Abstract
Deletions of chromosome 22q11 have been seen in association with DiGeorge syndrome (DGS) and velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS). In the present study, we analysed samples from 76 patients referred with a diagnosis of either DGS or VCFS to determine the prevalence of 22q11 deletions in these disorders. Using probes and cosmids from the DiGeorge critical region (DGCR), deletions of 22q11 were detected in 83% of DGS and 68% of VCFS patients by DNA dosage analysis, fluorescence in situ hybridisation, or by both methods. Combined with our previously reported patients, deletions have been detected in 88% of DGS and 76% of VCFS patients. The results of prenatal testing for 22q11 deletions by FISH in two pregnancies are presented. We conclude that FISH is an efficient and direct method for the detection of 22q11 deletions in subjects with features of DGS and VCFS as well as in pregnancies at high risk for a deletion.
Full text
PDF

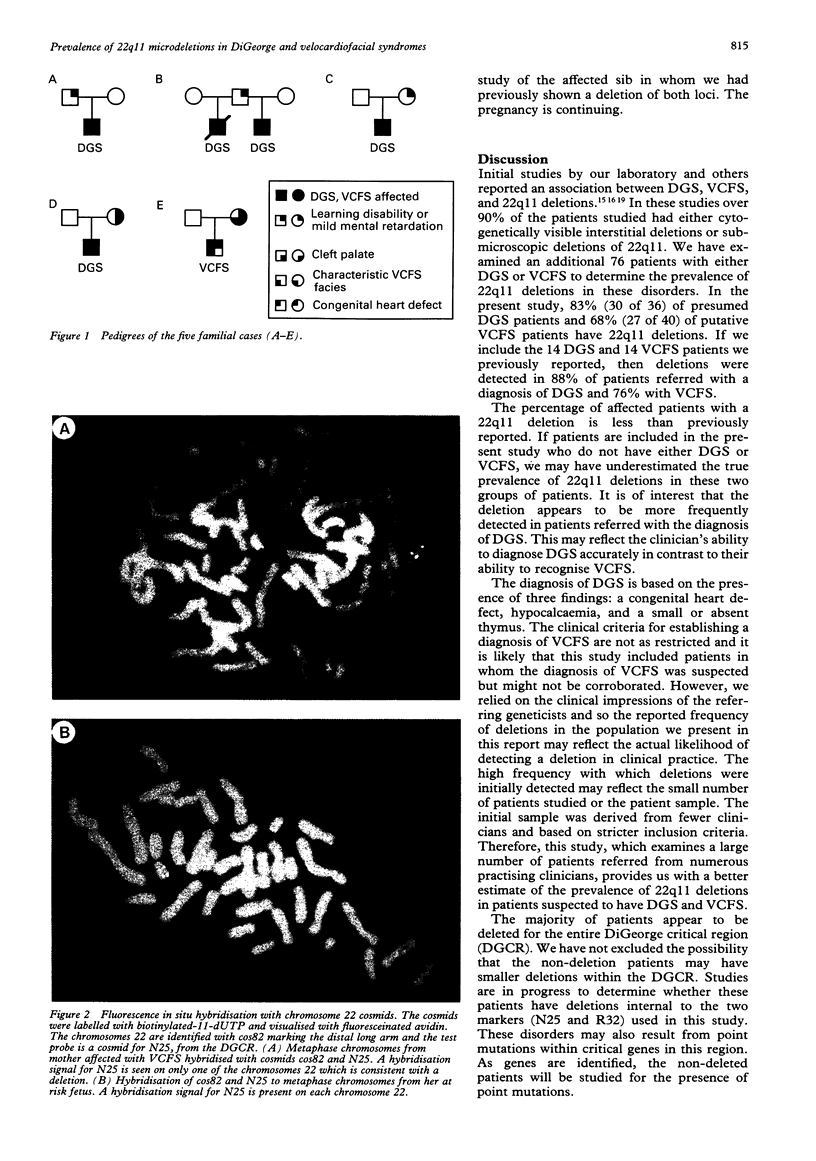


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altherr M. R., Bengtsson U., Elder F. F., Ledbetter D. H., Wasmuth J. J., McDonald M. E., Gusella J. F., Greenberg F. Molecular confirmation of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome with a subtle translocation of chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1235–1242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augusseau S., Jouk S., Jalbert P., Prieur M. DiGeorge syndrome and 22q11 rearrangements. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):206–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00282098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Stier R., Böhm N., Adlung A., Hameister H. Partial monosomy 22pter leads to q11 in a newborn with the clinical features of trisomy 13 syndrome. Ann Genet. 1980;23(4):244–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen P., Pabst H., Berry D., Collins-Nakai R., Hoo J. J. Thymus deficiency in an infant with a chromosome t(18;22)(q12.2;p11.2)pat rearrangement. Clin Genet. 1986 Feb;29(2):174–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey A. H., Kelly D., Halford S., Wadey R., Wilson D., Goodship J., Burn J., Paul T., Sharkey A., Dumanski J. Molecular genetic study of the frequency of monosomy 22q11 in DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):964–970. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S. A genetic etiology for DiGeorge syndrome: consistent deletions and microdeletions of 22q11. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):924–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S. Antenatal diagnosis of DiGeorge syndrome. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1390–1391. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Spinner N. B., Budarf M. L., McDonald-McGinn D. M., Zackai E. H., Goldberg R. B., Shprintzen R. J., Saal H. M., Zonana J., Jones M. C. Deletions and microdeletions of 22q11.2 in velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Sep 15;44(2):261–268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed M. J., Robertson J., Beck J. S., Cater J. I., Bose B., Madlom M. M. Features of di George syndrome in a child with 45,XX,-3,-22,+der(3),t(3;22)(p25;q11). J Med Genet. 1987 Apr;24(4):225–227. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.4.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibison W. J., Budarf M., McDermid H., Greenberg F., Emanuel B. S. Molecular studies of DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):888–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmuntz E., Driscoll D., Budarf M. L., Zackai E. H., McDonald-McGinn D. M., Biegel J. A., Emanuel B. S. Microdeletions of chromosomal region 22q11 in patients with congenital conotruncal cardiac defects. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):807–812. