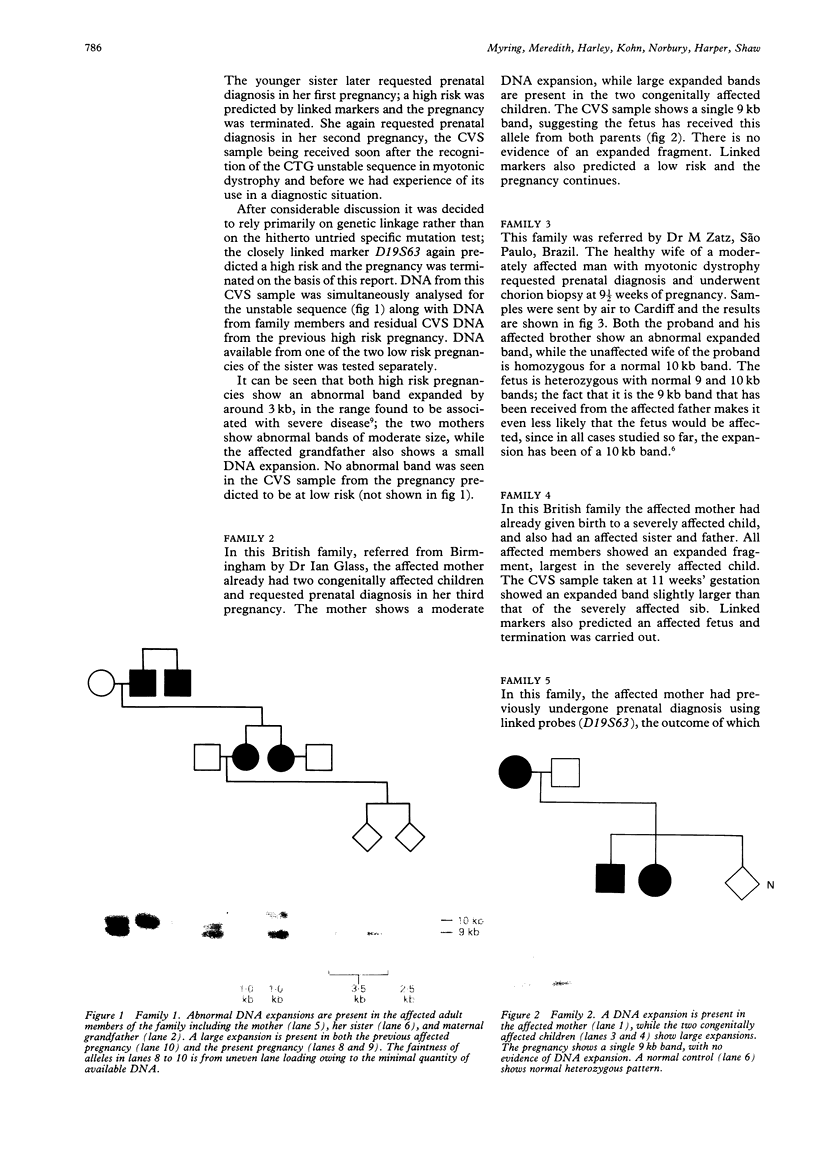
Abstract
The results of DNA analysis for the specific mutation of myotonic dystrophy are reported in eight pregnancies (two studied retrospectively) in six families. Four results were normal; in the other four, large DNA expansions were found, comparable to the range seen in severely affected children with congenital onset of the disorder. The results agreed with those obtained by linked DNA markers in the six cases where they were available. We conclude that specific molecular prenatal diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy is feasible, and that an abnormal result may also give a guide to possible severity, though this should be interpreted with caution until greater experience is available.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslanidis C., Jansen G., Amemiya C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Chen C., Alleman J., Wormskamp N. G., Vooijs M. Cloning of the essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):548–551. doi: 10.1038/355548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., McCurrach M. E., Harley H. G., Buckler A. J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V. P., Thirion J. P., Hudson T. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton J., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Jones C., Van Tongeren T., Aslanidis C., de Jong P., Jansen G., Anvret M., Riley B. Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):547–548. doi: 10.1038/355547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., Reardon W., Myring J., Crow S., Brook J. D., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J. Unstable DNA sequence in myotonic dystrophy. Lancet. 1992 May 9;339(8802):1125–1128. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90729-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Harley H. G., Reardon W., Shaw D. J. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: new light on an old problem. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):10–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. C., Grimm T., Harley H. G., Harper P. S. Genetic risks for children of women with myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1084–1091. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith A. L., Huson S. M., Lunt P. W., Sarfarazi M., Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Application of a closely linked polymorphism of restriction fragment length to counselling and prenatal testing in families with myotonic dystrophy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 22;293(6558):1353–1356. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6558.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. M., Floyd J. L., Meredith A. L., Harper P. S. Presymptomatic detection and prenatal diagnosis for myotonic dystrophy by means of linked DNA markers. J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;26(12):750–754. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.12.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T., Newcombe R. G., Harper P. S. Outlook for a clinically normal child in a sibship with congenital myotonic dystrophy. J Pediatr. 1983 Nov;103(5):762–763. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Meredith A. L., Sarfarazi M., Huson S. M., Brook J. D., Myklebost O., Harper P. S. The apolipoprotein CII gene: subchromosomal localisation and linkage to the myotonic dystrophy locus. Hum Genet. 1985;70(3):271–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00273455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Gedeon A., Kornman L., Donnelly A., Byard R. W., Mulley J. C., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S. Prenatal diagnosis of fragile X syndrome by direct detection of the unstable DNA sequence. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1720–1722. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






