Abstract
Backgroud
Paeonia holds considerable value in medicinal, ornamental horticultural, and edible oil industries, but the incomplete state of phylogenetic research in this genus poses a challenge to the effective conservation and development of wild germplasm, and also impedes the practical utilization of existing cultivars. Due to its uniparental inheritance and lack of recombination, the plastome (i.e., plastid genome), which is a valuable molecular marker for phylogenetic analyses, is characterized by an appropriate rate of nucleotide evolution.
Methods
In this study, 10 newly assembled data and available reported data were combined to perform a comparative genomics and phylogenetics analysis of 63 plastomes of 16 Paeonia species, primarily from East Asia, which is the origin and diversity center of Paeonia.
Results
Ranging between 152,153 and 154,405 bp, most plastomes displayed a conserved structure and relatively low nucleotide diversity, except for six plastomes, which showed obvious IR construction or expansion. A total of 111 genes were annotated in the Paeonia plastomes. Four genes (rpl22, rps3, rps19 and ycf1) showed different copy numbers among accessions while five genes (rpl36, petN, psbI, rpl33 and psbJ) showed strong codon usage biases (ENC < 35). Additional selection analysis revealed that no genes were under positive selection during the domestication of tree peony cultivars whereas four core photosynthesis-related genes (petA, psaA, psaB and rbcL) were under positive selection in herbaceous peony cultivars. This discovery might contribute to the wide adaption of these cultivars. Two types of molecular markers (SSR and SNP) were generated from the 63 plastomes. Even though SSR was more diverse than SNP, it had a weaker ability to delimit Paeonia species than SNP. The reconstruction of a phylogenetic backbone of Paeonia in East Asia revealed significant genetic divergence within the P. ostii groups. Evidence also indicated that the majority of P. suffruticosa cultivars had a maternal origin, from P. ostii. The results of this research also suggest that P. delavayi var. lutea, which likely resulted from hybridization with P. ludlowii, should be classified as a lineage within the broader P. delavayi group.
Conclusions
Overall, this study’s research findings suggest that the Paeonia plastome is highly informative for phylogenetic and comparative genomic analyses, and could be useful in future research related to taxonomy, evolution, and domestication.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12870-023-04246-3.
Keywords: Comparative genomics, Cultivar, Paeonia, Phylogenetics, Plastome
Introduction
The genus Paeonia, which is famous for its application in medicinal, ornamental horticultural and edible oil industries, consists of about 33 species that are mainly distributed in temperate regions in Asia, Europe and North America [1]. The history of Paeonia domestication is at least 1500 years old, both in China and in Europe, and even though it was initially introduced from the wild for its medicinal uses, its ornamental value was rapidly discovered [1]. The most widely used active compounds in Paeonia species are paeonol and paeoniflorin, which are extracted from dried roots, and these have been extensively studied given their wide range of pharmacological activities [2]. To honor the economic and cultural value of this genus, traditional Chinese woody peony cultivars were crowned the “King of Flowers”, while Greek herbaceous cultivars were crowned as the “Queen of Herbs” [3]. Moreover, since the seeds of some Paeonia species contain high levels of unsaturated fatty acids, peony seed oil was approved in 2011 as a new food resource by the Chinese Ministry of Health (http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/). For these reasons, the planting area of oil peonies in China has increased steadily and is predicted to reach 5 million ha in the next 5–10 years [4].
The utilization of only a few Paeonia species is well developed but has been ignored in many others, most of them being endangered due to the pressures caused by urbanization and climate change [3]. In addition, the unresolved and complex nature of phylogenetic research in Paeonia prevents the expanded conservation and development of wild germplasm and hinders the utilization of existing cultivars [3]. As the origin and one of the centers of diversity of Paeonia [1], East Asia is vital to understanding the complete evolutionary history of this genus because it encompasses 18 species, 14 of which are endemic, and several thousand traditional herbaceous and woody cultivars [3]. Several studies have attempted to resolve the genetic relationships among species, and between species and cultivars [5–7], but several findings remain controversial. One of them is the P. delavayi complex, which formerly comprised several species (P. lutea Delavay ex Franch, P. potaninii Kom., and P. trollioides Stapf ex Stern), but is now considered a single species according to Hong’s taxonomy [8]. Over the past two decades, numerous studies were conducted on the molecular phylogenetics of P. delavayi [5–7]. Some research supports the monophyletic nature of P. delavayi [6, 9], but other studies have contradicted this claim, suggesting that P. delavayi may be paraphyletic [5, 10]. Each study may have limitations related to the molecular tool used (for instance, findings based on single or limited molecular fragments might not be representative of the entire genome) or sampling technique (e.g., from a single population, thus not representing the whole species), so the phylogenetics of P. delavayi remains inconclusive. To advance an understanding of P. delavayi and related issues in Paeonia, there is a pressing need for more comprehensive sampling and the utilization of a wider range of valid molecular tools in phylogenetic research.
The plastome (i.e., plastid genome) is a widely used and effective molecular marker for plant phylogenetic and evolutionary studies due to several advantageous features, including its abundance, the presence of single-copy genes, the absence of recombination, and a suitable rate of nucleotide evolution [11]. The rbcL gene, which was the first plastid gene to be widely used in plant phylogeny [12], has also been employed as a barcode for species identification [13]. However, due to a high level of conservation among closely related genera, additional plastome genes, such as matK and rpoC, as well as non-coding fragments such as introns or intergenic regions, have been used to improve the accuracy of phylogenetic analyses [13]. Unfortunately, the use of single or multiple fragments still cannot reveal variation among closely related species and this may introduce conflicting findings in phylogenetics [11]. The optimization of sequencing and assembling technologies has enabled phylogenetic analyses based on whole plastomes, demonstrating their powerful ability to resolve complicated phylogenetic relationships at the species or population level [14]. Previous phylogenetic research in Paeonia employed the whole plastome, but the sample size of these studies was limited. For instance, the most comprehensive study to date [10] included only 15 samples representing seven species. Likewise, other studies utilizing whole plastomes have displayed similar limitations due to small sample sizes, leading to conflicting results. Gao et al. [15] found that P. brownii was more closely related to sect. Paeonia than to sect. Moutan, while Dong et al. [16] reported opposite results. Thus, a more comprehensive plastome-based phylogenetic study is needed to provide new insight into the evolutionary history of Paeonia. Furthermore, some research indicated that domestication can lead to variation in plastomes between wild and cultivated materials, including the positive selection of genes and single nucleotide variants [17, 18]. However, comparative studies related to domestication are still lacking in Paeonia.
By comprehensively exploring available reported resources and targeted sampling to supplement new plastomes, we generated a complete dataset of peony plastomes in East Asia, including both natural and cultivated accessions. This dataset was subjected to phylogenetic and comparative genomic analyses to achieve three objectives: (1) to comprehensively identify variation in the structure and content of the Paeonia plastome as a way to evaluate the level of genetic variation in East Asia; (2) to conduct a comparative genomic analysis between cultivars and natural germplasm as a way to explore the domestication history of peony cultivars in East Asia; (3) to perform a phylogenetic analysis to resolve the evolutionary history of Paeonia species in East Asia.
Materials and methods
Plant materials, DNA sequencing and plastome assembly
Four wild accessions were collected from their natural habitats, including three accessions of P. mairei from Qinling Mountains, Daba Mountains and Hengdaun Mountains, which represent its three main regions of distribution [1], and one P. sterniana accession from southeastern Tibet where its distribution is limited [1]. All samples were identified and collected by the first author in 2020 and further checked by Yong Yang (Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences). Voucher specimens were preserved in Beijing Forestry University Museum (BJFC001128-BJFC001130 for P. mairei accessions from Qinling, Daba and Hengduan populations, BJFC001131 for the P. sterniana accession). Young leaves were dried over silica gel and total DNA was extracted from each accession using a modified CTAB method [19]. Genomic DNA was fragmented into 350–500 bp to construct libraries with the TruSeq DNA Sample LT Prep kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, US) and sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq platform.
