Abstract
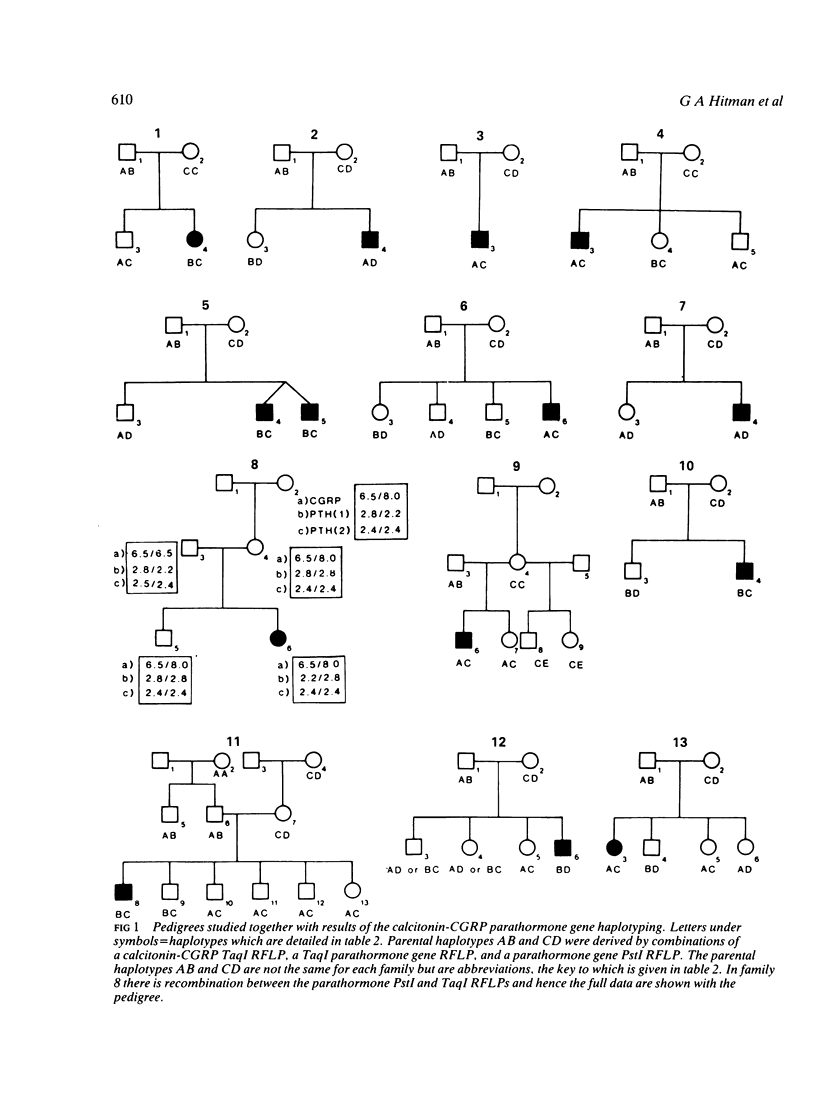
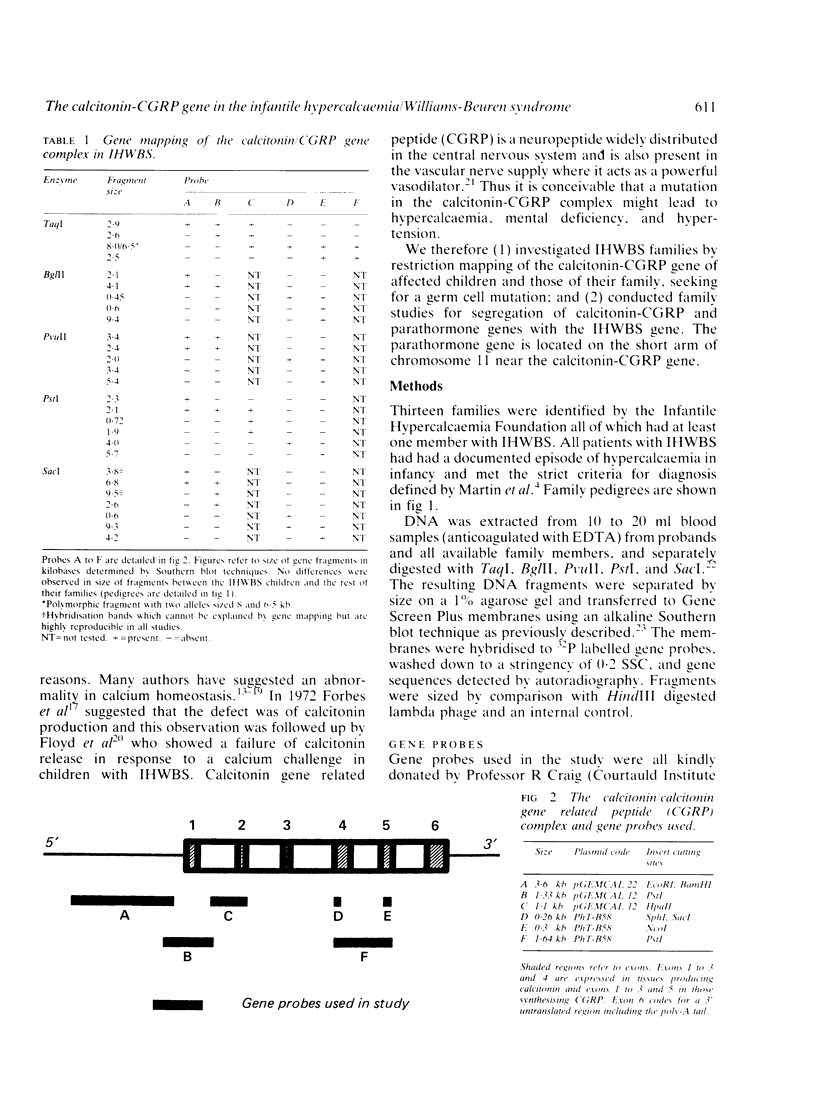
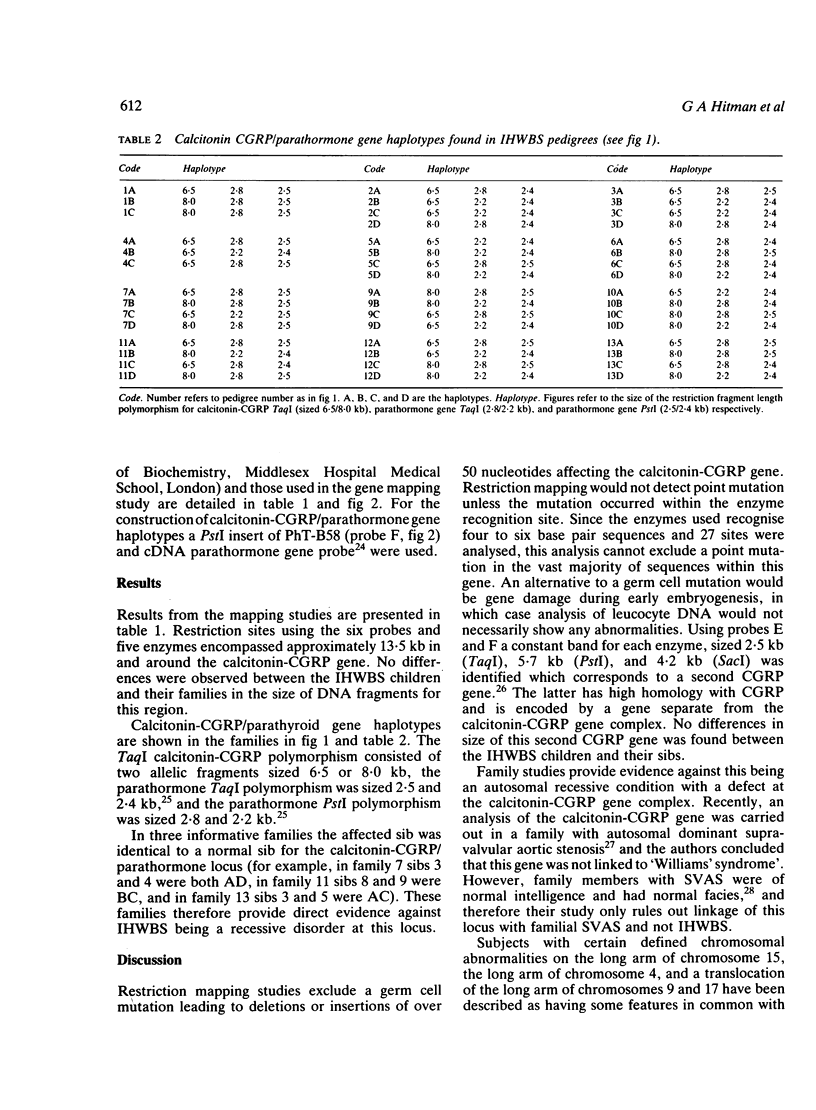
We have investigated 13 families, each of which have one member with infantile hypercalcaemia/Williams-Beuren syndrome (IHWBS), for either a germ cell mutation of, or an association with, the calcitonin-CGRP gene. Restriction fragment mapping studies of the calcitonin-CGRP gene using five restriction enzymes (TaqI, Bg/II, PvuII, PstI, and SacI) and region specific probes failed to show any abnormalities of this gene complex. NO association of IHWBS with polymorphism of the calcitonin-CGRP/parathormone locus was found. Therefore, although the aetiology of IHWBS may be caused by a new dominant mutation, there is no evidence to implicate major rearrangements of the calcitonin-CGRP and parathormone genes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEUREN A. J., SCHULZE C., EBERLE P., HARMJANZ D., APITZ J. THE SYNDROME OF SUPRAVALVULAR AORTIC STENOSIS, PERIPHERAL PULMONARY STENOSIS, MENTAL RETARDATION AND SIMILAR FACIAL APPEARANCE. Am J Cardiol. 1964 Apr;13:471–483. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK J. A., CARTER R. E. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN AORTIC STENOSIS AND FACIES OF SEVERE INFANTILE HYPERCALCAEMIA. Lancet. 1963 Oct 12;2(7311):745–749. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr D. G., Forfar J. O. Oral calcium-loading test in infancy, with particular reference to idiopathic hypercalcaemia. Br Med J. 1969 Feb 22;1(5642):477–480. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5642.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becroft D. M., Chambers D. Supravalvular aortic stenosis-infantile hypercalcaemia syndrome: in vitro hypersensitivity to vitamin D2 and calcium. J Med Genet. 1976 Jun;13(3):223–228. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. P., Burn J., Moore G. E., Chambers J., Williamson R., Wilkinson J. Exclusion of calcitonin as a candidate gene for the basic defect in a family with autosomal dominant supravalvular aortic stenosis. J Med Genet. 1988 May;25(5):311–312. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.5.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. Williams syndrome. J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;23(5):389–395. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.5.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortada X., Taysi K., Hartmann A. F. Familial Williams syndrome. Clin Genet. 