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodship J., Curtis A., Cross I., Brown J., Emslie J., Wolstenholme J., Bhattacharya S., Burn J. A submicroscopic translocation, t(4;10), responsible for recurrent Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome identified by allele loss and fluorescent in situ hybridisation. J Med Genet. 1992 Jul;29(7):451–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Crowder W. E., Paschall V., Colon-Linares J., Lubianski B., Ledbetter D. H. Familial DiGeorge syndrome and associated partial monosomy of chromosome 22. Hum Genet. 1984;65(4):317–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00291554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Elder F. F., Haffner P., Northrup H., Ledbetter D. H. Cytogenetic findings in a prospective series of patients with DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):605–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I., Zackai E. H., Emanuel B. S., Kistenmacher M., Greenberg F., Punnett H. H. The association of the DiGeorge anomalad with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Goldberg R., Wilson D., Lindsay E., Carey A., Goodship J., Burn J., Cross I., Shprintzen R. J., Scambler P. J. Confirmation that the velo-cardio-facial syndrome is associated with haplo-insufficiency of genes at chromosome 22q11. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 1;45(3):308–312. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Ledbetter S. A., Dobyns W. B., Emanuel B. S., Ledbetter D. H. Detection of deletions and cryptic translocations in Miller-Dieker syndrome by in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):707–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Opitz J. M. The DiGeorge anomaly as a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;2:113–127. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco G., Pignata C., Rossi E., Mascellaro O., Cocozza S., Ciccimarra F. DiGeorge anomaly associated with 10p deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1991 May 1;39(2):215–216. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320390220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivnick E. K., Wilroy R. S., Summitt J. B., Tucker B., Herrod H. G., Tharapel A. T. Adjacent-2 disjunction of a maternal t(9;22) leading to duplication 9pter----q22 and deficiency of 22pter----q11.2. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):92–96. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shprintzen R. J., Goldberg R. B., Lewin M. L., Sidoti E. J., Berkman M. D., Argamaso R. V., Young D. A new syndrome involving cleft palate, cardiac anomalies, typical facies, and learning disabilities: velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Cleft Palate J. 1978 Jan;15(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shprintzen R. J., Goldberg R. B., Young D., Wolford L. The velo-cardio-facial syndrome: a clinical and genetic analysis. Pediatrics. 1981 Feb;67(2):167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Shprintzen R. J., Goldberg R. B. Male-to-male transmission of the velo-cardio-facial syndrome: a case report and review of 60 cases. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1985;5(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. I., Cross I. E., Goodship J. A., Brown J., Scambler P. J., Bain H. H., Taylor J. F., Walsh K., Bankier A., Burn J. A prospective cytogenetic study of 36 cases of DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):957–963. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Herva R., Koivisto M., Aula P. A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Fouly M. H., Higgins J. V., Kapur S., Sankey B. J., Matisoff D. N., Costa-Fox M. DiGeorge anomaly in an infant with deletion of chromosome 22 and dup(9p) due to adjacent type II disjunction. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Mar 15;38(4):569–573. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]