Abstract
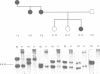
We report a female infant born to a mother with incontinentia pigmenti (IP) and a father with haemophilia A, who manifests both disorders. Analysis of peripheral blood DNA from the infant, her mother, and two female relatives with IP showed a highly skewed pattern of X inactivation. Random patterns were observed in the infant's two sisters, who do not have IP and have normal carrier activity of factor VIII. Preferential inactivation of the X chromosome bearing the IP mutation, probably by negative selection, appears to have unmasked the factor VIII mutation on the infant's other X chromosome. This illustrates an unusual mechanism for the manifestation of an X linked disease in a heterozygous female.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew M., Paes B., Milner R., Johnston M., Mitchell L., Tollefsen D. M., Powers P. Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs R. Haemophilia treatment in the United Kingdom from 1969 to 1974. Br J Haematol. 1977 Apr;35(4):487–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
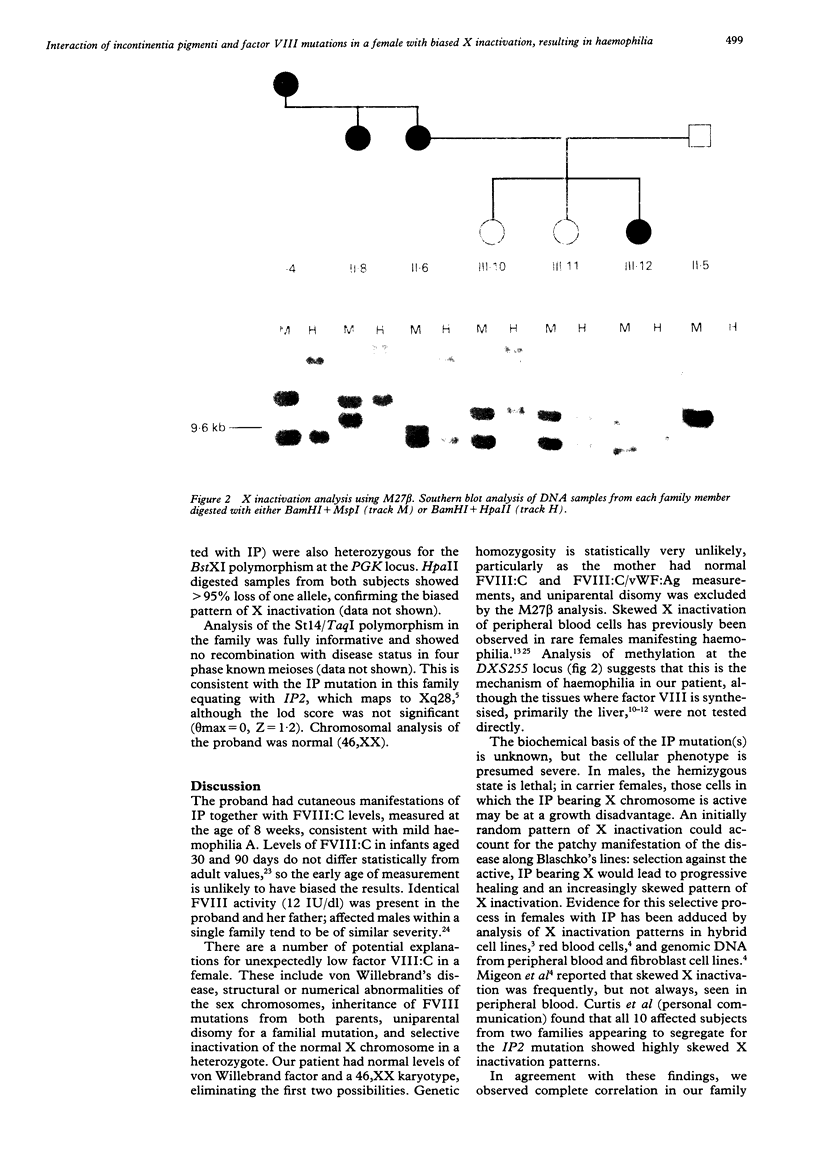
- Boyd Y., Fraser N. J. Methylation patterns at the hypervariable X-chromosome locus DXS255 (M27 beta): correlation with X-inactivation status. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):182–187. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney R. G. Incontinentia pigmenti. A world statistical analysis. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Apr;112(4):535–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Goralka T. M., Wion K. L., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Vehar G. A., Capon D. J., Lawn R. M. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):326–330. doi: 10.1038/312326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A., Collins J., Vetrie D., Cole C., Bobrow M. X inactivation as a mechanism of selection against lethal alleles: further investigation of incontinentia pigmenti and X linked lymphoproliferative disease. J Med Genet. 1992 Sep;29(9):608–614. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.9.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., Kraakman M. E., Mensink R. G., Schuurman R. K. Differential methylation at the 5' and the 3' CCGG sites flanking the X chromosomal hypervariable DXS255 locus. Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;88(1):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00204939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Neville B., Jones R. W., Fear C., Bobrow M. Two cases of X/autosome translocation in females with incontinentia pigmenti. Hum Genet. 1985;71(3):231–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00284581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kling S., Coffey A. J., Ljung R., Sjörin E., Nilsson I. M., Holmberg L., Giannelli F. Moderate haemophilia B in a female carrier caused by preferential inactivation of the paternal X chromosome. Eur J Haematol. 1991 Oct;47(4):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1991.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Axelman J., Jan de Beur S., Valle D., Mitchell G. A., Rosenbaum K. N. Selection against lethal alleles in females heterozygous for incontinentia pigmenti. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):100–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisen P. D., Waber P. G. Nonrandom X chromosome DNA methylation patterns in hemophiliac females. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1400–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI114028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberle I., Camerino G., Heilig R., Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Crapanzano C., Mannucci P. M., Mandel J. L. Genetic screening for hemophilia A (classic hemophilia) with a polymorphic DNA probe. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 14;312(11):682–686. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503143121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefiani A., M'rad R., Simard L., Vincent A., Julier C., Holvoet-Vermaut L., Heuertz S., Dahl N., Stalder J. F., Peter M. O. Linkage relationship between incontinentia pigmenti (IP2) and nine terminal X long arm markers. Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;86(3):297–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00202414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short P. E., Williams C. E., Picken A. M., Hill F. G. Factor VIII related antigen: an improved enzyme immunoassay. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Oct;39(4):351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stel H. V., van der Kwast T. H., Veerman E. C. Detection of factor VIII/coagulant antigen in human liver tissue. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):530–532. doi: 10.1038/303530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. X inactivation patterns in two syndromes with probable X-linked dominant, male lethal inheritance. Clin Genet. 1985 Sep;28(3):238–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wion K. L., Kelly D., Summerfield J. A., Tuddenham E. G., Lawn R. M. Distribution of factor VIII mRNA and antigen in human liver and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):726–729. doi: 10.1038/317726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Littell A. S. Detection of carriers of classic hemophilia using an immunologic assay for antihemophilic factor (factor 8(). J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):255–258. doi: 10.1172/JCI106481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kamp H., Jansen R., Willemze R., Fibbe W. E., Landegent J. E. Studies on clonality by PCR analysis of the PGK-1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2794–2794. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kwast T. H., Stel H. V., Cristen E., Bertina R. M., Veerman E. C. Localization of factor VIII-procoagulant antigen: an immunohistological survey of the human body using monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]