Abstract
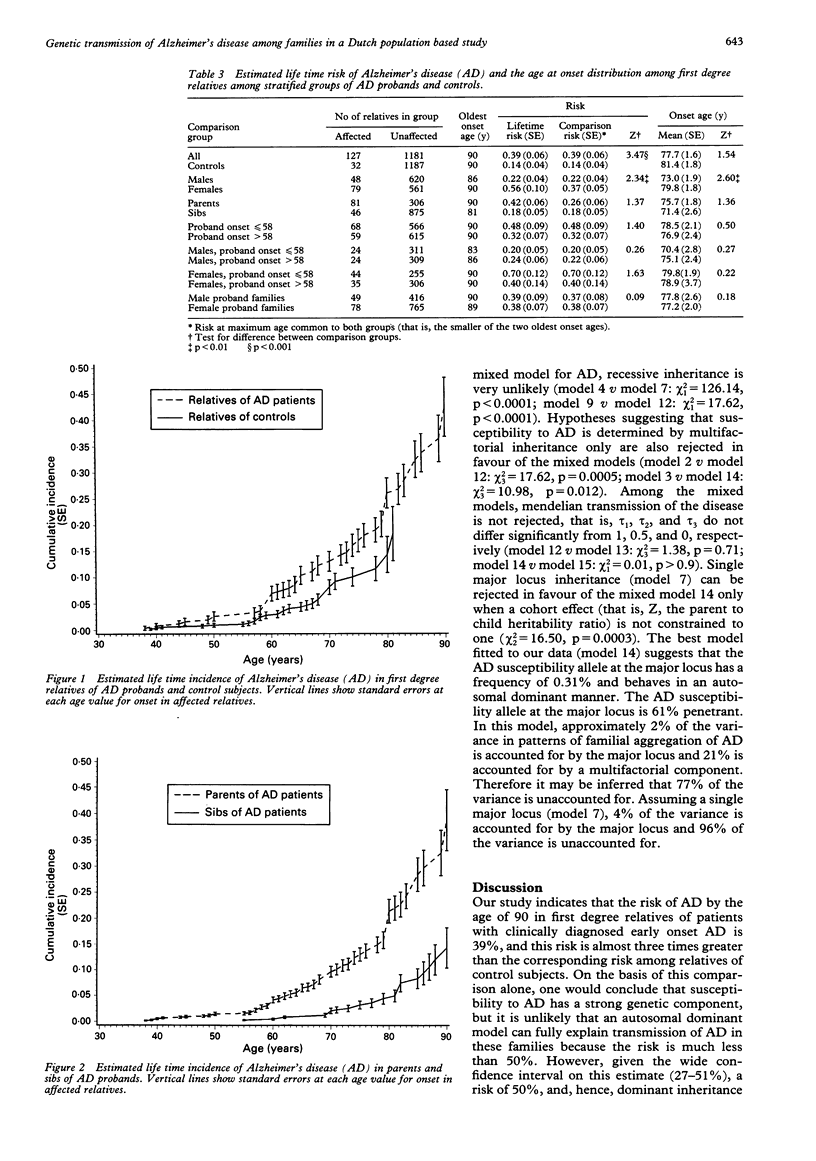
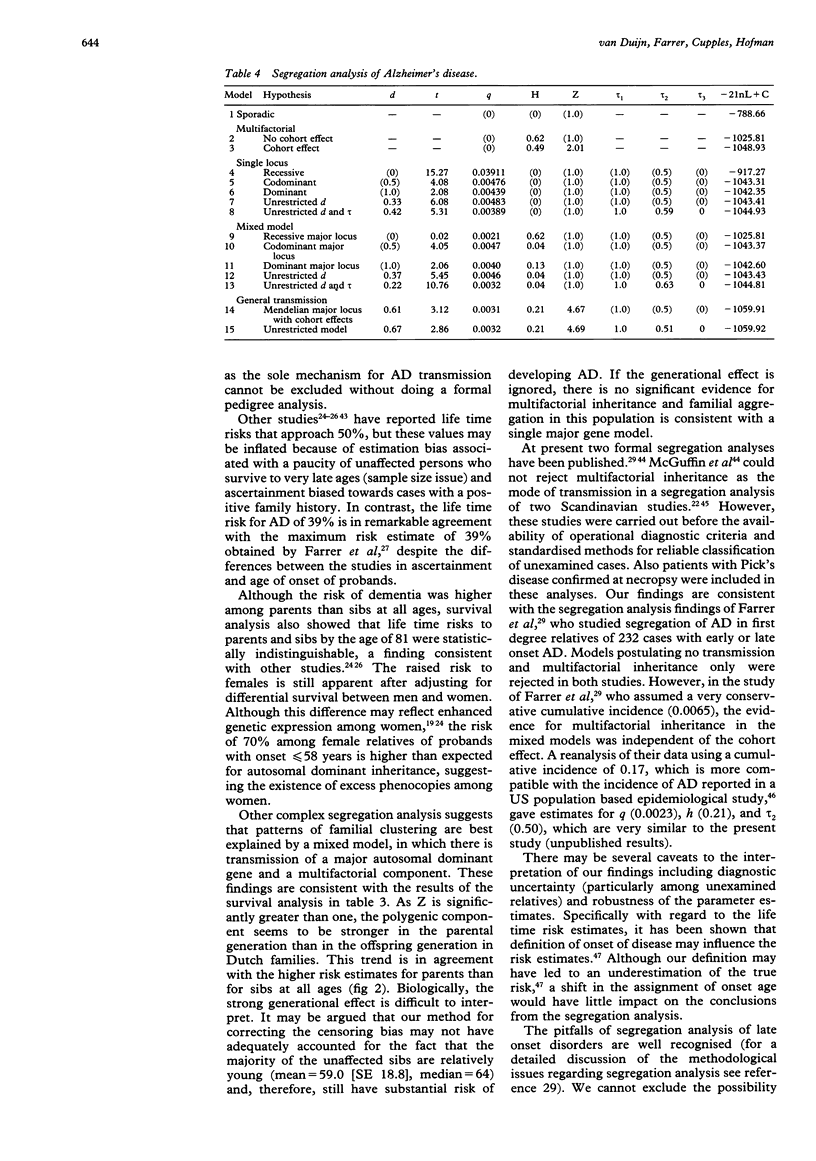
We evaluated age at onset and transmission patterns of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in families of 198 patients who had onset of symptoms before the age of 65 years and were diagnosed before the age of 70 years. Patients were ascertained in a population based study in The Netherlands. The results suggest that the risk of AD by the age of 90 in first degree relatives is 39% (95% confidence interval 27 to 51). By the age of 90, this risk is 2.8 (95% confidence interval 1.5-5.2) times greater than the corresponding risk of 14% among relatives of age and sex matched control subjects. Segregation analysis indicated that patterns of familial clustering are best explained by transmission of a major autosomal dominant gene with reduced penetrance and a multifactorial component. However, the single major locus model could be rejected in favour of the mixed model only when a cohort effect for heritability was allowed for. The frequency of the AD susceptibility allele was estimated to be 0.48% in the single major locus model and 0.31% in the mixed model. Although our study confirms that a dominant major gene is implicated in early onset AD, the results suggest that other genetic or perhaps non-genetic factors may account for the disease in a considerable number of patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaducci L. A., Fratiglioni L., Rocca W. A., Fieschi C., Livrea P., Pedone D., Bracco L., Lippi A., Gandolfo C., Bino G. Risk factors for clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease: a case-control study of an Italian population. Neurology. 1986 Jul;36(7):922–931. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.7.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney G. E. On the statistical determination of major gene mechanisms in continuous human traits: regressive models. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;18(4):731–749. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C., Magruder-Habib K. M. Criteria for onset critically influence the estimation of familial risk in Alzheimer's disease. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(6):663–669. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C., Silverman J. M., Mohs R. C., Davis K. L. Familial aggregation in Alzheimer's disease: comparison of risk among relatives of early-and late-onset cases, and among male and female relatives in successive generations. Neurology. 1988 Feb;38(2):207–212. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Crawford F., Houlden H., Warren A., Hughes D., Fidani L., Goate A., Rossor M., Roques P., Hardy J. Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):844–846. doi: 10.1038/353844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples L. A., Risch N., Farrer L. A., Myers R. H. Estimation of morbid risk and age at onset with missing information. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):76–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples L. A., Terrin N. C., Myers R. H., D'Agostino R. B. Using survival methods to estimate age-at-onset distributions for genetic diseases with an application to Huntington disease. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(2):361–371. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elandt-Johnson R. C. Segregation analysis for complex modes of inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):129–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Conneally P. M. A genetic model for age at onset in Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):350–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Myers R. H., Connor L., Cupples L. A., Growdon J. H. Segregation analysis reveals evidence of a major gene for Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1026–1033. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Myers R. H., Cupples L. A., St George-Hyslop P. H., Bird T. D., Rossor M. N., Mullan M. J., Polinsky R., Nee L., Heston L. Transmission and age-at-onset patterns in familial Alzheimer's disease: evidence for heterogeneity. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):395–403. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., O'Sullivan D. M., Cupples L. A., Growdon J. H., Myers R. H. Assessment of genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease among first-degree relatives. Ann Neurol. 1989 May;25(5):485–493. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch N., Becker R., Heller A. The inheritance of Alzheimer's disease: a new interpretation. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):14–19. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz W. J. Projecting Motion Pictures. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951 Dec;41(12):1544–1545. doi: 10.2105/ajph.41.12.1544-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Lange K. L. A maximum likelihood test of the two locus model for coeliac disease. Am J Med Genet. 1982 May;12(1):75–82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320120110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. Simulation studies of segregation analysis: application to two-locus models. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):167–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L. L., Mastri A. R. The genetics of Alzheimer's disease: associations with hematologic malignancy and Down's syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Aug;34(8):976–981. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770200114017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman A., Wilkinson W. E., Stafford J. A., Helms M. J., Sigmon A. H., Weinberg T. Alzheimer's disease: a study of epidemiological aspects. Ann Neurol. 1984 Apr;15(4):335–341. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman A., Schulte W., Tanja T. A., van Duijn C. M., Haaxma R., Lameris A. J., Otten V. M., Saan R. J. History of dementia and Parkinson's disease in 1st-degree relatives of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1989 Dec;39(12):1589–1592. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.12.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff F. J., Auerbach J., Chakravarti A., Boller F. Risk of dementia in relatives of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1988 May;38(5):786–790. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. P., Berg L., Danziger W. L., Coben L. A., Martin R. L. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;140:566–572. doi: 10.1192/bjp.140.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik L. F., Ruth V., Matsuyama S. S. Organic brain syndrome and aging. A six-year follow-up of surviving twins. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Mar;37(3):280–286. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780160050005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E. Complex segregation analysis with pointers. Hum Hered. 1981;31(5):312–321. doi: 10.1159/000153231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Elston R. C. A unified model for complex segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):816–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Boehnke M. Extensions to pedigree analysis. V. Optimal calculation of Mendelian likelihoods. Hum Hered. 1983;33(5):291–301. doi: 10.1159/000153393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Genetic tests under incomplete ascertainment. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Mar;11(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. L., Gerteis G., Gabrielli W. F., Jr A family-genetic study of dementia of Alzheimer type. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Oct;45(10):894–900. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800340016002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Sano M., Chen J., Tatemichi T., Stern Y. Risk of dementia in first-degree relatives of patients with Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Arch Neurol. 1991 Mar;48(3):269–273. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530150037014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., MacLean C. J. Analysis of family resemblance. 