Abstract
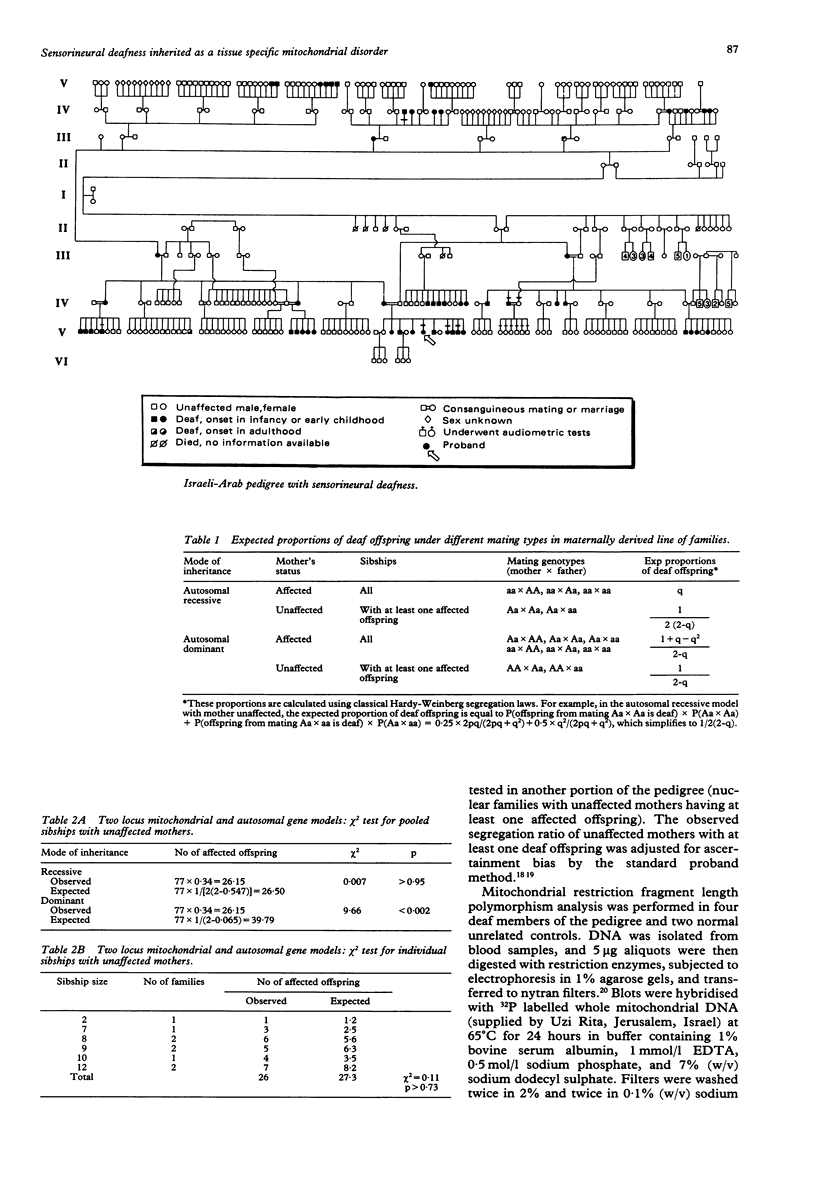
We present here a large Israeli-Arab kindred with hereditary deafness. In this family 55 deaf subjects (29M, 26F), who are otherwise healthy, have been identified and traced back five generations to one common female ancestor. The deafness is progressive in nature, usually presenting in infancy and childhood. Audiometry on six deaf and seven unaffected subjects was consistent with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. Based on formal family segregation analysis, the inheritance of deafness in this family closely fits the expectation of a two locus model owing to the simultaneous mutation of a mitochondrial gene and an autosomal recessive gene. Thus, this disorder appears to have the unusual features of being an inherited tissue specific mitochondrial disease and apparently requiring the homozygous presence of a nuclear gene for clinical expression. Most importantly, this disorder presents a unique opportunity to investigate the molecular basis of hereditary non-syndromic deafness and normal hearing.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. F., Hostikka S. L., Zhou J., Chow L. T., Oliphant A. R., Gerken S. C., Gregory M. C., Skolnick M. H., Atkin C. L., Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1224–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.2349482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., George M., Jr, Wilson A. C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu X. D., Rotter J. I. X chromosome-linked and mitochondrial gene control of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: evidence from segregation analysis for dependence on X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8198–8202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):31–36. doi: 10.1038/325031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Halphen D. G., Zhang Y. Z., Yanamura W. Complexity and tissue specificity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1988 Jun;20(3):291–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00769634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. S., Brown K. S. Family studies of early childhood deafness ascertained through the Clarke School for the Deaf. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Nov;22(6):630–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy C., Newton V., Wellesley D., Harris R., Read A. P. Assignment of the locus for Waardenburg syndrome type I to human chromosome 2q37 and possible homology to the Splotch mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1017–1023. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. Genomic imprinting: review and relevance to human diseases. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):857–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. N., Qui W. Q., Wu B. T., Fang L. Z., Zhou F., Gu Y. P., Zhang Q. H., Yan J. H., Ding Y. Q., Wong H. Genetic aspects of antibiotic induced deafness: mitochondrial inheritance. J Med Genet. 1991 Feb;28(2):79–83. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.2.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Weston M. D., Möller C., Davenport S. L., Shugart Y. Y., Priluck I. A., Martini A., Milani M., Smith R. J. Localization of Usher syndrome type II to chromosome 1q. