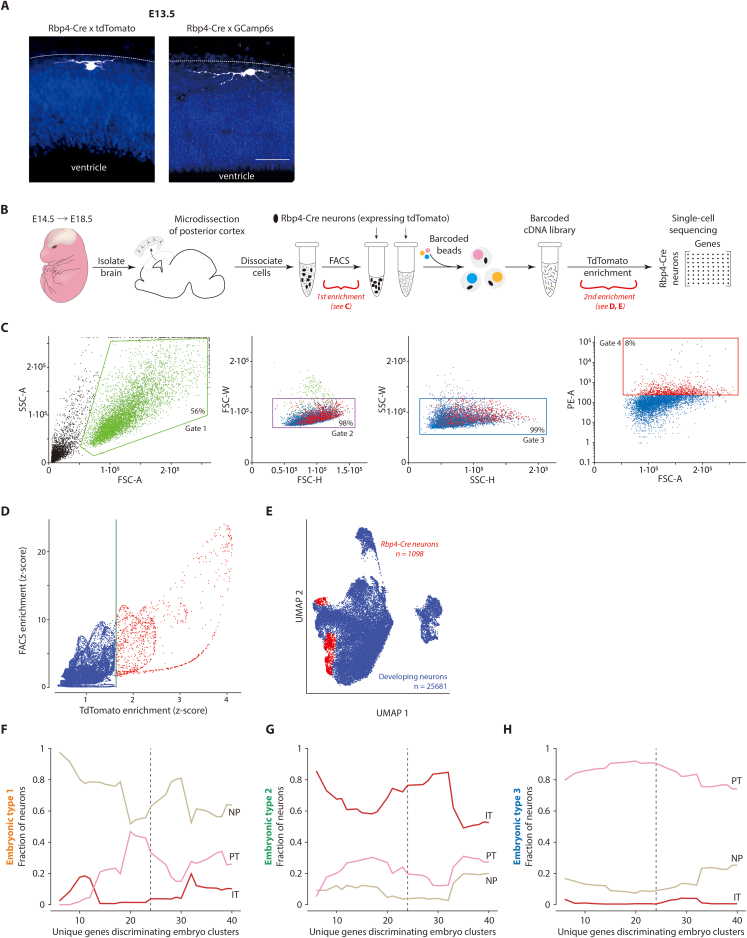
Figure S1.
Rbp4-Cre neurons appear in cortex from E13.5 onwards, and divide into three embryonic types, related to Figure 1
(A) Rbp4-Cre neurons at E13.5, near surface of developing cortex (dotted line), immunostained against either tdTomato (left) or GCaMP6s (right) (white), counterstained with Hoechst (blue).
(B) Single cell RNA sequencing workflow overview demonstrating two distinct stages of enrichment for tdTomato-expressing Rbp4-Cre neurons, from dissociated embryonic cortical tissue (red brackets).
(C) Initial enrichment of Rbp4-Cre neurons was performed by isolating cells positive for the tdTomato marker from the dissociated cortical tissue using FACS. Gates were selected based on the size and granularity of sorted events. Gate 1 was chosen to exclude debris, while gates 2 and 3 were chosen to exclude doublets. Gate 4 was chosen to select cells with higher tdTomato fluorescence. Box: events filtered at each gate.
(D) Additional enrichment for positively identified tdTomato-expressing Rbp4-Cre neurons. Relative enrichment of cells over a negatively FACS sorted population (blue) was used to define a baseline tdTomato expression level. Cells with significantly greater tdTomato expression than in the baseline were selected as positively identified Rbp4-Cre neurons (red). Green line: 6σ threshold of tdTomato expression.
(E) UMAP embedding of all 25681 excitatory neuron transcriptomes (blue) demonstrating the location of the subset of 1098 positively identified Rbp4-Cre neurons (red).
(F–H) Rbp4-Cre neuron divide into three embryonic types, each associated with one adult layer 5 type, stably across an increasing number of genes. Fraction of neurons within each Rbp4-Cre neuron type (1 (F), 2 (G), and 3 (H)) with a significant conditional probability of being sampled from the expression profile of one of the three adult cell types. Adult types: near-projecting neurons (NP) (beige), intratelencephalic neurons (IT) (red), and pyramidal tract neurons (PT) (pink) (as sequenced and identified in8 from VISp). Genes were selected to best discriminate the embryonic clusters, while still being differentially expressed across the three adult types. Dotted line: 24 differentially expressed genes used to generate Figure 1E. Scale bars: 50 μm (A).