1980 Sep;18(3):173–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. K., Hall L., Edbrooke M. R., Allison J., MacIntyre I. Partial nucleotide sequence of human calcitonin precursor mRNA identifies flanking cryptic peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):345–347. doi: 10.1038/295345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culler F. L., Jones K. L., Deftos L. J. Imparied calcitonin secretion in patients with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):720–723. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Miller M., Romeo G., Parsons M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Vitamin-D-binding protein in the Williams syndrome and idiopathic hypercalcemia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):687–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes G. B., Bryson M. F., Manning J., Amirhakimi G. H., Reina J. C. Impaired calcium homeostasis in the infantile hypercalcemic syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 May;61(3):305–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb16104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman W. F., Mills L. F. The relationship between vitamin D and the craniofacial and dental anomalies of the supravalvular aortic stenosis syndrome. Pediatrics. 1969 Jan;43(1):12–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman W. F., Roberts W. C. Vitamin D and the supravalvar aortic stenosis syndrome. The transplacental effects of vitamin D on the aorta of the rabbit. Circulation. 1966 Jul;34(1):77–86. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.34.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendy G. N., Kronenberg H. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNAs encoding human preproparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7365–7369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitman G. A., Niven M. J., Festenstein H., Cassell P. G., Awad J., Walker-Smith J., Leonard J. N., Fry L., Ciclitira P., Kumar P. HLA class II alpha chain gene polymorphisms in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, dermatitis herpetiformis, and celiac disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):609–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI112854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höppener J. W., Steenbergh P. H., Zandberg J., Bakker E., Pearson P. L., Geurts van Kessel A. H., Jansz H. S., Lips C. J. Localization of the polymorphic human calcitonin gene on chromosome 11. Hum Genet. 1984;66(4):309–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00287635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. D., Burn J., Gaunt K. L., Hunter S., Davison E. V. A terminal deletion of the long arm of chromosome 4 [46,XX,del(4)(q33)] in an infant with phenotypic features of Williams syndrome. J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;23(5):474–477. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.5.