Abstract
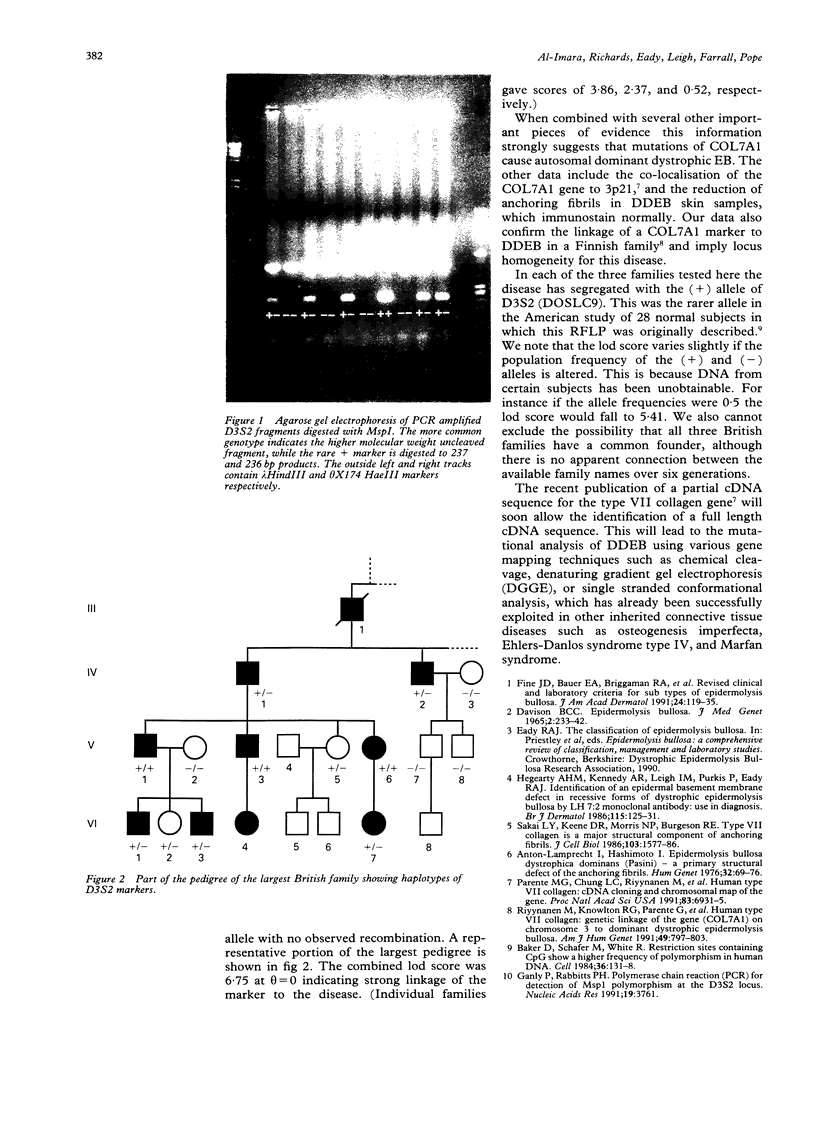
Linkage of the anonymous marker D3S2 at 3p21 has been shown in three British families with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa with a combined lod score of 6.75 at theta = 0. This locus is close to the collagen type VII locus implying that abnormalities of this gene cause dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton-Lamprecht I., Hashimoto I. Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica dominans (Pasini)-a primary structural defect of the anchoring fibrils. Hum Genet. 1976 Apr 15;32(1):69–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00569978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. C. Epidermolysis bullosa. J Med Genet. 1965 Dec;2(4):233–242. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.4.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. D., Bauer E. A., Briggaman R. A., Carter D. M., Eady R. A., Esterly N. B., Holbrook K. A., Hurwitz S., Johnson L., Lin A. Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. A consensus report by the Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Classification of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Jan;24(1):119–135. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70021-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganly P. S., Rabbitts P. H. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of MspI polymorphism at the D3S2 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3761–3761. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagerty A. H., Kennedy A. R., Leigh I. M., Purkis P., Eady R. A. Identification of an epidermal basement membrane defect in recessive forms of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa by LH 7:2 monoclonal antibody: use in diagnosis. Br J Dermatol. 1986 Aug;115(2):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente M. G., Chung L. C., Ryynänen J., Woodley D. T., Wynn K. C., Bauer E. A., Mattei M. G., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Human type VII collagen: cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6931–6935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryynänen M., Knowlton R. G., Parente M. G., Chung L. C., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Human type VII collagen: genetic linkage of the gene (COL7A1) on chromosome 3 to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):797–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen is a major structural component of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1577–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]