Abstract
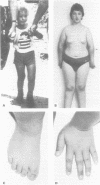
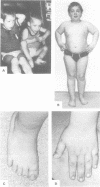
A special subphenotype of the fragile X syndrome is reported which is characterised by extreme obesity with a full, round face, small, broad hands/feet, and regional skin hyperpigmentation. It resembles the Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and might therefore be named 'Prader-Willi-like'. Unlike the PWS, these PW-like fragile X patients lack the neonatal hypotonia with feeding problems during infancy followed by hyperphagia from toddlerhood. We describe five new fragile X patients and present a clinical update of three previously described patients with the PW-like phenotype. In one family, segregation of either the classical Martin-Bell or the PW-like phenotype was observed and in another family there was repeated transmission of the PW-like phenotype. Previously, one of the patients had been misdiagnosed as having classical PWS, based on clinical findings. Molecular studies of the FMR-1 gene showed the typical full mutations as seen in fragile X syndrome males. Molecular analysis of the 15q11-13 region, which is deleted in the majority of classical PWS patients, did not show any detectable abnormalities. In a group of 26 patients with suspected Prader-Willi syndrome but without detectable molecular abnormalities of chromosome 15, one fragile X patient was found. These clinical and molecular findings illustrate the necessity to perform DNA analysis of the FMR-1 gene in mentally retarded patients presenting with a PW phenotype but without the PWS specific cytogenetic/molecular abnormalities of chromosome 15.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Bradley D., Gillespie K., Rees D., Holland A., Thomas N. S. Fragile X mental retardation and the iduronate sulphatase locus: testing Laird's model of fra(X) inheritance. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):299–306. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Haspeslagh M., Dereymaeker A. M., Volcke P., Van den Berghe H. A peculiar subphenotype in the fra(X) syndrome: extreme obesity-short stature-stubby hands and feet-diffuse hyperpigmentation. Further evidence of disturbed hypothalamic function in the fra(X) syndrome? Clin Genet. 1987 Dec;32(6):388–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Blomquist H. K., Holmgren G. Prevalence of the fragile-X syndrome in mentally retarded boys in a Swedish county. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):581–587. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman R., Kouts S., Woodage T., Smith A., Trent R. J. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism of D15S10 in the Prader-Willi chromosome region (PWCR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5449–5449. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5449-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Glatt K., Hersh J. H., Brewster T. D., Graham J. M., Jr, Wurster-Hill D., Wharton R., Latt S. A. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms within proximal 15q and their use in molecular cytogenetics and the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 May;33(1):66–77. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Rousseau F., Heitz D., Kretz C., Devys D., Hanauer A., Boué J., Bertheas M. F., Mandel J. L. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1097–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., Verkerk A. J. The fragile X syndrome: isolation of the FMR-1 gene and characterization of the fragile X mutation. Chromosoma. 1992 Apr;101(7):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00582832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Heitz D., Biancalana V., Blumenfeld S., Kretz C., Boué J., Tommerup N., Van Der Hagen C., DeLozier-Blanchet C., Croquette M. F. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1673–1681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Ashforth P. L. X-linked mental retardation with macro-orchidism and the fragile site at Xq 27 or 28. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 17;48(1):117–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00273283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Fragile sites on human chromosomes: demonstration of their dependence on the type of tissue culture medium. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):265–266. doi: 10.1126/science.877551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Fragile sites on human chromosomes: demonstration of their dependence on the type of tissue culture medium. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):265–266. doi: 10.1126/science.877551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Daniel A., Frost M. X-linked mental retardation, macro-orchidism, and the Xq27 fragile site. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. P., Bundey S. E., Thake A. I., Todd J. Population incidence and segregation ratios in the Martin-Bell syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):573–580. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavodny P. J., Petro M. E., Kumar C. C., Dailey S. H., Lonial H. K., Narula S. K., Leibowitz P. J. The nucleotide sequence of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain two. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1214–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]