Abstract
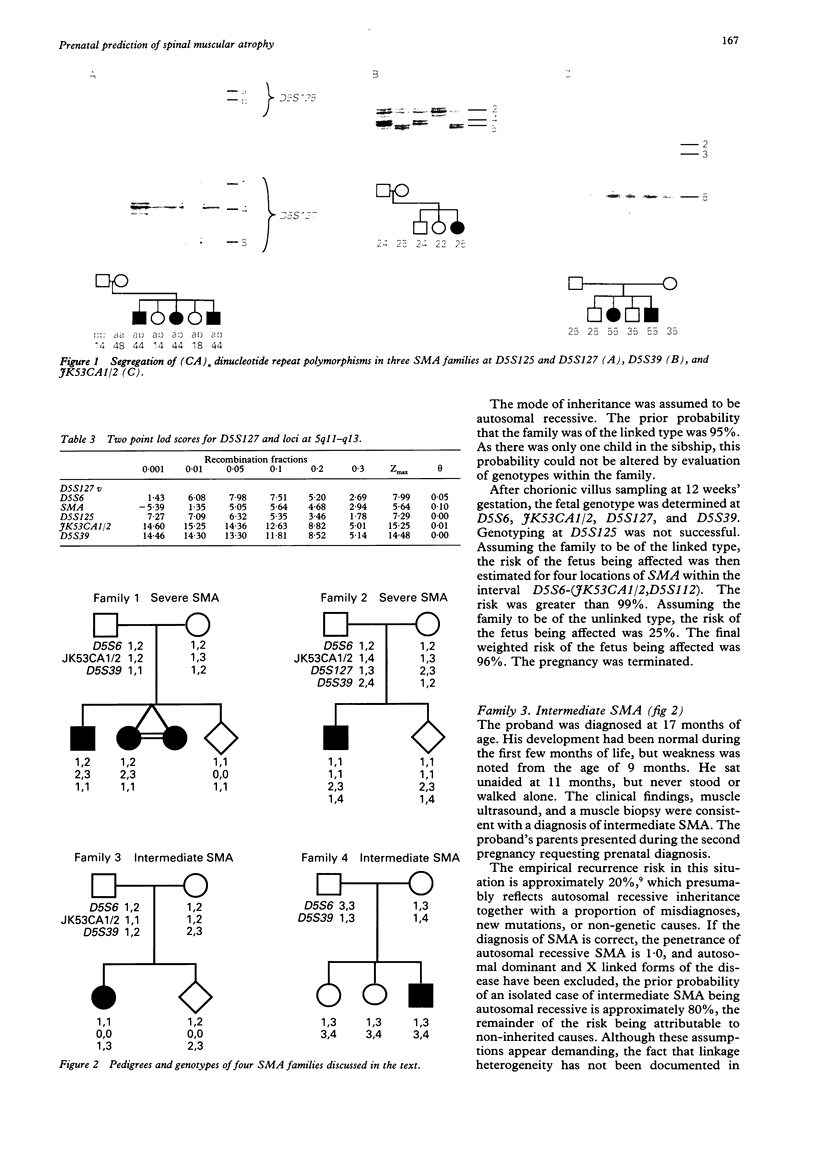
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a common cause of inherited morbidity and mortality in childhood. The wide range of phenotypes in SMA, uncertainty regarding its mode of inheritance, and the suggestion of linkage heterogeneity have complicated the genetic counselling of parents of affected children. The locus responsible for autosomal recessive SMA has been mapped to 5q11.2-q13.3. The most likely order of loci is cen-D5S6-(SMA,D5S125)-(JK53CA1/2,D5S112)-D5S3 9-qter, with highly polymorphic loci being identified at JK53CA1/2 and D5S39. We describe linkage studies with another highly polymorphic locus, D5S127, that is closely linked to D5S39. This genetic map can be used as the basis for genetic counselling in families with autosomal recessive SMA. Appropriate allowance can be made for sporadic cases owing to non-inherited causes and for linkage heterogeneity or misdiagnoses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouwsma G., Leschot N. J. Unusual pedigree patterns in seven families with spinal muscular atrophy; further evidence for the allelic model hypothesis. Clin Genet. 1986 Sep;30(3):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V. Chaos in classification of the spinal muscular atrophies of childhood. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(2):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90051-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Brzustowicz L. M., Castilla L. H., Lehner T., Penchaszadeh G. K., Daniels R. J., Byth B. C., Knowles J., Hislop J. E., Shapira Y. Genetic homogeneity between acute and chronic forms of spinal muscular atrophy. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):823–825. doi: 10.1038/345823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczak M. Genetic risk and recombination fraction--an example of non-monotonic dependency. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):189–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00591085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K. Approximate confidence intervals for risk prediction in genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 May;38(5):681–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankoo B. S., Sherrington R., De La Concha A., Kalsi G., Curtis D., Melmer G., Gurling H. M. Two microsatellite polymorphisms at the D5S39 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1963–1963. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1963-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Abdelhak S., Sheth P., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Marcadet A., Aicardi J., Barois A., Carriere J. P., Fardeau M. Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):767–768. doi: 10.1038/344767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Sheth P., Abdelhak S., Burlet P., Bachelot M. F., Lathrop M. G., Frezal J., Munnich A. Mapping of acute (type I) spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q12-q14. The French Spinal Muscular Atrophy Investigators. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91803-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsat T. L., Skerry L., Korf B., Pober B., Schapira Y., Gascon G. G., al-Rajeh S. M., Dubowitz V., Davies K., Brzustowicz L. M. Phenotypic heterogeneity of spinal muscular atrophy mapping to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3 (SMA 5q). Neurology. 1990 Dec;40(12):1831–1836. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.12.1831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Clerget-Darpoux F. Becker's model and prenatal diagnosis in proximal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): a note of caution. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):238–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narod S. Counselling under genetic heterogeneity: a practical approach. Clin Genet. 1991 Feb;39(2):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb02998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth P., Abdelhak S., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Masset M., Hillaire D., Clerget-Darpoux F., Frézal J., Lathrop G. M., Munnich A. Linkage analysis in spinal muscular atrophy, by six closely flanking markers on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;48(4):764–768. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90195-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Ott J. Risk calculations under heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):819–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]