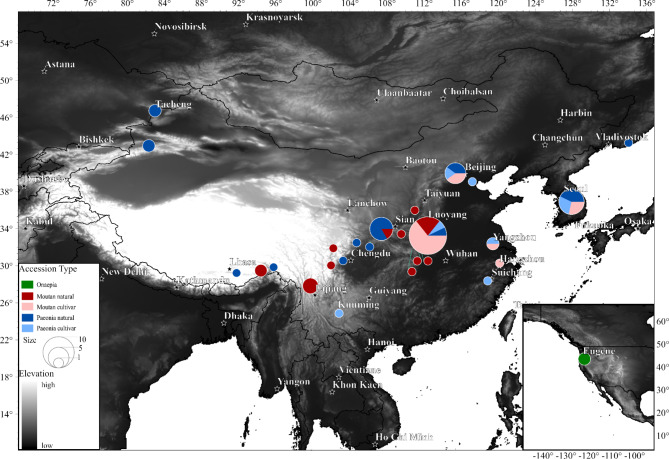
Available datasets were searched in NCBI’s GenBank (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and SRA (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/) databases in April 2022, and a total of 67 reported plastome assemblies and 17 whole genome sequencing (WGS) datasets were collected. Data were filtered out if they were duplicated or missing exact sample information. If both assembly and WGS data were available (seven accessions) for a sample, then only WGS data was retained to ensure consistency in assembly methods. The final dataset covered 46 plastomes and 17 WGS datasets, including four newly sequenced accessions. The data preparation pipeline is illustrated in Supplementary Fig. 1, and the full list of analyzed accessions is presented in Fig 1 and Table 1. The GetOrganelle pipeline [20], which was used to assemble all WGS data, has been shown to outperform other common assemblers in terms of consistency, accuracy, and success rate [20, 21]. In GetOrganelle, the automated pipeline of the de novo assembly was performed from reads using default settings. Finally, a total of 63 Paeonia plastomes, including of 23 cultivars and 40 natural accessions that cover 16 wild Paeonia species in East Asia, were available for downstream analysis (Fig. 1; Table 1). However, P. cathayana, which is now considered to be extinct in the wild [1], was not included in the analysis. Two P. brownii accessions were also included, allowing the genetic relationship between peonies from East Asia and North America to be explored. Hong’s taxonomy [1], which divides all Paeonia species into three sections (sect. Onaepia, Moutan, and Paeonia), was used in this research. Specifically, sect. Onaepia includes two species that are endemic to North America, sect. Moutan includes eight species that are endemic to East Asia, and sect. Paeonia includes 23 species that are widely distributed throughout Eurasia. To compare plastome variation and genetic diversity among the three sections, as well as between cultivars and natural accessions, the 63 accessions were manually clustered into five groups (Table 1): ONAE (N = 2), MOUT_WILD (N = 17), MOUT_CULT (N = 15), PAEO_WILD (N = 21), and PAEO_CULT (N = 8).
Fig. 1.
Geographic distribution and sample size of 63 Paeonia accessions analyzed in this research. The focus was on Paeonia germplasm in East Asia, but also included two accessions from North America to explore the genetic relationship between East Asian and North American peonies. The map was generated by ArcGIS Pro (Esri, Redlands), and elevation was illustrated according Harmonized World Soil Database (https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/harmonized-world-soil-database-v12)
Table 1.
Accessions analyses in the present research
| Group | ID | Species | Section | Infra species | Cultivar | Life type | Sample region | Assembly accession | SRA accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONAE | brownii_1 | P. brownii | onaepia | no | herbaceous | California, USA | JQ952560 | ||
| brownii_2 | P. brownii | onaepia | no | herbaceous | California, USA | MH191385 | |||
| MOUT_WILD | decomposita_1 | P. decomposita | moutan | no | woody | Sichuan, China | MG571273 | ||
| delavayi_1 | P. delavayi | moutan | no | woody | Xizang, China | KY817591 | |||
| delavayi_2 | P. delavayi | moutan | var. lutea | no | woody | Yunnan, China | MK701989* | ||
| delavayi_3 | P. delavayi | moutan | var. potaninii | no | woody | Yunnan, China | MK701991 | ||
| delavayi_4 | P. delavayi | moutan | no | woody | Yunnan, China | MN463100 | |||
| delavayi_5 | P. delavayi | moutan | var. lutea | no | woody | Yunnan, China | MT210546 | ||
| jishanensis_1 | P. jishanensis | moutan | no | woody | Henan, China | MT210545 | |||
| jishanensis_2 | P. jishanensis | moutan | no | woody | Shaanxi, China | MG991935 | |||
| jishanensis_3 | P. jishanensis | moutan | no | woody | Shanxi, China | MK701988 | |||
| ludlowii_1 | P. ludlowii | moutan | no | woody | Xizang, China | KY817592 | |||
| ostii_1 | P. ostii | moutan | no | woody | Henan, China | MK701990 | |||
| ostii_2 | P. ostii | moutan | no | woody | Henan, China | OM179763 | SRR19122852 | ||
| ostii_3 | P. ostii | moutan | no | woody | Henan, China | OM291541 | SRR19122851 | ||
| qiui_1 | P. qiui | moutan | no | woody | Hubei, China | MK701992 | |||
| qiui_2 | P. qiui | moutan | no | woody | Hubei, China | MT210544 | |||
| rockii_1 | P. rockii | moutan | subsp. rockii | no | woody | Shaanxi, China | MF488719* | ||
| rockii_2 | P. rockii | moutan | subsp. avata | no | woody | Shaanxi, China | MW192444 | ||
| MOUT_CULT | ostii_4 | P. ostii | moutan | cv. FengDan | yes | woody | Henan, China | MG572457 | |
| ostii_5 | P. ostii | moutan | cv. FengDan | yes | woody | Henan, China | MG585274 | ||
| ostii_6 | P. ostii | moutan | cv. FengDan | yes | woody | Henan, China | OP324591** | SRR6476733 | |
| ostii_7 | P. ostii | moutan | cv. FengDan | yes | woody | Jiangsu, China | OP324592** | SRR7614768 | |
| rockii_3 | P. rockii | moutan | cv. FenEJiao | yes | woody | Henan, China | MK701993 | ||
| suffruticosa_1 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | yes | woody | Beijing, China | JQ952559 | |||
| suffruticosa_2 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | yes | woody | Beijing, China | MH191384 | |||
| suffruticosa_3 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | cv. DouLv | yes | woody | Henan, China | MK701994 | ||
| suffruticosa_4 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | cv. LuoYangHong | yes | woody | Henan, China | MK701995 | ||
| suffruticosa_5 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | cv. ShouAnHong | yes | woody | Henan, China | MK701996 | ||
| suffruticosa_6 | P. × lemoinei | moutan | cv. HighNoon | yes | woody | Henan, China | MK701997 | ||
| suffruticosa_7 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | yes | woody | Incheon, South Korea | MH793271 | |||
| suffruticosa_8 | P. × lemoinei | moutan | cv. HwangMoran | yes | woody | Incheon, South Korea | MK860970 | ||
| suffruticosa_9 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | cv. LianHe | yes | woody | Henan, China | OM179764 | SRR19122853 | |
| suffruticosa_10 | P. × suffruticosa | moutan | cv. YuLuoChun | yes | woody | Zhejiang, China | OK662586* | ||
| PAEO_WILD | anomala_1 | P. anomala | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xinjiang, China | MT210549 | ||
| emodi_1 | P. emodi | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xizang, China | MT210548 | |||
| intermedia_1 | P. intermedia | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xinjiang, China | MT210547 | |||
| intermedia_2 | P. intermedia | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xinjiang, China | OP324584** | ERR3525038 | ||
| intermedia_3 | P. intermedia | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xinjiang, China | OP324585** | ERR3525039 | ||
| lactiflora_1 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Primorskiy Kray, Russian | MG897127 | |||
| lactiflora_2 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | MN061945* | |||
| mairei_1 | P. mairei | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | OP324589** | |||
| mairei_2 | P. mairei | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | OP324590** | |||
| mairei_3 | P. mairei | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Sichuan, China | MN508366* | |||
| mairei_4 | P. mairei | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Sichuan, China | OP324588** | |||
| obovata_1 | P. obovata | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Beijing, China | JQ952561 | |||
| obovata_2 | P. obovata | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Beijing, China | MH191383 | |||
| obovata_3 | P. obovata | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea | KJ206533 | |||
| obovata_4 | P. obovata | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea | MT821944* | |||
| obovata_5 | P. obovata | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea | MT821946 | SRR13840229 | ||
| obovata_6 | P. obovata | paeonia | subsp.willmottiae | no | herbaceous | Henan, China | MN149613 | ||
| obovata_7 | P. obovata | paeonia | subsp.willmottiae | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | MN840851 | ||
| sterniana_1 | P. sterniana | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Xizang, China | OP324593** | |||
| veitchii_1 | P. veitchii | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | KT894821 | |||
| veitchii_2 | P. veitchii | paeonia | no | herbaceous | Shaanxi, China | MW762596 | SRR17202104 | ||
| PAEO_CULT | lactiflora_3 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | var.trichocarpa | no | herbaceous | Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea | MT821945 | SRR13840230 |
| lactiflora_4 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Beijing, China | OP324586** | SRR15412863 | ||
| lactiflora_5 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | cv. LvHe | yes | herbaceous | Henan, China | MN149612 | ||
| lactiflora_6 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Incheon, South Korea | MK860971 | |||
| lactiflora_7 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Jiangsu, China | OP324587** | SRR7614723 | ||
| lactiflora_8 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Tianjin, China | MW762595 | SRR17202105 | ||
| lactiflora_9 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Yunnan, China | KF753636 | |||
| lactiflora_10 | P. lactiflora | paeonia | yes | herbaceous | Zhejiang, China | MN868412 |
*, annotation reference
**, newly reported assembly
Plastome annotation, characterization, and comparison
A total of six reported and annotated Paeonia plastomes (Table 1) were downloaded from NCBI and manually checked for the use of annotated references in this work. PGA.pl [22] was then applied for the annotation of elements (including inverted repeat boundaries, genes, CDS, tRNA and rRNA) on all plastomes. Repeat sequences were annotated using three methods. Tandem repeats in each plastome were identified using the Tandem Repeats Finder (TRF) [23] with default parameters. Microsatellites, also known as simple sequence repeats (SSR), were predicted using MISA [24] with repeat thresholds of ten for mononucleotides, five for di- and trinucleotide SRRs, and four for tetra-, penta- and hexanucleotides. Interspersed repetitive sequences (forward, reverse, complement, or palindromic) were identified using REPuter [25], with a maximum hamming distance set to three and the minimum repeat size set to 30 bp. SeqKit [26] was used to summarize the statistics of characteristics pertaining to all plastomes, including sequence length and GC content. All plastome features were compared among the five groups to identify variations in patterns. In this case, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare mean values, and coefficients of variation (CVs) were calculated in R version 4.1.3.
