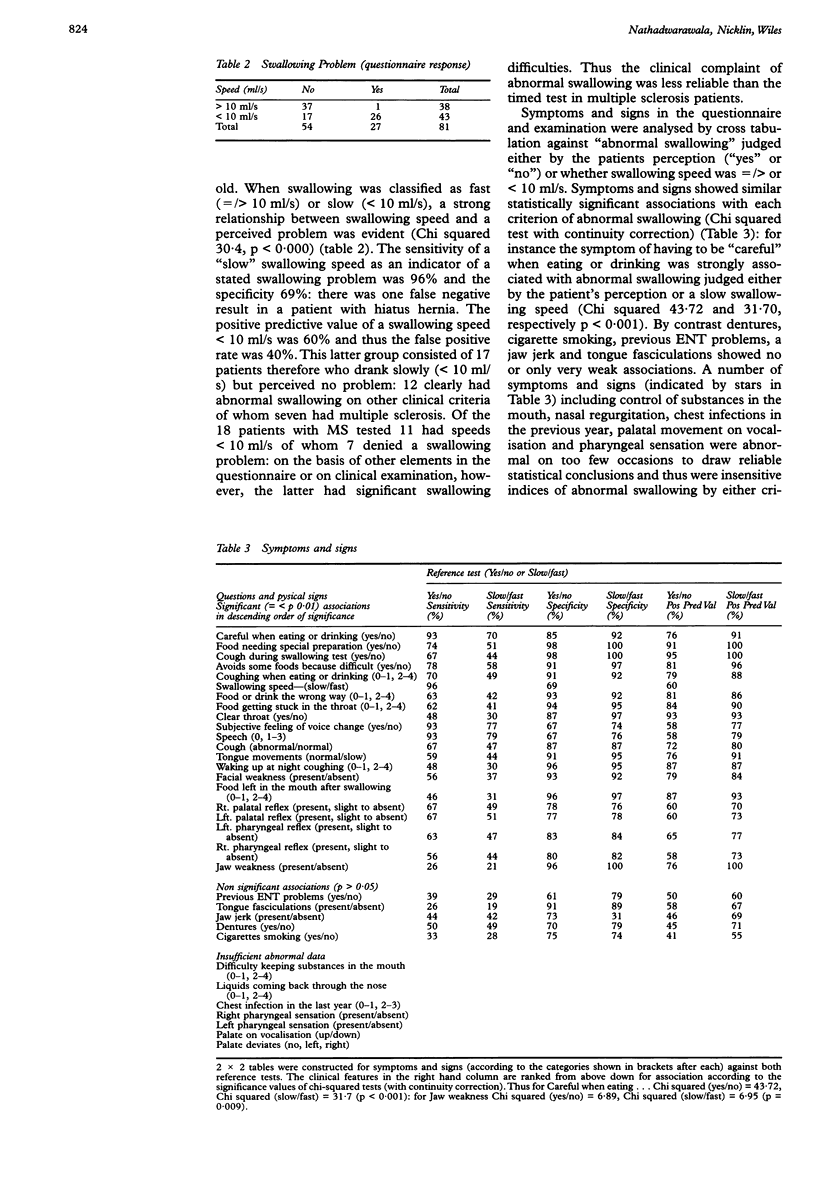
Abstract
A timed test of swallowing capacity has been designed for use in patients with neurogenic dysphagia. Swallowing speed (ml/s) has been demonstrated to have high intra- and inter- rater and test- retest reliability, and to be essentially independent of flavour or temperature. "Guideline" normal values were established in individuals without a swallowing disorder: swallowing speed was less in females than males and declined in both groups with age. The validity of a swallowing speed less than 10 ml/s as an index of abnormal swallowing was tested by comparison with the complaint of abnormal swallowing in a group of 81 neurological patients. Swallowing speed had a sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 69%: some apparent false positive responses were found in patients with disordered swallowing, mainly due to multiple sclerosis. Using a standard questionnaire and examination a similar pattern of symptoms and signs were statistically associated with both the clinical complaint of abnormal swallowing and swallowing speed. It is concluded that swallowing speed is a reliable and valid index for assessing disordered swallowing in neurological patients and may be of value in monitoring response to therapy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloem B. R., Lagaay A. M., van Beek W., Haan J., Roos R. A., Wintzen A. R. Prevalence of subjective dysphagia in community residents aged over 87. BMJ. 1990 Mar 17;300(6726):721–722. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6726.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner J., Massey E. W., Brazer S. R. Aspiration in bilateral stroke patients. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1686–1688. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden P., Siebens A. A. Dysphagia: predicting laryngeal penetration. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1983 Jun;64(6):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J. A. Effects of aging on the swallowing mechanism. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1990 Dec;23(6):1045–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth N., Diner W. C. Swallowing problems in the elderly. Dysphagia. 1988;2(4):209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02414428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splaingard M. L., Hutchins B., Sulton L. D., Chaudhuri G. Aspiration in rehabilitation patients: videofluoroscopy vs bedside clinical assessment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988 Aug;69(8):637–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Karni Y., Nicklin J. Laboratory testing of muscle function in the management of neuromuscular disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 May;53(5):384–387. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.5.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