3. Complex segregation of quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;26(4):489–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Houlden H., Windelspecht M., Fidani L., Lombardi C., Diaz P., Rossor M., Crook R., Hardy J., Duff K. A locus for familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease on the long arm of chromosome 14, proximal to the alpha 1-antichymotrypsin gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):340–342. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell J., Farlow M., Ghetti B., Benson M. D. A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):97–99. doi: 10.1126/science.1925564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse S., Igarashi S., Kobayashi H., Aoki K., Inuzuka T., Kaneko K., Shimizu T., Iihara K., Kojima T., Miyatake T. Mis-sense mutation Val----Ile in exon 17 of amyloid precursor protein gene in Japanese familial Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1991 Apr 20;337(8747):978–979. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nee L. E., Eldridge R., Sunderland T., Thomas C. B., Katz D., Thompson K. E., Weingartner H., Weiss H., Julian C., Cohen R. Dementia of the Alzheimer type: clinical and family study of 22 twin pairs. Neurology. 1987 Mar;37(3):359–363. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Bebout J. L., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Yamaoka L. H., Hung W. Y., Alberts M. J., Walker A. P., Bartlett R. J., Haynes C. A., Welsh K. A. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1034–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer E. A short portable mental status questionnaire for the assessment of organic brain deficit in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975 Oct;23(10):433–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1975.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Pettigrew K. D., Schapiro M. B. Discordance and concordance of dementia of the Alzheimer type (DAT) in monozygotic twins indicate heritable and sporadic forms of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1991 Oct;41(10):1549–1553. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.10.1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley R. M., Frith C. D., Crow T. J., Conneally P. M. Anticipation in Huntington's disease is inherited through the male line but may originate in the female. J Med Genet. 1988 Sep;25(9):589–595. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.9.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg B. S., Kokmen E., Okazaki H. Alzheimer's disease and other dementing illnesses in a defined United States population: incidence rates and clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):724–729. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman J. M., Breitner J. C., Mohs R. C., Davis K. L. Reliability of the family history method in genetic studies of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Am J Psychiatry. 1986 Oct;143(10):1279–1282. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.10.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Myers R. H., Haines J. L., Farrer L. A., Tanzi R. E., Abe K., James M. F., Conneally P. M., Polinsky R. J., Gusella J. F. Familial Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P., Haines J., Rogaev E., Mortilla M., Vaula G., Pericak-Vance M., Foncin J. F., Montesi M., Bruni A., Sorbi S. Genetic evidence for a novel familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):330–334. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Backhovens H., Cruts M., De Winter G., Bruyland M., Cras P., Martin J. J. Mapping of a gene predisposing to early-onset Alzheimer's disease to chromosome 14q24.3. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):335–339. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Hendriks L., Cruts M., Hardy J. A., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. Amyloid precursor protein gene mutation in early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1991 Apr 20;337(8747):978–978. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91611-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Hofman A. Risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: the EURODEM collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. Neuroepidemiology. 1992;11 (Suppl 1):106–113. doi: 10.1159/000111000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