The codon usage bias of each coding sequence (CDS) was assessed using codonW [27]. Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) was used to determine the codon preference pattern. The effective number of codons (ENC) was used to evaluate the usage bias of a specific sequence. ENC ranges from 20 (indicating absolute bias, where each amino acid has only one valid codon) to 61 (indicating no bias, where all codons are used evenly) [28]. HyPhy software [29] was used to identify instances of diversifying and episodic selections in Paeonia. The fixed-effects likelihood (FEL) [30] and Fast Unconstrained Bayesian AppRoximation (FUBAR) [31] models were applied to infer the rates of non-synonymous (dN) and synonymous (dS) substitutions to identify instances of diversifying selection among all accessions. The MEME model [32] was used to identify episodic selection in two cultivar groups (MOUT_CULT and PAEO_CULT) using a mixed-effects maximum likelihood approach.
Detection of genetic variation and diversity analysis
Plastome arrangement and structure variations were identified by multiple sequence alignment using Mauve [33] with default parameters. Since no plastome rearrangement was detected by Mauve, the 63 plastomes were further aligned in MAFFT [34] using the local pair mode. Sites with less than six accessions were trimmed by trimAl [35] to generate a high-quality sequence matrix. The nucleotide diversity index (Pi) along plastomes was calculated by a sliding window with a 1000-bp width and a 500-bp step using pegas [36] based on the sequence matrix. To understand the distribution pattern and diversity of nucleotides along the plastome, a consensus plastome was generated by the consensus function in the seqinr package [37] and annotated by PGA.pl [22].
Two types of molecular markers (SSR and single nucleotide polymorphorphisms (SNPs)) were also used to analyze genetic diversity and delimit species. To identify shared SSRs from plastome sequences, a 30-bp sequence upstream of each SSR, as detected by MISA.pl [24], was extracted and checked through a blast algorithm. SNPs were detected in the aligned plastome matrix using adegenet [38]. To control bias caused by sample size during the analysis of genetic diversity, eight accessions were randomly resampled from each group (ONAE was excluded as it only has two accessions). The genetic diversity based on each marker method was measured using Poppr [39]. A series of indexes was calculated, including eMLG (the expected number of multilocus genotypes in the lowest common sample size) to measure genotype abundance, three indexes to measure genotype diversity (H, Shannon-Weiner index; G, Stoddard and Taylor’s index; λ, Simpson’s index), and an index to measure genotype evenness (E5). Discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC) [40] was used to identify genetic structures and potential key markers for distinguishing the five groups for each marker method in adegenet [38]. Dendrograms with bootstrap support were generated in Poppr for both SSR and SNP markers to assess their effectiveness in delimiting species. Nei’s distance method was applied for SSR and Hamming distance was used for SNP.
Phylogeny based on whole plastomes
Given that Paeonia is distant from other lineages, having diverged from the nearest lineage in Saxifragales about 100 Ma ago [41], it was difficult to select a suitable outgroup for the Paeonia phylogeny. As an alternative, the direction of evolution was inferred using a Bayesian evolutionary analysis with BEAST [42]. BEAST can generate time-trees based on prior distributions of the tree (e.g. coalescent and birth–death families) [43]. The full plastome was divided into two partitions, coding and non-coding, to account for the different evolutionary pressures each experiences [17], and each partition was modeled separately using different parameters. To generate the coding partition, the protein-coding CDS for all accessions, which had been annotated by PGA.pl, were extracted by bedtools [44]. The resulting CDS sequences were then aligned and trimmed based on codons using prank [45] and trimAl [35]. To generate the non-coding partition, all coding sequences (including CDS, tRNA and rRNA) and repeat sequences (including tandem and interspersed) were masked from plastomes by bedtools, and the resulting masked plastomes were aligned by MAFFT [34] and trimmed by trimAl [35]. For each data partition (coding and non-coding), the best site model was selected using ModelFinder [46], which implements the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) to identify the best-fit substitution model. The best clock model and tree prior were identified by path sampling [47], which is a Bayesian method for model selection and averaging that estimates the marginal likelihood of competing models. Zhou et al. [7] proposed an age estimate for the crown group of Paeonia at 28 Ma based on fossil calibration points. Therefore, in the current study, the age of the MRCA was constrained to a normal distribution with a mean of 28 Ma, and the lower and upper limits were set at 25 Ma and 32 Ma, respectively. A Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) chain of 100 million generations was run, and samples were assessed every 2000th generation. The results were verified using Tracer [48] to ensure that the effective sample size (ESS) of each parameter was greater than 200. After discarding the first 20% of trees as burn-in using TreeAnnotator (in BEAST), a maximum clade credibility (MCC) tree was generated. The final phylogenetic tree with divergence time bars was plotted with ggtree [49]. A dataset of benthic δ 18O content [50], which is related to global paleoclimate, was downloaded and used to compare it with the rate of divergence branches in Paeonia. To examine the genetic structure of clusters generated by Bayesian phylogeny, a principle component analysis (PCA) based on SNPs generated in Sect. 1.3 was performed in adegenet.
Results
Features of the Paeonia plastome
Structure and size
In this research, a total of 17 complete plastomes were assembled and 10 newly reported plastomes were submitted to the NCBI database. The Paeonia plastome exhibits a quadripartite structure, consisting of two identical copies of the inverted repeat (IR) region separated by a large single copy (LSC) region and a small single copy (SSC) region. The plastome sequence length of the 63 accessions ranged from 152,153 to 154,405 bp, with an average length of 152,741 bp (Table 2). The length of the four regions among the five groups was analyzed by ANOVA. The results indicate that there was significant variation in SSC length among the groups (p < 0.01). The ONAE group had the shortest SSC (16,679 bp) while the Paeonia groups (16,969 bp in PAEO_CULT, 17,019 bp in PAEO_WILD) exhibited a shorter SSC region than Moutan groups (17,051 bp in MOUT_CULT, 17,045 bp in MOUT_WILD). The CV for the length of the IR region was higher (0.99%) than that of the LSC (0.33%) and SSC (0.41%) regions, and Moutan accessions showed a higher sequence length CV than Paeonia and Onaepia accessions (Table 2). The plastome GC content for all accessions ranged from 38.32 to 38.55%, with an average of 38.42% (Table 2). The IR region had a higher GC content (43.09%) than the LSC (36.71%) and SSC (32.70%) regions. There was significant variation in GC content among the groups (p < 0.01), regardless of whether this referred to the whole plastome or the four regions. Onaepia accessions exhibited the highest GC content (38.55%) while Moutan accessions showed the lowest value (38.36%).
Table 2.
