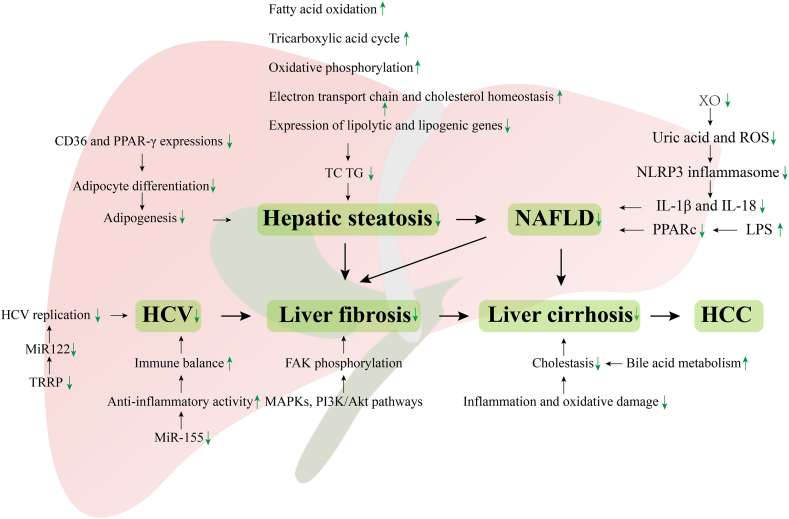
Fig. 2.
Protective effects of APG on hepatic steatosis, NAFLD, HCV, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Hepatic steatosis can develop into cirrhosis, which ultimately leads to HCC. HCV can also progress to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, eventually leading to HCC. APG could be used to treat these liver diseases through its anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation properties, as well as its regulation of lipid and bile acid metabolism and inhibition of HCV replication. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma, HCV: Hepatitis C virus, NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, PPARα: Proliferator-activated receptor alpha, ROS: Reactive oxygen species, TC: Total cholesterol, TG: Triglyceride, TRRP: Trans-activating response RNA-binding protein, XO: Xanthine oxidase.