Abstract
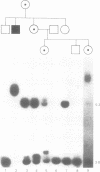
Genetic recombination near the fragile X locus (Xq27.3) has frequently been a problem in linkage studies of families in which the fragile X is segregating. This case report illustrates the resolution of a difficult situation in a fragile X family for whom cytogenetic studies were inconclusive and where recombination had twice confounded attempts at prenatal DNA diagnosis by RFLP analysis. Using a newly developed DNA probe, StB12.3, for direct detection of DNA instability in the fragile X locus, the presence of the fragile X was ascertained definitively in a prenatal DNA sample.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Fragile X syndrome: a unique mutation in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:109–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti M., Zhang F. P., Fu Y. H., Warren S. T., Oostra B. A., Caskey C. T., Nelson D. L. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Heitz D., Biancalana V., Blumenfeld S., Kretz C., Boué J., Tommerup N., Van Der Hagen C., DeLozier-Blanchet C., Croquette M. F. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1673–1681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Fratini A. Excess thymidine induces folate sensitive fragile sites. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Oct;22(2):433–443. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320220234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Mulley J. C., Voelckel M. A., Dahl N., Väisänen M. L., Steinbach P., Glass I. A., Schwartz C. E., van Oost B. A., Thibodeau S. N. Genetic mapping of new DNA probes at Xq27 defines a strategy for DNA studies in the fragile X syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):460–467. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]