Sequence length and GC content of different Paeonia groups
| Group | Mean | CV | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastome | LSC | SSC | IR | Plastome | LSC | SSC | IR | |||
| Sequence length | Whole | 152,741 ± 301 | 84,402 ± 277 | 17,016 ± 69 | 25,662 ± 247 | 0.20% | 0.33% | 0.41% | 0.99% | |
| ONAE | 152,227 ± 1 | 84,261 ± 0 | 16,679 ± 0 | 25,644 ± 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| MOUT_WILD | 152,849 ± 441 | 84,330 ± 392 | 17,046 ± 22 | 25,736 ± 373 | 0.29% | 0.47% | 0.13% | 1.46% | ||
| MOUT_CULT | 152,688 ± 290 | 84,530 ± 367 | 17,050 ± 12 | 25,554 ± 283 | 0.19% | 0.44% | 0.07% | 1.14% | ||
| PAEO_WILD | 152,709 ± 60 | 84,383 ± 46 | 17,014 ± 20 | 25,656 ± 11 | 0.04% | 0.06% | 0.12% | 0.04% | ||
| PAEO_CULT | 152,822 ± 236 | 84,400 ± 31 | 16,978 ± 23 | 25,722 ± 132 | 0.15% | 0.04% | 0.13% | 0.51% | ||
| GC content | Whole | 38.4 ± 0.05% | 36.7 ± 0.05% | 32.7 ± 0.09% | 43.09 ± 0.07% | 0.13% | 0.13% | 0.28% | 0.17% | |
| ONAE | 38.55 ± 0% | 36.83 ± 0% | 33.02 ± 0% | 43.16 ± 0% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| MOUT_WILD | 38.37 ± 0.04% | 36.68 ± 0.04% | 32.64 ± 0.07% | 43.05 ± 0.11% | 0.10% | 0.12% | 0.22% | 0.26% | ||
| MOUT_CULT | 38.36 ± 0.04% | 36.66 ± 0.03% | 32.65 ± 0.06% | 43.09 ± 0.03% | 0.09% | 0.10% | 0.18% | 0.07% | ||
| PAEO_WILD | 38.43 ± 0.01% | 36.72 ± 0.01% | 32.75 ± 0.04% | 43.13 ± 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.03% | 0.11% | 0.05% | ||
| PAEO_CULT | 38.43 ± 0.01% | 36.74 ± 0.01% | 32.72 ± 0.01% | 43.1 ± 0.05% | 0.02% | 0.03% | 0.04% | 0.11% | ||
CV, coefficient of variation; IR, inverted repeat sequence; LSC, large single-copy sequence; SSC, small single-copy sequence
IR expansion and contraction
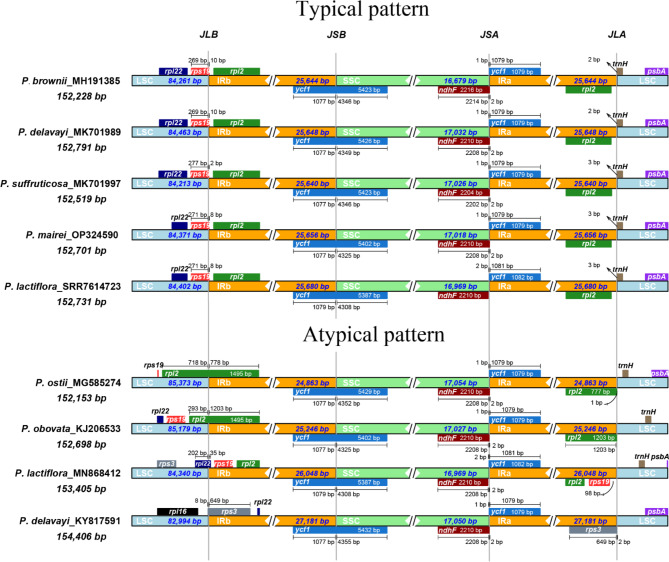
As indicated by the results above, the IR region exhibited higher variation in sequence length than the LSS and SSC regions. This variation may be attributed to the process of IR expansion and contraction, which often occurs due to changes in IR borders. The results show that the borders of two IRs (IRa and IRb) in Paeonia plastomes are conserved in most of the analyzed accessions (57/63). The typical junction pattern for most accessions was plotted in Fig. 2 (the complete version of all accessions can be observed in Supplementary Fig. 2), in which all of the LSC/IRb junctions fell into rps19, although the specific loci varied slightly. The IRb/SSC, SSC/IRa and IRa/LSC junctions fell into ycf1, ndhF and trnH, respectively, with slightly modified loci. While most accessions were conserved, significant expansion and contraction were observed in six accessions. Four accessions (P. ostii MG585274 and MG572457, P. rockii MF488719, and P. obovata KJ206533) showed IR contraction. In those cases, their LSC/IRb junctions fell into rpl12 rather than rps19. In two accessions (P. lactiflora MN868412 and P. delavayi KY817591) that showed IR expansion, their IRs covered the entire rpl19 gene.
Fig. 2.
Distribution and structure of the inverted repeat region (IR) in Paeonia plastomes. Most plastomes have a conserved IR structure (typical pattern). Five accessions were selected to represent the five groups. Atypical patterns, i.e., IR expansion and contraction, were detected in several accessions
Repeat sequences
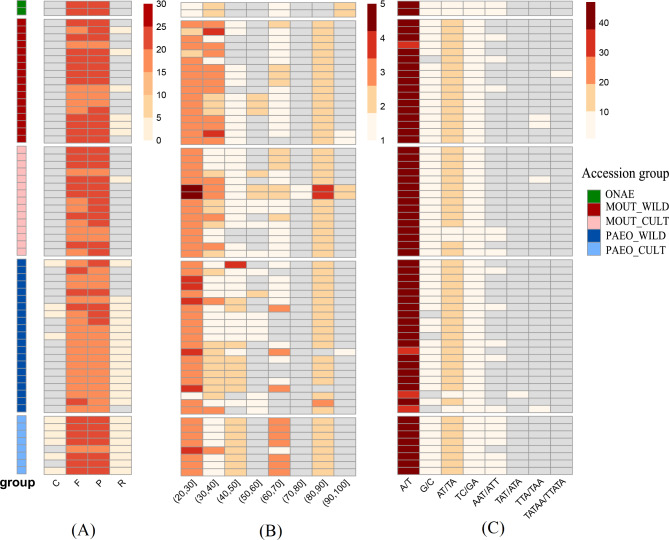
REPuter detected forward (F) and palindromic (P) repeats in all accessions whereas inverted (R) and complementary (C) repeats were mainly detected in sect. Paeonia. Four types of interspersed repeats were most abundant in PAEO_CULT (Fig. 3A). Long tandem repeat sequences of varying length (20–100 bp) were identified by TRF, and there were two regions of abundance (20–30 and 80–90) (Fig. 3B). SSR detection results revealed the existence of eight motifs (including two monomeric, two dimeric, three trimeric and one pentameric repeats) in Paeonia, with monomeric repeats being the most abundant (Fig. 3C). Each accession contained 46–64 SSRs, 32 of which were shared among at least half of all accessions.
Fig. 3.
Abundance of repeat sequences annotated in Paeonia plastomes. (A) Interspersed repeat sequences (C, complement; F, forward; P, palindromic; R, reverse); (B) Long tandem repeat sequences; length range: 20 to 100; two regions of abundance (20–30, 80–90); (C) Short tandem repeat sequences, seven motifs were detected
Gene annotation and detection of features
Gene annotation
A total of 111 genes were annotated in the Paeonia plastomes, including 78 protein-encoding genes, 29 tRNA-encoding genes and four rRNA-encoding genes (Table 3; Fig. 4). Based on their functions, all genes were classified into three groups: those related to plastome replication, those involved in photosynthesis, and those with other functions. Duplicate copies of genes were found in the Paeonia plastomes, with 20 genes having two copies in at least one accession, while 89 genes had only one copy. Most genes (107/111, including 74 protein-encoding genes, four rRNA-encoding genes and 29 tRNA-encoding genes) were consistent among all accessions, while four genes (rpl22, rps3, rps19 and ycf1) showed different copy numbers among accessions (Supplementary Table 1).
Table 3.
Genes annotated in Paeonia plastomes
| Category | Gene functions | Names of genes |
|---|---|---|
| Self-replication | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | rpoA, B, C1, C2 |
| Self-replication | Large subunit of ribosomal proteins | rpl2, 14, 16, 20, 22, 23, 33, 36 |
| Self-replication | rRNA genes | rrn16, rrn23, rrn4.5, rrn5 |
| Self-replication | Small subunit of ribosomal proteins | rps11, rps12, rps14, rps15, rps16, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7, rps8 |
| Self-replication | tRNA genes | trnA-UGC, trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU, trnI-GAU, trnK-UUU, trnL-CAA, trnL-UAA, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU, trnP-GGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG, trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC, trnV-UAC, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA |
| Photosynthesis | ATP synthase | atpA, B, E, F, H, I |
| Photosynthesis | Cytochrome b6/f complex | petA, B, D, G, L, N |
| Photosynthesis | NADH oxidoreductase | ndhA, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K |
| Photosynthesis | photosystem assembly factor | pafI, pafII |
| Photosynthesis | Photosystem I | psaA, B, C, I, J |
| Photosynthesis | Photosystem II | psbA, B, C, D, E, F, H, I, J, K, L, M, T, Z |
| Photosynthesis | Rubisco | rbcL |
| Other genes | c-Type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA |
| Other genes | Conserved open reading frames | ycf1, 2 |
| Other genes | Envelope membrane protein | cemA |
| Other genes | Maturase | matK |
| Other genes | Protease | clpP1 |
| Other genes | Subunit acetyl-CoA-carboxylase | accD |
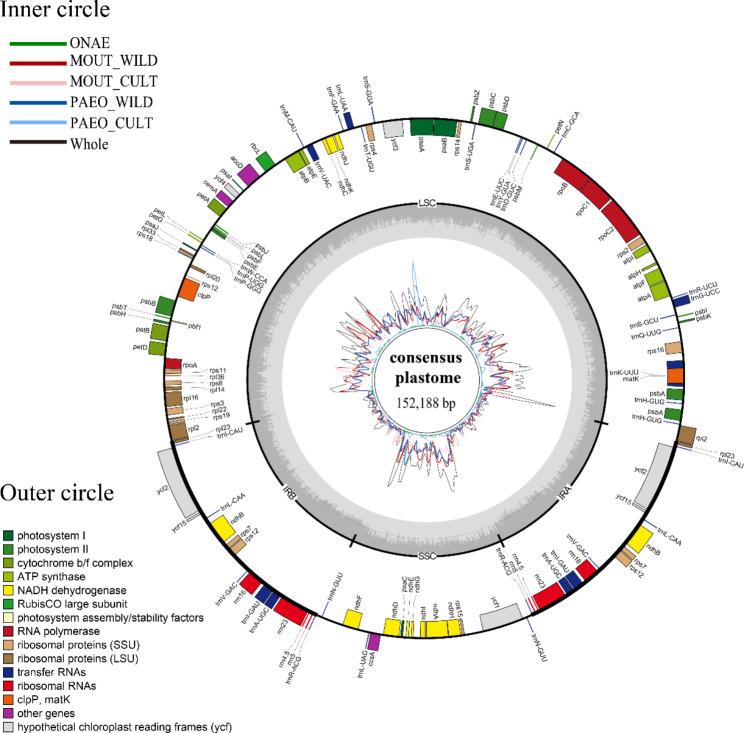
Fig. 4.
