Full text
PDF


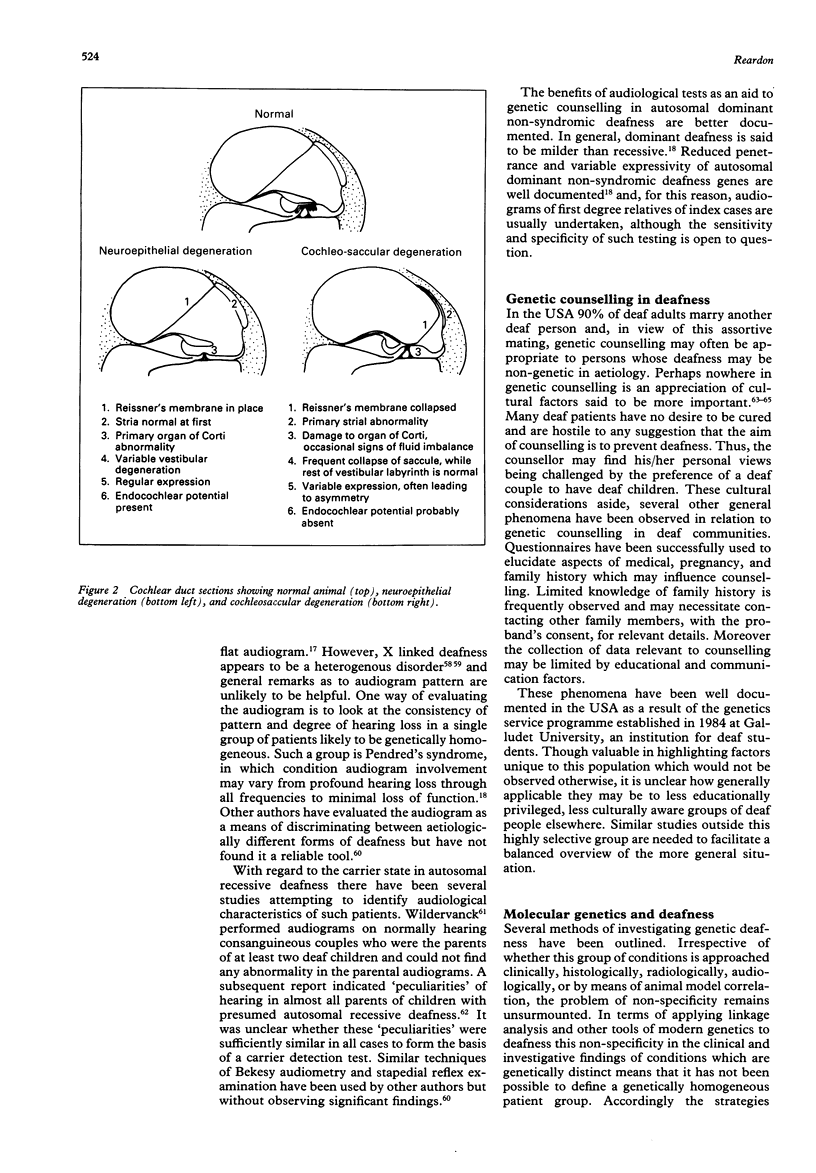


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann F. Histological findings in congenital deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 1968 Jan-Feb;65(1):115–119. doi: 10.3109/00016486809120949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H., Wedenberg E. Identification of normal hearing carriers of genes for deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 1976 Sep-Oct;82(3-4):245–248. doi: 10.3109/00016487609120895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnos K. S., Israel J., Cunningham M. Genetic counseling of the deaf. Medical and cultural considerations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:212–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom L., Hemenway W. G., Downs M. P. A high risk registry to find congenital deafness. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1971 Jun;4(2):369–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Brown K. A., Sutcliffe M. J., Cavanna J. S., Greenfield A. J., Steel K. P. Reverse genetic approaches to cloning deafness genes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. B. Sociological implications of hearing loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:230–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranefield P. F., Federn W. Paulus Zacchias on mental deficiency and on deafness. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1970 Jan;46(1):3–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., Diergaarde P. J., Wieringa B., Nussbaum R. L., Schwartz M., Ropers H. H. Physical fine mapping of the choroideremia locus using Xq21 deletions associated with complex syndromes. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEOL M. S. THE ABNORMALITIES OF THE INNER EAR IN KREISLER MICE. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1964 Sep;12:475–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEOL M. S. THE ORIGIN OF THE ABNORMALITIES OF THE INNER EAR IN DREHER MICE. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1964 Dec;12:727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. C. The prevalence of hearing impairment and reported hearing disability among adults in Great Britain. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Dec;18(4):911–917. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.4.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S. Influence of the neural tube on the differentiation of the inner ear in the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1966 Jan 8;209(5019):219–220. doi: 10.1038/209219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S. Inherited diseases of the inner ear in man in the light of studies on the mouse. J Med Genet. 1968 Jun;5(2):137–158. doi: 10.1136/jmg.5.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S. The probable mode of gene action in the circling mutants of the mouse. Genet Res. 1966 Jun;7(3):363–371. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. J., Read A. P., Donnai D., Colley A., Dixon J., Williamson R. The gene for Treacher Collins syndrome maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy C., Newton V., Wellesley D., Harris R., Read A. P. Assignment of the locus for Waardenburg syndrome type I to human chromosome 2q37 and possible homology to the Splotch mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1017–1023. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. R. Sex-linked recessive congenital deafness and the excess of males in profound childhood deafness. Ann Hum Genet. 1965 Nov;29(2):171–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1965.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E. The mitochondrial genome--breaking the magic circle. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 18;320(20):1341–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905183202009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. N., Qui W. Q., Wu B. T., Fang L. Z., Zhou F., Gu Y. P., Zhang Q. H., Yan J. H., Ding Y. Q., Wong H. Genetic aspects of antibiotic induced deafness: mitochondrial inheritance. J Med Genet. 1991 Feb;28(2):79–83. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.2.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackler R. K., Luxford W. M., House W. F. Congenital malformations of the inner ear: a classification based on embryogenesis. Laryngoscope. 1987 Mar;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 40):2–14. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540971301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan I. K. Ethical issues in the genetic study of deafness. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:236–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Weston M. D., Möller C., Davenport S. L., Shugart Y. Y., Priluck I. A., Martini A., Milani M., Smith R. J. Localization of Usher syndrome type II to chromosome 1q. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90546-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Otterud B., Stauffer D., Lalouel J. M., Leppert M. Mapping recessive ophthalmic diseases: linkage of the locus for Usher syndrome type II to a DNA marker on chromosome 1q. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsell E. M., Jackler R. K., Motta G., Linthicum F. H., Jr Congenital malformations of the inner ear: histologic findings in five temporal bones. Laryngoscope. 1987 Mar;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 40):18–24. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540971303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance W. E. Nonsyndromic deafness. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1980;16(7):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'RAHILLY R. THE EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF THE OTIC VESICLE IN STAGED HUMAN EMBRYOS. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1963 Dec;11:741–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD F. C. The pathology of congenital deafness. J Laryngol Otol. 1960 Dec;74:919–950. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100057376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paparella M. M. Mondini's deafness. A review of histopathology. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1980 Mar-Apr;89(2 Pt 3):1–10. doi: 10.1177/00034894800892s301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. D. Congenital lesions of the inner ear, demonstrated by tomography. Arch Otolaryngol. 1974 Jul;100(1):11–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. D., Reardon W., Pembrey M., Bellman S., Luxom L. X-linked deafness, stapes gushers and a distinctive defect of the inner ear. Neuroradiology. 1991;33(4):326–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00587816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. D., Sheldon P. W., Lloyd G. A. Hearing in patients with congenital deformity of the inner ear. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1976;1(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1976.tb00639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiney R. E., Mitchell D. B., Djazeri B., Evans J. N. Recurrent meningitis in children due to inner ear abnormalities. J Laryngol Otol. 1989 May;103(5):473–480. doi: 10.1017/s002221510015666x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Middleton-Price H. R., Sandkuijl L., Phelps P., Bellman S., Luxon L., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. A multipedigree linkage study of X-linked deafness: linkage to Xq13-q21 and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Pembrey M. The genetics of deafness. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Nov;65(11):1196–1197. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.11.1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W. Sex linked deafness: Wilde revisited. J Med Genet. 1990 Jun;27(6):376–379. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.6.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Johnson D. K., Margolis F. L., Jackson I. J., Russell L. B., Carpenter D. A. Reverse genetics in the mouse and its application to the study of deafness. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;630:80–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb19577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd L. The availability of statistics relating to deafness in the United Kingdom. Br J Audiol. 1978 Feb;12(1):3–8. doi: 10.3109/03005367809078847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel K. P., Barkway C. Another role for melanocytes: their importance for normal stria vascularis development in the mammalian inner ear. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):453–463. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel K. P., Bock G. R. Hereditary inner-ear abnormalities in animals. Relationships with human abnormalities. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Jan;109(1):22–29. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800150026005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. G., Hine W. D., Brasier V. J., Chiveralls K., Morris T. A study of the causes of hearing loss in a population of deaf children with special reference to genetic factors. J Laryngol Otol. 1975 Sep;89(9):899–914. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100081184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDERVANCK L. S. Audiometric examination of parents of children deaf from birth; the influence of consanguineous marriage. AMA Arch Otolaryngol. 1957 Mar;65(3):280–295. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1957.03830210078012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. Kramer v Wilde: an ideological debate. J Laryngol Otol. 1990 May;104(5):381–386. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100158517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



