Abstract
Six Parkinsonian patients on long term levodopa therapy complained of short-lived deterioration of Parkinsonian symptoms immediately after levodopa intake. After withdrawal of the drug overnight, and following an oral challenge with levodopa/carbidopa (250/25) in all six cases, and with subcutaneous apomorphine (3 mg) in two, deterioration below base line levels of disability were observed which would not be explained by loss of sleep benefit. This occurred 10-20 minutes after levodopa challenge and lasted for 10-20 minutes. The latency and duration of this phenomenon were shorter with apomorphine but the characteristics were similar. This phenomenon may be due to an inhibitory effect of levodopa acting via presynaptic dopamine receptors.
Full text
PDF
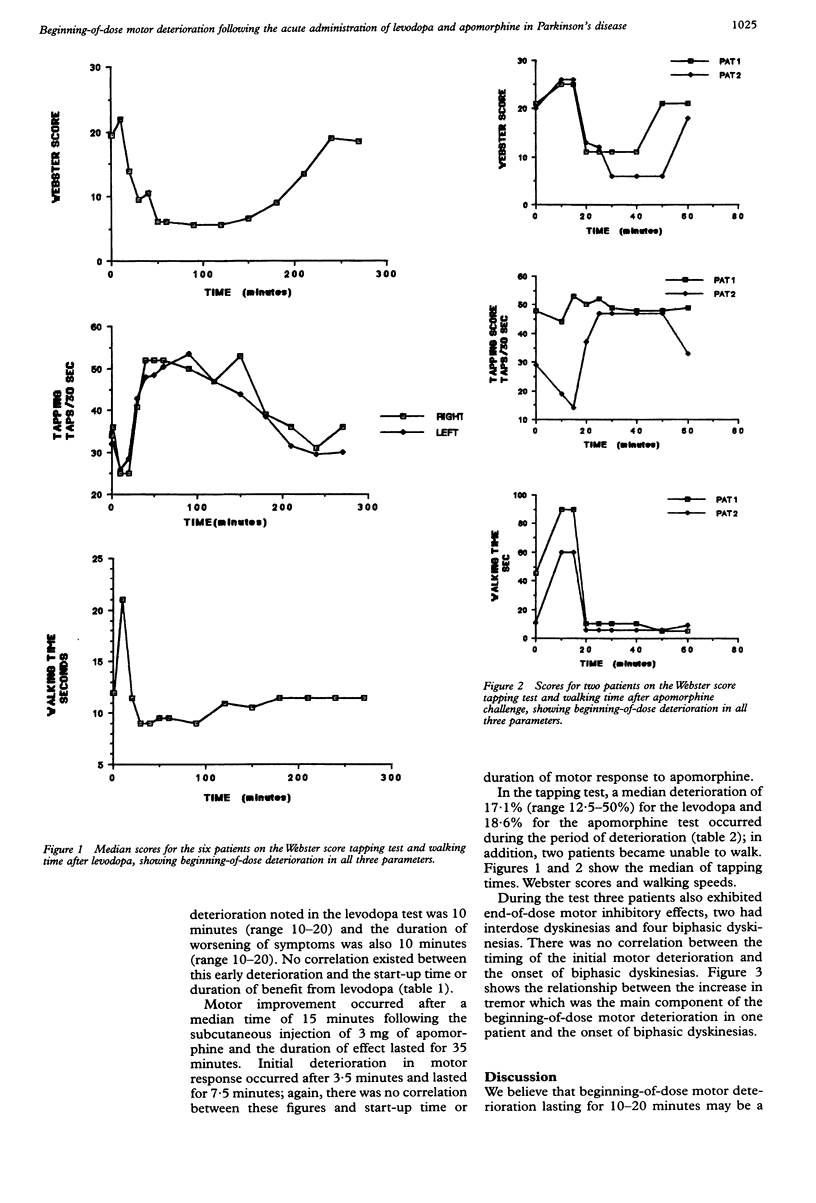

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury A. J., Cannon J. G., Costall B., Naylor R. J. A comparison of dopamine agonist action to inhibit locomotor activity and to induce stereotyped behaviour in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 1;105(1-2):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90646-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsini G. U., Onali P., Masala C., Cianchetti C., Mangoni A., Gessa G. Apomorphine hydrochloride-induced improvement in Huntington's chorea: stimulation of dopamine receptor. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jan;35(1):27–30. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500250031006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. L., Brughitta G., Baronti F., Mouradian M. M. Acute effects of pulsatile levodopa administration on central dopamine pharmacodynamics. Neurology. 1991 May;41(5):630–633. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstler L. K. Medicare 1986: can society afford quality physician care? Part II. Geriatrics. 1986 Oct;41(10):15-6, 19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. J., Lees A. J., Stern G. M. Apomorphine test to predict dopaminergic responsiveness in parkinsonian syndromes. Lancet. 1990 Jul 7;336(8706):32–34. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91531-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y., Kolakowska T., Robertson A., Tricou B. J. Effect of low-dose bromocriptine in treatment of psychosis: the dopamine autoreceptor-stimulation strategy. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;81(1):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00439271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena I., Cotzias G. C. Protein intake and treatment of Parkinson's disease with levodopa. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 23;292(4):181–184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501232920404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt J. G., Gancher S. T., Woodward W. R. Does an inhibitory action of levodopa contribute to motor fluctuations? Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1553–1557. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protais P., Dubuc I., Costentin J. Pharmacological characteristics of dopamine receptors involved in the dual effect of dopamine agonists on yawning behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 28;94(3-4):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirboll L. R., Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Dopamine auto- and postsynaptic receptors: electrophysiological evidence for differential sensitivity to dopamine agonists. Science. 1979 Oct 5;206(4414):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.482929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa E. S., Sparber S. B. Apomorphine in Huntington's chorea: clinical observations and theoretical considerations. Life Sci. 1974 Oct 1;15(7):1371–1380. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]