Distribution of annotated genes on the consensus plastome and nucleotide diversity along the plastome. A consensus plastome was generated by aligning and trimming 63 plastomes. The outer circle displays a distribution pattern of annotated genes on plastome genes, the middle circle illustrates the GC content along consensus plastomes, and the inner circle illustrates nucleotide diversity (Pi) along the consensus plastome
Codon usage bias
Codon usage bias was analyzed in all 78 protein-coding CDSs. The average RSCU values are listed in Supplementary Table 2. Thirty-one codons had a mean RSCU value greater than 1, 29 of which included A or U at the third position, indicating a preference for A and U bases in Paeonia codons. Based on the RSCU value, UUA, GCU and AGA were identified as the optimal codons in Paeonia plastomes. The mean ENC value of 78 CDS ranged from 25.29 (rpl36) to 61 (rps18 and rpl22) (Supplementary Fig. 3), suggesting a high variance of codon usage bias. Five genes (rpl36, petN, psbI, rpl33 and psbJ) had a mean ENC less than 35, indicating strong codon usage bias, while most genes (56/79) had a mean value greater than 45 and exhibited weak codon usage bias.
Selection analysis
Based on the results of the FUBAR and FEL models in HyPhy, most genes (52/78) (Supplementary Table 3) had sites under diversifying positive selection in at least one model. Out of 17 genes identified in both models, three were self-replication genes (out of 24), nine were photosynthesis genes (out of 46), and five were genes with other functions (out of 8). Episodic positive diversifying selection in two cultivar groups (MOUT_CULT and PAEO_CULT) was analyzed using the MEME model. In the MOUT_CULT group, no genes (p < 0.05) were identified while in the PAEO_CULT group, seven genes (one gene with another function (ycf1), four photosynthesis-related genes (petA, psaA, psaB and rbcL) and two self-replication genes (rpoB, rps14)) were found to have one-six significant loci (p < 0.05) under positive selection (Supplementary Table 4).
Genetic diversity and phylogeny
Nucleotide diversity and promising DNA barcode regions
In the 63 analyzed plastomes, no genome rearrangement was detected by Mauve and the entire plastome was identified as a locally collinear block (Supplementary Fig. 4). Additionally, a sequence matrix of 152,188 bases was generated for the 63 accessions through alignment and trimmed by MAFFT and TrimAl, and a consensus plastome with a length of 152,188 bases was generated by seqinr. The nucleotide diversity (Pi value) of the five groups and all accessions’ datasets along the plastome was calculated based on the sequence matrix (Fig. 4), which demonstrates lower nucleotide diversity in the IR regions than the LSC/SSC regions. The Pi value calculated for the entire plastome indicates that natural accessions have higher nucleotide diversity (0.0020 for MOUT_WILD and 0.0018 for PAEO_WILD) than cultivars, which exhibited lower nucleotide diversity (0.0015 for MOUT_CULT and 0.0001 for PAEO_CULT). Nucleotide regions with high diversity were identified by comparing Pi values using a sliding window approach. The top three regions, including two intergenic regions (ycf1-trnI_CAU with a Pi value of 0.015 and rrn23-trnR_CAU with a Pi value of 0.011) and one genic region (within ndhH, 0.012) exhibited the highest diversity. Other regions that are promising for their development as DNA barcodes are listed in Supplementary Tables 5, notably the intergenic region between ycf3 and psbA which demonstrated high nucleotide diversity in PAEO_CULT.
Genetic diversity and structure based on molecular markers
From the 63 plastomes, a total of 32 SSR markers and 4476 SNPs were identified. These were then used to investigate the accessions’ genetic structure. Analysis of both marker types revealed similar patterns of genetic diversity among the 63 accessions (Table 4). The expected number of multilocus genotypes (eMLG, a measure of genotype abundance) was much lower in PAEO_CULT than in the remaining three groups, which exhibited similar levels of eMLG. Similarly, the genotype diversity index (including H, G and λ) and evenness index (E5) showed similar patterns among the four groups (Table 4).
Table 4.
Genotype diversity of two types molecular markers on five groups of the Paeonia plastome
| Marker | Group | N | eMLG | H | G | λ | E5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR | MOUT_CULT | 8 | 6 | 1.73 | 5.33 | 0.81 | 0.93 |
| MOUT_WILD | 8 | 8 | 2.08 | 8.00 | 0.88 | 1 | |
| PAEO_CULT | 8 | 5 | 1.39 | 3.20 | 0.69 | 0.73 | |
| PAEO_WILD | 8 | 8 | 2.08 | 8.00 | 0.88 | 1 | |
| Whole | 32 | 26 | 3.13 | 18.29 | 0.95 | 0.79 | |
| SNP | MOUT_CULT | 8 | 7 | 1.91 | 6.40 | 0.84 | 0.94 |
| MOUT_WILD | 8 | 8 | 2.08 | 8.00 | 0.88 | 1 | |
| PAEO_CULT | 8 | 4 | 1.07 | 2.29 | 0.56 | 0.67 | |
| PAEO_WILD | 8 | 8 | 2.08 | 8.00 | 0.88 | 1 | |
| Whole | 32 | 9 | 3.09 | 16.00 | 0.94 | 0.72 |
E5, genotype evenness; eMLG, the expected number of multilocus genotypes at the lowest common sample size; H, Shannon-Weiner index; G, Stoddard and Taylor’s index; λ, Simpson’s index; N, sample size
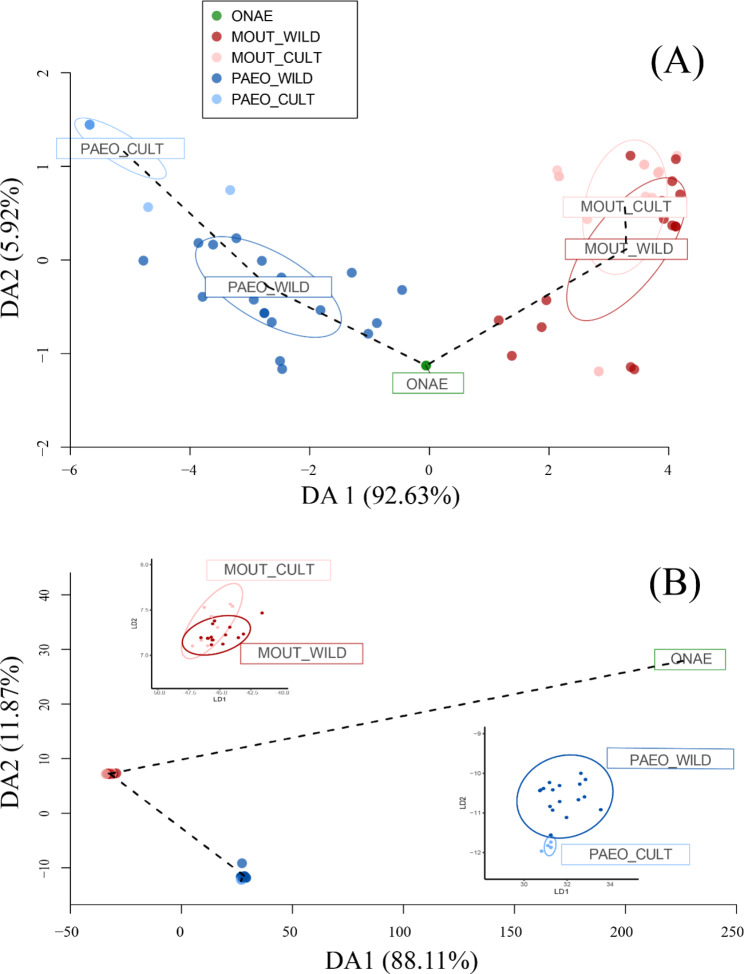
The DAPC results showed that both marker types effectively distinguished the three sections, although SNPs revealed longer distances between sect. Onaepia and the other two sections than SSRs (Fig. 5). The minimum spanning tree based on SSRs indicated that sect. Onaepia was located between the other two sections, while SNPs revealed that sect. Onaepia had a shorter distance to sect. Moutan than to sect. Paeonia. Both marker methods effectively distinguished PAEO_CULT from PAEO_WILD, but could not differentiate MOUT_CULT from MOUT_WILD. A phylogenetic analysis was used to assess the ability of both markers to delimit species. The results showed that SSRs only effectively delimited five species (P. brownii, P. obovata, P. mairei, P. jishanensis and P. qiui) whereas SNPs effectively delimited all species except for three (P. veitchii, P. delavayi and P. rockii) (Supplementary Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
The distribution of five groups on the first 2 discriminant axes of DAPC. (A) results based on SSR; (B) results based on SNP. Both markers (SSR and SNP) could effectively distinguish the three sections, while SNP revealed much longer distances between sect. Onaepia with the two other sections than SSR
Phylogenetics of Paeonia based on plastomes
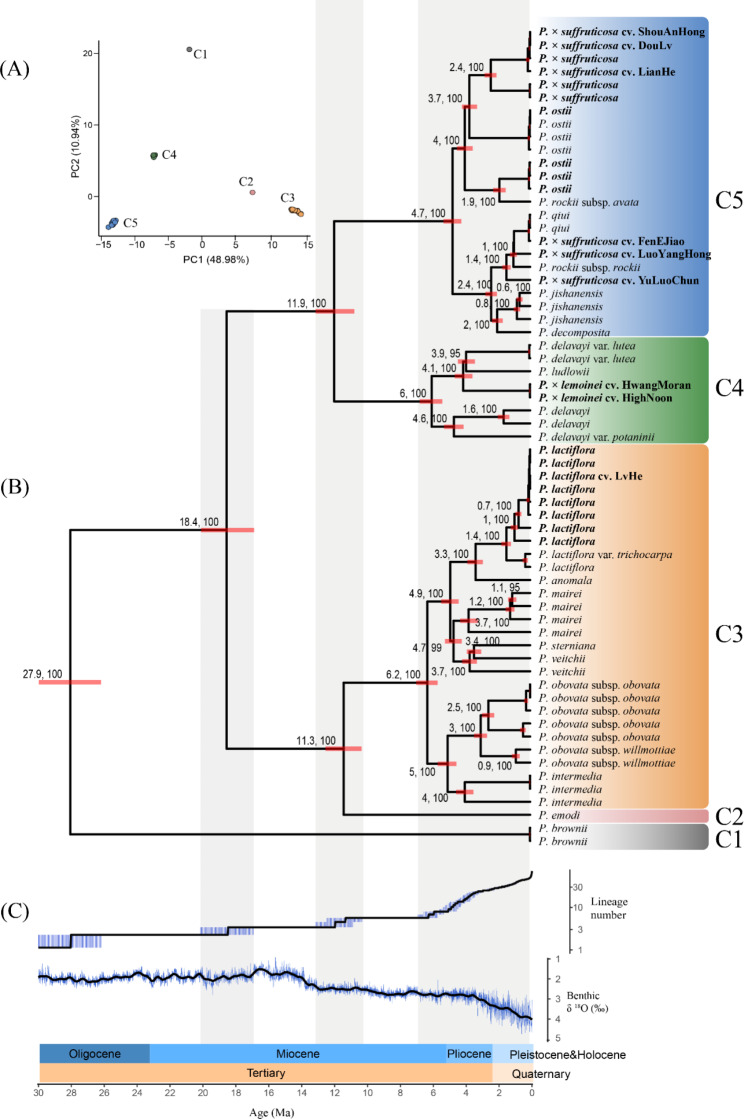
PCA results based on SNPs (Fig. 6A) revealed five distinct clusters of all accessions, corresponding to the five branches revealed in the MCC tree (Fig. 6B). These clustering results provide support for the current taxonomic treatment of the three sections in Paeonia. The MCC tree showed that sect. Onaepia diverged from the two other Sects. 26–30 million years ago (Ma), followed by three periods of speciation. The first divergence occurred between sect. Paeonia and Moutan 17–20 Ma. The second period, which took place 11–13 Ma, resulted in the divergence of both sections into two branches. One of the branches is now distributed in pan-Himalaya while the other is widely distributed throughout East Asia. This period was followed by a sharp temperature drift, as shown in Fig. 6C. The last period, which spanned from 6.5 Ma to the present, resulted in the majority of the currently known species. Remarkably, this period coincided with a continuous decrease in global temperatures.
Fig. 6.
Results of Bayesian evolutionary analysis. (A) Distribution of 63 plastomes on the first 2 component based on 4476 SNPs; (B) maximum clade credibility tree with divergence time of 63 accessions; (C) lineage size and global temperature (inferred by the content of benthic δ 18O) changes along ages. Bayesian phylogeny revealed that P. brownii firstly diverged from other accessions, and that all accessions could be divided into five branches (C1-C5), corresponding to the five clusters of PCA results based on SNPs
