Abstract
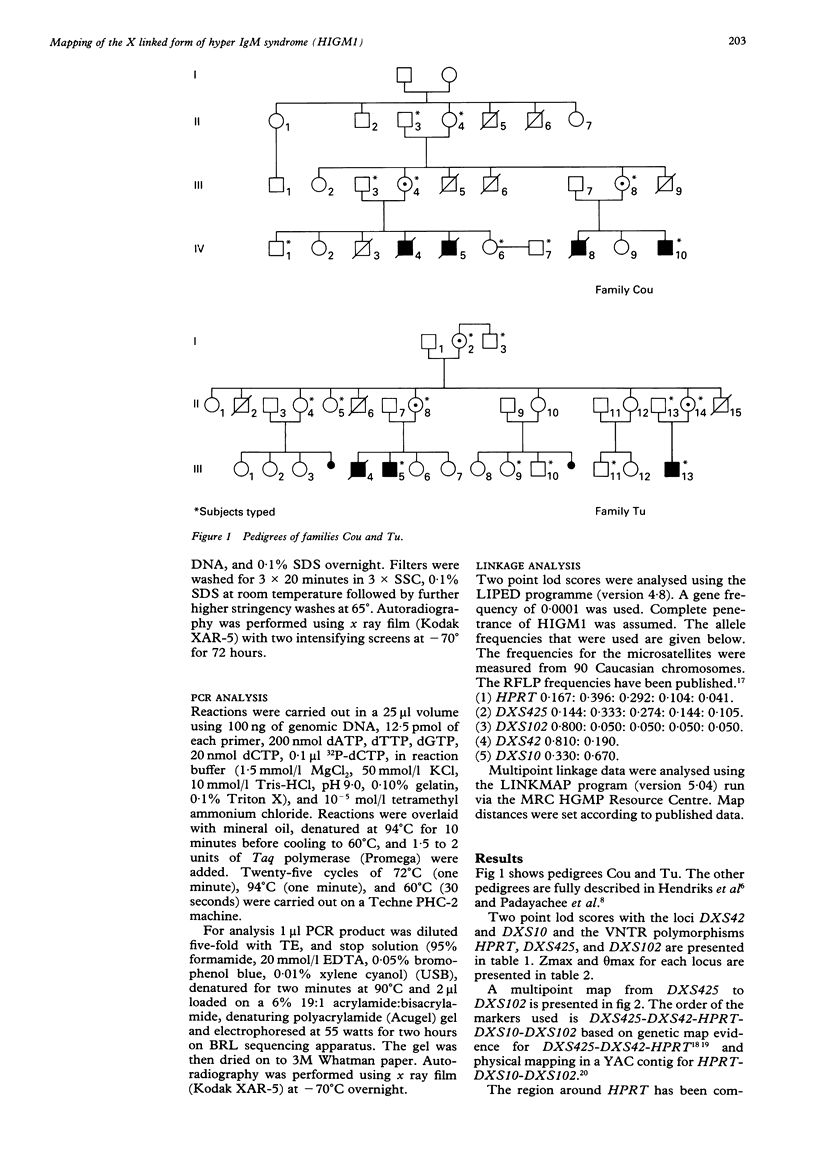
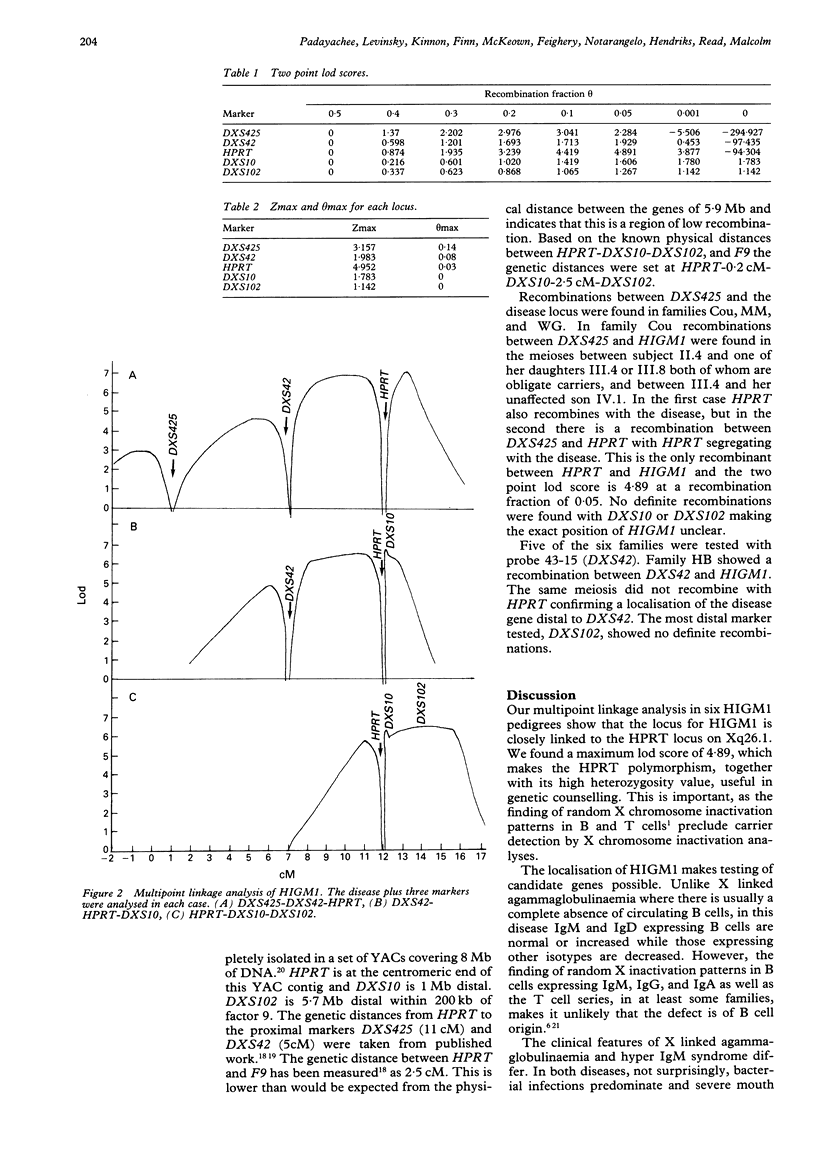
X linked immunodeficiency with hyperimmunoglobulinaemia M (HIGM1), which is characterised by agammaglobulinaemia together with excess IgM production reflecting an impairment of the immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch of B lymphocytes, has been mapped to Xq26. We report multipoint linkage data in six families with HIGM1 which show that the most likely position for the gene is close to HPRT with a maximum lod score of 4.89. The finding of recombinations between HIGM1 and both HPRT and DXS42 implies that HIGM1 is not allelic to X linked lymphoproliferative disease. These data will be useful in genetic counselling in families and will also be useful in testing candidate genes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage R. J., Fanslow W. C., Strockbine L., Sato T. A., Clifford K. N., Macduff B. M., Anderson D. M., Gimpel S. D., Davis-Smith T., Maliszewski C. R. Molecular and biological characterization of a murine ligand for CD40. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):80–82. doi: 10.1038/357080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Civitello A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T. DNA typing and genetic mapping with trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeats. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):746–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascan H., Gauchat J. F., Aversa G., Van Vlasselaer P., de Vries J. E. Anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies or CD4+ T cell clones and IL-4 induce IgG4 and IgE switching in purified human B cells via different signaling pathways. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne C. M., Todd J. A. Tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism at the HPRT locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5450–5450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., Kraakman M. E., Craig I. W., Espanol T., Schuurman R. K. Evidence that in X-linked immunodeficiency with hyperimmunoglobulinemia M the intrinsic immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch mechanism is intact. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2603–2608. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., Schuurman R. K. Genetics of human X-linked immunodeficiency diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):182–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Cottingham R. W., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Zoghbi H. Y. Genetic mapping of four dinucleotide repeat loci, DXS453, DXS458, DXS454, and DXS424, on the X chromosome using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90256-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Edwards A., Pettigrew A. L., Herrera C. A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T., Zoghbi H. Y., Ledbetter D. H. Linkage of the gene for an X-linked mental retardation disorder to a hypervariable (AGAT)n repeat motif within the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) locus (Xq26). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1312–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMIESON W. M., KERR M. R. A family with several cases of hypogammaglobulinaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1962 Jun;37:330–336. doi: 10.1136/adc.37.193.