Abstract
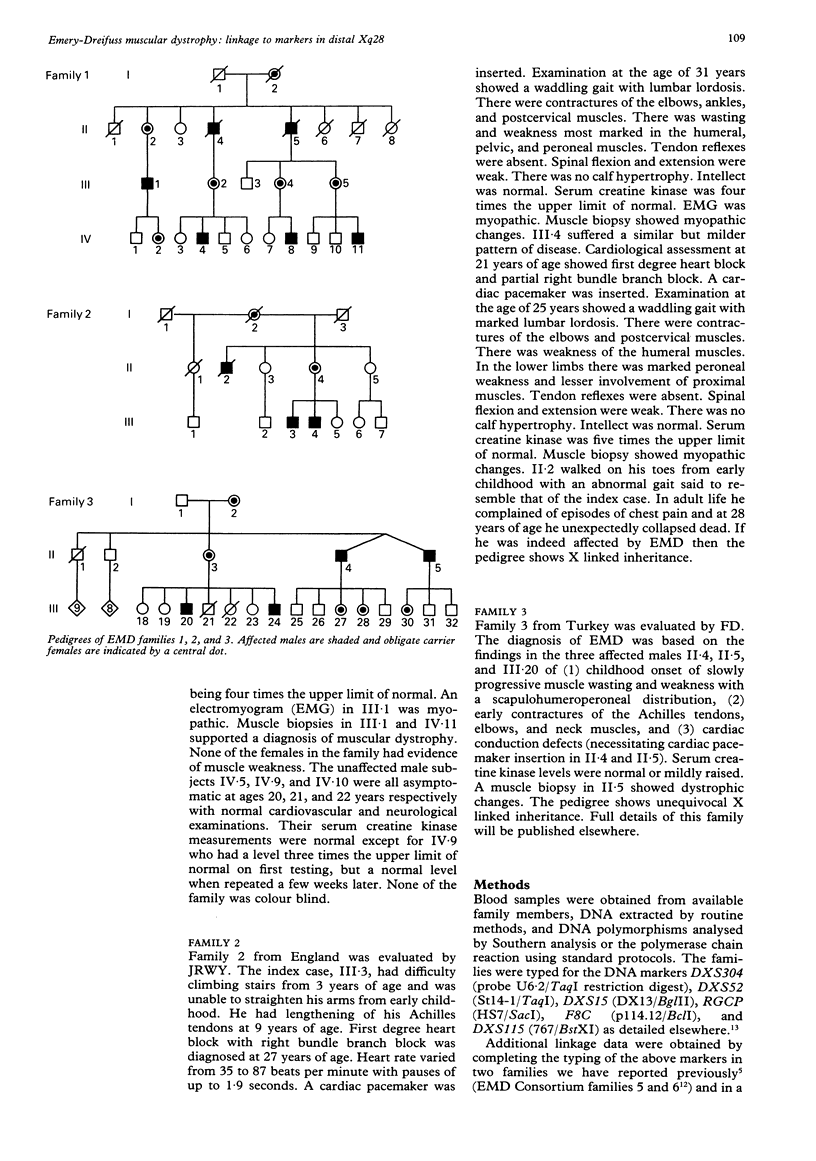
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EMD) is characterised by (1) early contractures of the Achilles tendons, elbows, and postcervical muscles, (2) slowly progressive muscle wasting and weakness with a predominantly humeroperoneal distribution in the early stages, and (3) cardiomyopathy with conduction defects and risk of sudden death. Inheritance is usually X linked recessive but can be autosomal dominant. Family linkage studies have mapped X linked EMD to the distal long arm of the X chromosome but precise genetic localisation has been hampered by the rarity of this condition. We report three new families with X linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy studied with DNA markers from Xq27-qter and three previously published families typed for additional markers. No recombination was observed with the red/green cone pigment locus, RGCP (lod score, Z = 2.46), the factor VIII coagulant gene locus, F8C (Z = 6.39), or with DXS115 (Z = 4.94). Two recombinants were observed which mapped EMD distal to DXS15 (DX13) and DXS52 (St14) respectively. Multipoint linkage analysis gave odds exceeding 200:1 for EMD being distal to these markers. A multipoint analysis incorporating published data gave the map cen-DXS304-9cM-DXS15-3cM-DXS52-2 cM-(RGCP,EMD)-3cM-F8C-2cM-DXS115 with odds of 120:1 in favour of a location for EMD between DXS52 and F8C as compared to the next best position distal to F8C.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole C. G., Abbs S. J., Dubowitz V., Hodgson S. V., Warner J., Merlini L., Bobrow M. Linkage of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the red/green cone pigment (RGCP) genes, proximal to factor VIII. Neuromuscul Disord. 1992;2(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(92)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consalez G. G., Thomas N. S., Stayton C. L., Knight S. J., Johnson M., Hopkins L. C., Harper P. S., Elsas L. J., Warren S. T. Assignment of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the distal region of Xq28: the results of a collaborative study. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):468–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Emery-Dreifuss syndrome. J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;26(10):637–641. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.10.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Schram L. J., Wallis G., Oswald A., Beighton P. Emery-Dreifuss syndrome and X-linked muscular dystrophy with contractures: evidence for homogeneity. Clin Genet. 1989 Jan;35(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S., Boswinkel E., Cole C., Walker A., Dubowitz V., Granata C., Merlini L., Bobrow M. A linkage study of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1986 Dec;74(4):409–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00280495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Andrews V. MAP, an expert system for multiple pairwise linkage analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;53(Pt 3):263–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquis V., Philip N., Voelckel M. A., Pouget J., Lemieux B., Mattei J. F., Giraud F. Etudes de liaison dans la dystrophie musculaire d'Emery-Dreifuss. J Genet Hum. 1989 Jun;37(2):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Dietrich A., Langenstein G., Toniolo D., Warren S. T., Lehrach H. Physical map of human Xq27-qter: localizing the region of the fragile X mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8302–8306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Lindsten J., Hultén M., Yee S. A mapping function for man. Hum Hered. 1977;27(2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000152856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., Roncuzzi L., Sangiorgi S., Giacanelli M., Liguori M., Tessarolo D., Rocchi M. Mapping of the Emery-Dreifuss gene through reconstruction of crossover points in two Italian pedigrees. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):59–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00451457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Williams H., Elsas L. J., Hopkins L. C., Sarfarazi M., Harper P. S. Localisation of the gene for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the distal long arm of the X chromosome. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):596–598. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Calne D. B., Elliott C. F. X-linked scapuloperoneal syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Apr;35(2):208–215. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Affara N. A., Jamieson D. M., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Zaremba J., Borkowska J., Johnston A. W., Kelly K. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: localisation to Xq27.3----qter confirmed by linkage to the factor VIII gene. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):587–590. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R. European workshop on Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 1991. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(6):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90002-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