Discussion
Plastome evolution in Paeonia
Since the sequencing of the first plastome in the 1980s [51], thousands of plastomes from land plant species have been reported over the past three decades, revealing abundant diversity in dynamic structure and content [11]. These plastomes have made a significant contribution to our understanding of both interspecies and intraspecies evolutionary history. With 10 newly reported Paeonia plastome assemblies, a total of 63 accessions were subjected to comprehensive analyses in this research to explore the plastome evolutionary pattern in Paeonia. Despite variations mainly attributed to IR variation and nucleotide diversity, the plastome structure was found to be conserved in Paeonia, with no rearrangements detected among all accessions, as is typically observed in most angiosperm genera [52],
IR contraction or expansion can result in gene loss or gain, and can also affect the dosage of genes located within them [13]. Genes located in IR undergo copy-dependent repair and experience doubling dosage affects, which can help stabilize and strengthen their biological function [52]. In this research, four accessions exhibited IR contraction, resulting in the loss of a complete copy of rpl2. Conversely, two accessions showed IR expansion, resulting in a duplicate copy of three genes (rps19, rpl22 and rps3). These genes are crucial for ribosome assembly and protein synthesis in the plastid, so any variation in dosage may impact leaf development and overall plant growth [53]. Notably, the two accessions showing IR expansion were samples from the margin of distribution of their respective species. P. delavayi (KY817591) was collected from Tibet, which has a higher altitude than other P. delavayi accessions, which were collected from Yunnan province in China. Whereas P. lactiflora (MN868412) was collected from southern China, most other P. lactiflora accessions were collected from northern China. IR expansion followed by gene duplication may have contributed to the ability of these two accessions to withstand environmental pressures, such as high altitude or temperature [54].
Despite the typically stable nucleotide content and highly conserved gene structure of chloroplast genomes, mutation hotspots can still occur [55]. In this research, 10 potential loci were identified that could serve as DNA barcodes for future research in Paeonia. Among them, the ycf1 region exhibited the highest level of nucleotide diversity. The high variability of the ycf1 region has also been observed in other genera [56, 57], making it a recommended plastid barcode for land plants [58]. In our study, the Pi value showing the longest genetic distance (~ 0.01) among the 63 accessions was between P. brownii and P. obovata. Notably, this distance is considerably lower than in other genera like Musa (0.03) [59] and Miscanthus (0.05) [60]). As the only genus in the Paeoniaceae and a single lineage within the Saxifragales, Paeonia is often considered to be ancient due to its possession of ancient biological traits such as the centrifugal development of stamens [1]. However, this research suggests that while it has an ancient origin, it diverged relatively late. This is supported by the low genetic diversity observed in our study, which suggests that ancient Paeonia branches may have experienced wide extinction events, while currently existing species may have arisen from recent speciation events. High hybridization affinity among Moutan species and reports of intersectional crosses [3] suggest that reproductive isolation among Paeonia species may be relatively weak. Collectively, those observations suggest close genetic relationships among Paeonia species, or at least among those found in East Asia.
Plastome reveals the domestication history of Paeonia cultivars
Genetic analysis is essential for cultivar breeding and utilization, and plastomes can significantly contribute to these efforts, particularly in the fields of pedigree analysis [17, 61], evaluation of genetic diversity [53], and exploration of domestication [18]. To compare the genetic structure of cultivated and natural Paeonia accessions, we manually clustered 63 accessions into five groups. However, these groups did not align with the five clusters generated by Bayesian phylogenetics and PCA. This is not surprising given the ancient nature of the Paeonia genus [1]. Compared to the five deep clusters revealed by phylogenetics and PCA, genetic variation between cultivated and natural accessions was relatively minor. Cultivated and natural accessions were grouped despite these inconsistencies because this approach might provide valuable insight into the domestication of cultivars.
The origin of the first reported tree peony species, P. suffruticosa, is a topic of debate [3]. According to some researchers, it is a hybrid formed by repeated hybridization among several species in sect. Moutan, based on both morphological and DNA markers (ADLP and RAPD) [62, 63]. Others, however, have argued that P. suffruticosa is not a hybrid but rather a cultivated variant of P. cathayana [6, 64]. Our results indicate that nine P. suffruticosa accessions were divided into two groups with different maternal origins, suggesting that P. suffruticosa is a hybrid complex resulting from multiple hybridizations. Additionally, our results revealed that P. ostii exhibits high genetic diversity, branching into three clades that include six P. suffruticosa cultivars whose maternal origin was traced back to P. cathayana [6]. This finding suggests that P. cathayana may be a specialized form of P. ostii, supported by the fact that they share a similar nuclear genome [6]. A previous study suggested that the cultivar ‘Luo Yang Hong’ was maternally inherited from species such as P. rockii and P. qiui, but the precise maternal origin was unclear [6]. Our results indicate that ‘Luo Yang Hong’ was maternally inherited from P. rockii subsp. rockii, rather than P. qiui, while cultivar ‘Fen E Jiao’ may have been inherited from P. qiui. These findings underscore the utility of the entire plastome in revealing high-resolution domestication history in Paeonia.
Chinese herbaceous peony cultivars were reported to have originated from wild P. lactiflora, without hybridizing with other species [65]. Our results are consistent with that finding. Additionally, all herbaceous cultivars were clustered into a monophonic group that was independent of wild P. lactiflora accessions. These results suggest that herbaceous peony cultivars were likely introduced from the wild on a single occasion and subsequently underwent a common domestication process. This may have resulted in the low genetic diversity of PAEO_CULT, highlighting the importance of introducing other wild Paeonia germplasm. Seven genes were identified as being under positive selection in herbaceous peony cultivars, including four photosynthesis-related genes: petA, psaA, psaB and rbcL. The petA gene encodes cytochrome f, a protein that plays a critical role in electron transfer during photosynthesis [66]. The psaA and psaB genes encode the large core subunit of photosystem I, which is involved in a variety of metabolic and physiological responses in plants [67]. The rbcL gene encodes the large subunit of Rubisco, a key enzyme in CO2 assimilation [68]. The positive selection of these genes, all of which are crucial for photosynthesis, may have contributed to the strong photosynthetic ability of Chinese herbaceous peony cultivars, potentially explaining their wide ecological range throughout China [1, 3]. However, further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between positive selection of photosynthesis-related genes and the ecological success of Chinese herbaceous peony cultivars.