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanpierre M. A rapid method for the purification of DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9611–9611. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little R. D., Pilia G., Johnson S., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Yeast artificial chromosomes spanning 8 megabases and 10-15 centimorgans of human cytogenetic band Xq26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luty J. A., Guo Z., Willard H. F., Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S., Litt M. Five polymorphic microsatellite VNTRs on the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):776–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., de Saint Basile G., Arveiler B., Lau Y. L., Szabo P., Fischer A., Griscelli C., Debre M., Mandel J. L., Callard R. E. Close linkage of random DNA fragments from Xq 21.3-22 to X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA). Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;77(2):172–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00272387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Kwan S. P., Thompson C., Ko H. S., Chiorazzi N., Waldmann T., Rosen F. Evidence for a defect in "switch" T cells in patients with immunodeficiency and hyperimmunoglobulinemia M. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):409–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensink E. J., Thompson A., Sandkuyl L. A., Kraakman M. E., Schot J. D., Espanol T., Schuurman R. K. X-linked immunodeficiency with hyperimmunoglobulinemia M appears to be linked to the DXS42 restriction fragment length polymorphism locus. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):96–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00283057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarangelo L. D., Duse M., Ugazio A. G. Immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM (HIM). Immunodefic Rev. 1992;3(2):101–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarangelo L. D., Parolini O., Albertini A., Duse M., Mazzolari E., Plebani A., Camerino G., Ugazio A. G. Analysis of X-chromosome inactivation in X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM (HIGM1): evidence for involvement of different hematopoietic cell lineages. Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;88(2):130–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00206059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padayachee M., Feighery C., Finn A., McKeown C., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C., Malcolm S. Mapping of the X-linked form of hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM1) to Xq26 by close linkage to HPRT. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):551–553. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F. S., KEVY S. V., MERLER E., JANEWAY C. A., GITLIN D. Recurrent bacterial infections and dysgamma-globulinemia: deficiency of 7S gamma-globulins in the presence of elevated 19S gamma-globulins. Report of two cases. Pediatrics. 1961 Aug;28:182–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly D. S., Lewis R. A., Nussbaum R. L. Genetic and physical mapping of Xq24-q26 markers flanking the Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90226-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


