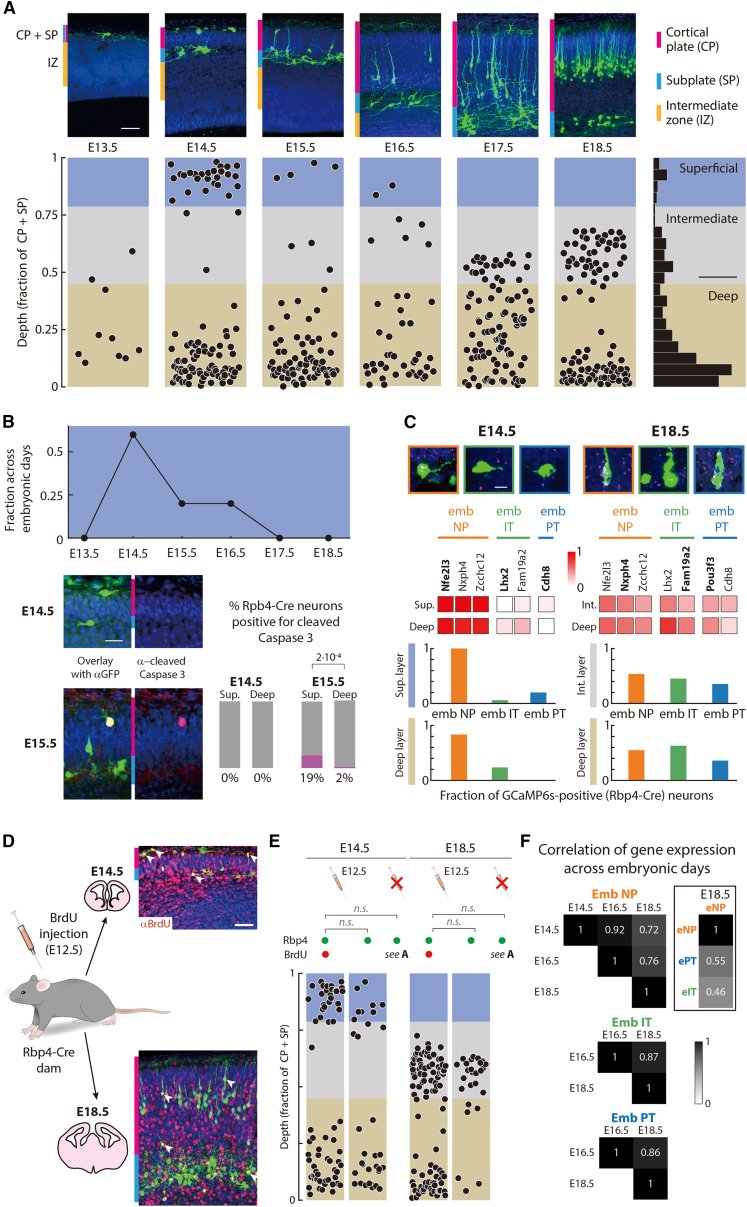
Figure 2.
Rbp4-Cre neurons distribute into superficial, intermediate, and deep layers
(A) Top: Rbp4-Cre neurons (green), Hoechst (blue). Bottom left: Rbp4-Cre neuron depths normalized to the cortical plate and subplate thickness, (Figure S2). Bottom right: distribution of Rbp4-Cre neuron depths across days (blue: superficial layer; gray: intermediate layer; beige: deep layer).
(B) Top: Fraction of all superficial layer Rbp4-Cre neurons found on each embryonic day. Bottom left: Immunostaining Rbp4-Cre neurons (green), cleaved Caspase 3 (magenta), Hoechst (blue). Bottom right: Fraction of Rbp4-Cre neurons expressing cleaved Caspase 3. Fisher’s exact test.
(C) Top: Example in situ hybridizations of type-specific markers (magenta) (Figure S2), Rbp4-Cre neurons (green), Hoechst (blue). Middle: Fraction of Rbp4-Cre neurons containing embryonic-NP, IT, and PT-specific in situ hybridization markers; bold: genes shown in examples, above. Bottom: fractions of embryonic-NP, IT, and PT Rbp4-Cre neurons (based on in situ hybridizations).
(D) Immunostaining Rbp4-Cre neurons (green), BrdU (red), Hoechst (blue). Arrowheads: example Rbp4-Cre neurons incorporating BrdU.
(E) Normalized depth of Rbp4-Cre neurons incorporating BrdU (left), compared to Rbp4-Cre neurons without BrdU in the same embryos (center) and control embryos without BrdU injection (as in A). χ2 test.
(F) Correlation of gene expression: comparing across time vs. type (on E18.5).
Scale bars: 50 μm (top, A), 10% (bottom right, A), 20 μm (bottom left, B), 10 μm (top, C), 25 μm (D).
See also Figure S2.