Plastome reveals the evolutionary history of Paeonia
Paeonia has undergone frequent instances of polyploidization and hybridization [7]. These have made it challenging to fully reconstruct the evolutionary history of this genus. However, technological advancements have made progress possible. In this study, several notable discoveries were made with the aid of the plastome.
The first issue in phylogenetic and taxonomic research of Paeonia may be how to deal with species in sect. Onaepia. In contrast to previous studies [7, 16], our findings suggest that sect. Onaepia represents the first branch to diverge from the ancient Paeonia lineage. This divergence likely occurred around 26–30 Ma, during a period of increased dispersal from Asia to North America associated with the late Oligocene warming [69]. Other closely related lineages, including Deutzia [70], Saxifraga [71] and Darmera [72], also experienced divergence around that time, suggesting that sect. Onaepia arose independently from Asian branches, and that at least two separate herbacelizing events occurred in Paeonia.
Our research revealed that P. delavayi var. lutea has a closer maternal relationship with P. ludlowii than with two other variants (P. delavayi var. delavayi and var. potaninii), indicating that the P. delavayi plastome is paraphyletic. However, prior assessment of the nuclear genome indicated that P. delavayi is monophyletic [7, 9]. These conflicting phylogenetic signals may be explained by plastid capture [73]. In this process, ancient P. delavayi captured the plastome from P. ludlowii and generated P. delavayi var. lutea. Another similar bi-species complex exists with P. veitchii and P. sterniana. Our results indicate that P. veitchii also has a paraphyletic plastome, consistent with findings from its nuclear genome [7]. This suggests that P. sterniana may be a specialized form of P. veitchii and that the taxonomy of P. veitchii may need to be revised accordingly.
Another interesting issue is the consistency between the abrupt global cooling since the Pliocene and the rapid divergence of the Paeonia lineage (5.3 Ma, Fig. 5C). Abrupt global cooling during the Pliocene may have rendered the habitats of ancient peonies unsuitable [74], reducing their ability to survive and reproduce. However, the heterogenic landscapes of the Pan-Himalayan region may have provided suitable refuge, allowing for the survival of some ancient Paeonia lineages [75]. As a result, the surviving lineages might have diverged from each other and eventually resulted in the present Paeonia species. Thus, both paleoclimatic and geographic events may have contributed to the process of Paeonia diversification. However, further research is needed to fully understand the origin and dispersal routes of specific species.
Conclusion
Utilizing 10 newly reported assemblies of Paeonia plastomes, a dataset covering all species in East Asia was generated. Based on this dataset, a comprehensive phylogenetic and comparative genomic analysis was performed. The results showed an overall conserved structure and low nucleotide variation among all plastomes, although several accessions exhibited IR expansion and contraction. These findings suggest that woody cultivars had multiple maternal origins although no plastome gene showed traces of selection via domestication. Conversely, herbaceous cultivars were only inherited from P. lactiflora. Several genes related to photosynthesis showed evidence of selection during domestication. The phylogenetic results validated the ability of plastomes to delimit species, revealed a consistency between Paeonia speciation and global paleoclimatic change, and supported an independent taxonomic treatment of sect. Onaepia. Collectively, these results provide a comprehensive set of valuable information for understanding the evolutionary and domestication history of Paeonia and are useful for the conservation and utilization of both natural and cultivated germplasm.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jianming Zeng (University of Macau) and the entire bioinformatics team at Biotrainee for sharing their valuable insight and experiences in comparative genomics, which greatly aided our research. We also acknowledge the support of Shanghai Hengsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd., which provided a high-performance computing cluster (https://biorstudio.cloud).
Author Contribution
XY and QC designed the experiments. QC and LC performed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. JS provided scientific advice. XY and JS revised the manuscript. All the authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (32071817).
Data Availability
The 10 newly reported plastomes are openly available in NCBI at the GenBank database with accession numbers OP324584-OP324593. Additional data are provided as supporting information in this article.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study complied with all relevant institutional, national and international guidelines with permissions from Beijing Forestry University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Hong DY. Peonies of the world: taxonomy and phytogeography. Richmond, UK: Royal Botanic Gardens; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li P, Shen J, Wang Z, Liu S, Liu Q, Li Y, He C, Xiao P. Genus Paeonia: a comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology. J ETHNOPHARMACOL. 2021;269:113708. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang Y, Sun M, Li SS, Chen QH, Teixeira da Silva JA, Wang AJ, Yu XN, Wang LS. Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: a systematic review. HORTIC RES. 2020;7(1):107–25. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0332-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deng R, Gao J, Yi J, Liu P. Peony seeds oil by-products: Chemistry and bioactivity. IND CROP PROD. 2022;187:115333. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115333. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang J, López-Pujol J, Gong X, Wang H, Vilatersana R, Zhou S. Population genetic dynamics of himalayan-hengduan tree peonies, Paeonia subsect. Delavayanae. MOL PHYLOGENET EVOL. 2018;125:62–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2018.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou SL, Zou X, Zhou Z, Liu J, Xu C, Yu J, Wang Q, Zhang D, Wang X, Ge S, et al. Multiple species of wild tree peonies gave rise to the ‘king of flowers’, Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews. Proc Royal Soc B: Biol Sci. 2014;281(1797):20141687. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou SL, Xu C, Liu J, Yu Y, Wu P, Cheng T, Hong DY. Out of the Pan-Himalaya: evolutionary history of the Paeoniaceae revealed by phylogenomics. J SYST EVOL. 2021;59(6):1170–82. doi: 10.1111/jse.12688. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hong DY, Pan KY, Yu H. Taxonomy of the Paeonia delavayi Complex (Paeoniaceae) ANN MO BOT GARD. 1998;85(4):554–64. doi: 10.2307/2992016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhao Y, Yin G, Pan Y, Tian B, Gong X. Climatic refugia and geographical isolation contribute to the speciation and genetic divergence in Himalayan-Hengduan tree peonies (Paeonia delavayi and Paeonia ludlowii) FRONT GENET. 2021;11:595334. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.595334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guo L, Guo S, Xu J, He L, Carlson JE, Hou X. Phylogenetic analysis based on chloroplast genome uncover evolutionary relationship of all the nine species and six cultivars of tree peony. IND CROP PROD. 2020;153:112567. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112567. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Daniell H, Jin S, Zhu XG, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis DE, Soltis PS. Green giant: a tiny chloroplast genome with mighty power to produce high-value proteins: history and phylogeny. PLANT BIOTECHNOL J. 2021;19(3):430–47. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chase MW, Soltis DE, Olmstead RG, Morgan D, Les DH, Mishler BD, Duvall MR, Price RA, Hills HG, Qiu Y, et al. Phylogenetics of seed plants: an analysis of nucleotide sequences from the plastid gene rbcL. ANN MO BOT GARD. 1993;80(3):528. doi: 10.2307/2399846. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rogalski M, do Nascimento Vieira L, Fraga HP, Guerra MP. Plastid genomics in horticultural species: importance and applications for plant population genetics, evolution, and biotechnology. FRONT PLANT SCI. 2015;6:586. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang R, Wang Y, Jin J, Stull GW, Bruneau A, Cardoso D, de Queiroz LP, Moore MJ, Zhang S, Chen S, et al. Exploration of plastid phylogenomic conflict yields new insights into the deep relationships of Leguminosae. SYST BIOL. 2020;69(4):613–22. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syaa013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gao C, Wang Q, Ying Z, Ge Y, Cheng R. Molecular structure and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genomes of medicinal species Paeonia lactiflora from Zhejiang Province. Mitochondrial DNA Part B. 2020;5(1):1077–8. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1721372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dong P, Zhang L, Lu Z, Wang Y, Song X, Wang J, He D, Lei X, Wang M, Fang M, et al. Characterization of the DNA molecular sequence of complete plastid genome of Paeonia rockii subsp. taibaishanica, an endemic species in China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B. 2021;6(9):2628–9. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1917311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carbonell-Caballero J, Alonso R, Ibañez V, Terol J, Talon M, Dopazo J. A phylogenetic analysis of 34 chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships between wild and domestic species within the genus Citrus. MOL BIOL EVOL. 2015;32(8):2015–35. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sielemann K, Pucker B, Schmidt N, Viehöver P, Weisshaar B, Heitkam T, Holtgräwe D. Complete pan-plastome sequences enable high resolution phylogenetic classification of sugar beet and closely related crop wild relatives. BMC Genomics. 2022;23(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08336-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pahlich E, Gerlitz C. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry. 1980;19(1):11–3. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(80)85004-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jin J, Yu W, Yang J, Song Y, DePamphilis CW, Yi T, Li D. GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. GENOME BIOL. 2020;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02154-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Freudenthal JA, Pfaff S, Terhoeven N, Korte A, Ankenbrand MJ, Förster F. A systematic comparison of chloroplast genome assembly tools. GENOME BIOL. 2020;21(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02153-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Qu X, Moore MJ, Li D, Yi T. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. PLANT METHODS. 2019;15(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13007-019-0435-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Benson G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. NUCLEIC ACIDS RES. 1999;27(2):573–80. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Beier S, Thiel T, Münch T, Scholz U, Mascher M. MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(16):2583–5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kurtz S, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E, Schleiermacher C, Stoye J, Giegerich R. REPuter: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. NUCLEIC ACIDS RES. 2001;29(22):4633–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.22.4633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shen W, Le S, Li Y, Hu F. SeqKit: a cross-platform and ultrafast toolkit for FASTA/Q file manipulation. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(10):e163962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peden J. Analysis of Codon usage. Nottingham: University of Nottingham; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wright F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene. 1990;87(1):23–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90491-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kosakovsky Pond SL, Poon AFY, Velazquez R, Weaver S, Hepler NL, Murrell B, Shank SD, Magalis BR, Bouvier D, Nekrutenko A, et al. HyPhy2.5: a customizable platform for evolutionary hypothesis testing using phylogenies. MOL BIOL EVOL. 2020;37(1):295–9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kosakovsky Pond SL, Frost SDW. Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. MOL BIOL EVOL. 2005;22(5):1208–22. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msi105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Murrell B, Moola S, Mabona A, Weighill T, Sheward D, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Scheffler K. FUBAR: a fast, unconstrained bayesian AppRoximation for inferring selection. MOL BIOL EVOL. 2013;30(5):1196–205. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Murrell B, Wertheim JO, Moola S, Weighill T, Scheffler K, Kosakovsky PS. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLOS GENET. 2012;8(7):e1002764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. GENOME RES. 2004;14(7):1394–403. doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nakamura T, Yamada KD, Tomii K, Katoh K. Parallelization of MAFFT for large-scale multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(14):2490–2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Capella-Gutierrez S, Silla-Martinez JM, Gabaldon T. trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(15):1972–3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Paradis E. Pegas: an R package for population genetics with an integrated-modular approach. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(3):419–20. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Charif D, Lobry JR. SeqinR 1.0–2: A contributed package to the R project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysis. In: Structural Approaches to Sequence Evolution: Molecules, Networks, Populations Edited by Bastolla U, Porto M, Roman HE, Vendruscolo M, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg; 2007: 207–232.