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90546-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. P., Attardi G. Injection of mitochondria into human cells leads to a rapid replacement of the endogenous mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Otterud B., Stauffer D., Lalouel J. M., Leppert M. Mapping recessive ophthalmic diseases: linkage of the locus for Usher syndrome type II to a DNA marker on chromosome 1q. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnane A. W., Marzuki S., Ozawa T., Tanaka M. Mitochondrial DNA mutations as an important contributor to ageing and degenerative diseases. Lancet. 1989 Mar 25;1(8639):642–645. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott M. T., Voljavec A. S., Wallace D. C. Variable genotype of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990 Jun 15;109(6):625–631. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H. Genetic disorders of mitochondrial function. J Pediatr. 1987 Feb;110(2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnat R. J., Jr, Loeb L. A. Nucleotide sequence preservation of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo J. T., Bateman J. B., Spence M. A., Cortessis V., Sparkes R. S., Kivlin J. D., Mohandas T., Inana G. Ornithine aminotransferase (OAT): recombination between an X-linked OAT sequence (7.5 kb) and the Norrie disease locus. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90456-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiloh Y., Litvak G., Ziv Y., Lehner T., Sandkuyl L., Hildesheimer M., Buchris V., Cremers F. P., Szabo P., White B. N. Genetic mapping of X-linked albinism-deafness syndrome (ADFN) to Xq26.3-q27.I. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):20–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., 4th, Wallace D. C. Oxidative phosphorylation diseases. Disorders of two genomes. Adv Hum Genet. 1990;19:267–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Lezza A. M., Seibel P., Ballinger S. W., Wallace D. C. Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fiber disease (MERRF) is associated with a mitochondrial DNA tRNA(Lys) mutation. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):931–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90059-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood R., Mulligan L. M., Poon R., White B. N., Holden J. J. Genetic mapping of two new DNA markers in Xq26-q28 relative to the fragile-X syndrome locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;47(3):395–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Ott J., Savontaus M. L., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E. K. Optic atrophy in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy is probably determined by an X-chromosomal gene closely linked to DXS7. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):486–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Singh G., Lott M. T., Hodge J. A., Schurr T. G., Lezza A. M., Elsas L. J., 2nd, Nikoskelainen E. K. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.3201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Barker D. F., Hostikka S. L., Gregory M. C., Atkin C. L., Tryggvason K. Single base mutation in alpha 5(IV) collagen chain gene converting a conserved cysteine to serine in Alport syndrome. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90215-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Hostikka S. L., Chow L. T., Tryggvason K. Characterization of the 3' half of the human type IV collagen alpha 5 gene that is affected in the Alport syndrome. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