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. C., Wharton R., Elias E., Mandell F., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Clinical heterogeneity associated with deletions in the long arm of chromosome 15: report of 3 new cases and their possible genetic significance. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOGAN W. F., JONES E. W., WALKER E., COULSHED N., EPSTEIN E. J. FAMILIAL SUPRAVALVAR AORTIC STENOSIS. Br Heart J. 1965 Jul;27:547–559. doi: 10.1136/hrt.27.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. D., Snodgrass G. J., Cohen R. D. Idiopathic infantile hypercalcaemia--a continuing enigma. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jul;59(7):605–613. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.7.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagon R. A., Bennett F. C., LaVeck B., Stewart K. B., Johnson J. Williams syndrome: features in late childhood and adolescence. Pediatrics. 1987 Jul;80(1):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J., Pape B., Krengel U., Langenbeck U., Cooper D. N., Breyel E., Mayer H. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the human parathyroid hormone gene locus. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):428–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00291404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergh P. H., Höppener J. W., Zandberg J., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S. A second human calcitonin/CGRP gene. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80820-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. B., Stern P. H., Bell N. H. Abnormal regulation of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the Williams syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 22;306(16):972–975. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204223061607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. C., BARRATT-BOYES B. G., LOWE J. B. Supravalvular aortic stenosis. Circulation. 1961 Dec;24:1311–1318. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.6.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westgren M., Eastham W. N., Ghandourah S., Woodhouse N. Intrauterine hypercalcaemia and non-immune hydrops fetalis--relationship to the Williams syndrome. Prenat Diagn. 1988 Jun;8(5):333–337. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970080504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltse H. E., Goldbloom R. B., Antia A. U., Ottesen O. E., Rowe R. D., Cooke R. E. Infantile hypercalcemia syndrome in twins. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 24;275(21):1157–1160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611242752103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