- 38.Jombart T, Ahmed I. Adegenet 1.3-1: New tools for the analysis of genome-wide SNP data. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(21):3070–1. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kamvar ZN, Tabima JF, Grünwald NJ. Poppr: an R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PEERJ. 2014;2:e281. doi: 10.7717/peerj.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F. Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC GENET. 2010;11:94. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Folk RA, Stubbs RL, Mort ME, Cellinese N, Allen JM, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Guralnick RP. Rates of niche and phenotype evolution lag behind diversification in a temperate radiation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 2019, 116(22):10874–10882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Suchard MA, Lemey P, Baele G, Ayres DL, Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. VIRUS EVOL. 2018;4(1):vey016. doi: 10.1093/ve/vey016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Drummond AJ, Bouckaert RR. Bayesian evolutionary analysis with BEAST. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Quinlan AR, Hall IM. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(6):841–2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Löytynoja A. Phylogeny-aware alignment with PRANK. In: Multiple Sequence Alignment Methods Edited by Russell DJ. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2014: 155–170. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. NAT METHODS. 2017;14(6):587–9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Baele G, Lemey P, Bedford T, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Alekseyenko AV. Improving the accuracy of demographic and molecular clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty. MOL BIOL EVOL. 2012;29(9):2157–67. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Xie D, Baele G, Suchard MA. Posterior summarization in bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. SYST BIOL. 2018;67(5):901–4. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yu G, Smith DK, Zhu H, Guan Y, Lam TTY. ggtree: an R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. METHODS ECOL EVOL. 2016;8(1):28–36. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12628. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Westerhold T, Marwan N, Drury AJ, Liebrand D, Agnini C, Anagnostou E, Barnet J, Bohaty SM, De Vleeschouwer D, Florindo F, et al. An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years. Science. 2020;369(6509):1383–7. doi: 10.1126/science.aba6853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T, Hayashida N, Matsubayashi T, Zaita N, Chunwongse J, Obokata J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986;5(9):2043–9. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mower JP, Vickrey TL. Structural diversity among plastid genomes of land plants. In: Advances in Botanical Research Edited by Chaw S, Jansen RK, vol. 85: Academic Press; 2018: 263–292.
- 53.Daniell H, Lin C, Yu M, Chang W. Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. GENOME BIOL. 2016;17(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1004-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Yi T, Li D, Soltis DE. Plastome phylogenetics: 30 years of inferences into plant evolution. In: Advances in Botanical Research Edited by Chaw S, Jansen RK, vol. 85: Academic Press; 2018: 293–313.
- 55.Ogoma CA, Liu J, Stull GW, Wambulwa MC, Oyebanji O, Milne RI, Monro AK, Zhao Y, Li D, Wu Z. Deep insights into the plastome evolution and phylogenetic relationships of the tribe Urticeae (family Urticaceae) FRONT PLANT SCI. 2022;13:870949. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.870949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Li J, Tang J, Zeng S, Han F, Yuan J, Yu J. Comparative plastid genomics of four Pilea (Urticaceae) species: insight into interspecific plastid genome diversity in Pilea. BMC PLANT BIOL. 2021;21(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02793-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang J, Moore MJ, Wang H, Zhu Z, Wang H. Plastome evolution and phylogenetic relationships among Malvaceae subfamilies. Gene. 2021;765:145103. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dong W, Xu C, Li C, Sun J, Zuo Y, Shi S, Cheng T, Guo J, Zhou S. ycf1, the most promising plastid DNA barcode of land plants. SCI REP. 2015;5(1):8348. doi: 10.1038/srep08348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fu N, Ji M, Rouard M, Yan H, Ge X. Comparative plastome analysis of Musaceae and new insights into phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genomics. 2022;23(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08454-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sheng J, Yan M, Wang J, Zhao L, Zhou F, Hu Z, Jin S, Diao Y. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of five Miscanthus species, and comparative analyses with other grass plastomes. IND CROP PROD. 2021;162:113248. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113248. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Duan Q, Liu F, Gui D, Fan W, Cui G, Jia W, Zhu A, Wang J. Phylogenetic analysis of wild species and the maternal origin of cultivars in the genus Lilium using 114 plastid genomes. FRONT PLANT SCI. 2022;13:865606. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.865606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yuan T. Studies on genetic relationship of some species and cultivars/ cultivars groups of Chinese tree peony (in Chinese). PhD thesis Beijing Forestry University, College of Landscape Architecture; 1998.
- 63.Li J, Zhang X, Zhao X. Tree peony of China (in chinese) Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Publishing House; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hong DY, Pan KY. Notes on taxonomy of Paeonia sect. Moutan DC. (Paeoniaceae). J SYST EVOL 2005, 43(2):169–177.
- 65.Guo XF. Studies on the relationship among some species and cultivars of Chinese herbaceous peonies (in Chinese). PhD thesis Beijing Forestry University, College of Landscape Architecture; 2003.
- 66.Takenaka K, Takabe T. Importance of local positive charges on cytochrome f for electron transfer to plastocyanin and potassium ferricyanide. J BIOCHEM. 1984;96(6):1813–21. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chitnis PR. PHOTOSYSTEM I: function and physiology. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2001;52(1):593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Andersson I, Backlund A. Structure and function of Rubisco. PLANT PHYSIOL BIOCH. 2008;46(3):275–91. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Jiang D, Klaus S, Zhang Y, Hillis DM, Li J. Asymmetric biotic interchange across the Bering land bridge between Eurasia and North America. NATL SCI REV. 2019;6(4):739–45. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kim C, Deng T, Wen J, Nie Z, Sun H. Systematics, biogeography, and character evolution of Deutzia (Hydrangeaceae) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequences. MOL PHYLOGENET EVOL. 2015;87:91–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zhang MH, Wang CY, Zhang C, Zhang DG, Li KG, Nie ZL, Meng Y. Phylogenetic relationships and biogeographic history of the unique Saxifraga sect. Irregulares (Saxifragaceae) from eastern Asia. J SYST EVOL. 2020;58(6):958–71. doi: 10.1111/jse.12547. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Deng J, Drew BT, Mavrodiev EV, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Soltis DE. Phylogeny, divergence times, and historical biogeography of the angiosperm family Saxifragaceae. MOL PHYLOGENET EVOL. 2015;83:86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tsitrone A, Kirkpatrick M, Levin DA. A model for chloroplast capture. EVOLUTION 2007, 57(8):1776–1782. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 74.Bennett KD. Intersection of quaternary climate oscillations and the generation of biodiversity: crucial or irrelevant? INTEGR COMP BIOL. 2018;58:E15. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Spicer RA, Su T, Valdes PJ, Farnsworth A, Wu F, Shi G, Spicer TEV, Zhou Z. Why ‘the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau’ is a myth. NATL SCI REV. 2021;8(1):nwaa091. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The 10 newly reported plastomes are openly available in NCBI at the GenBank database with accession numbers OP324584-OP324593. Additional data are provided as supporting information in this article.