Abstract
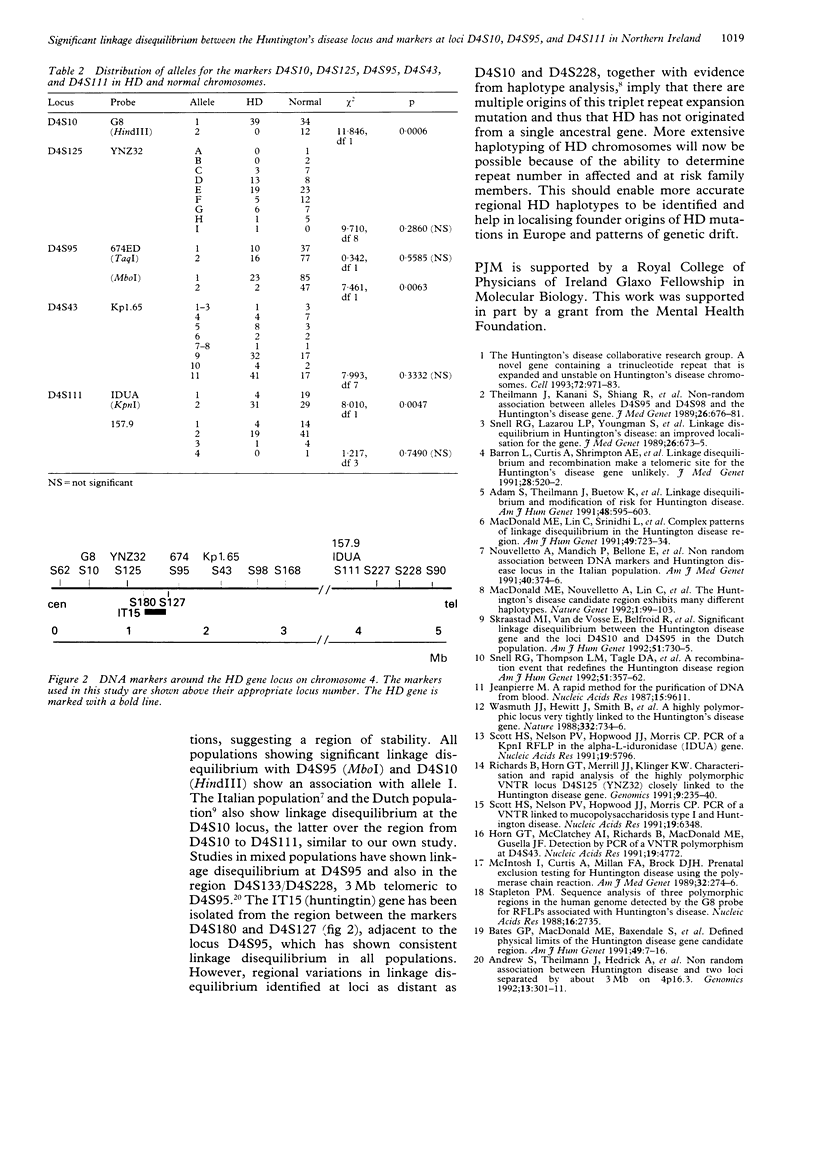
An analysis of the Northern Ireland Huntington's disease (HD) population of 75 families showed significant linkage disequilibrium between the HD gene and DNA markers at D4S95, D4S10, and D4S111. As the linkage disequilibrium at loci D4S10 and D4S111 is different from previous studies in the UK, but similar at locus D4S95, this suggests either that the HD mutation(s) in the Northern Ireland and British populations is not of common origin or that the haplotype of the common HD mutation has changed over time subsequent to divergence from a common origin.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew S., Theilmann J., Hedrick A., Mah D., Weber B., Hayden M. R. Nonrandom association between Huntington disease and two loci separated by about 3 Mb on 4p16.3. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90246-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron L., Curtis A., Shrimpton A. E., Holloway S., May H., Snell R. G., Brock D. J. Linkage disequilibrium and recombination make a telomeric site for the Huntington's disease gene unlikely. J Med Genet. 1991 Aug;28(8):520–522. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.8.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., McClatchey A. I., Richards B., MacDonald M. E., Gusella J. F. Detection by PCR of a VNTR polymorphism at D4S43. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4772–4772. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanpierre M. A rapid method for the purification of DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9611–9611. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Novelletto A., Lin C., Tagle D., Barnes G., Bates G., Taylor S., Allitto B., Altherr M., Myers R. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):99–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh I., Curtis A., Millan F. A., Brock D. J. Prenatal exclusion testing for Huntington disease using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):274–276. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrício M. B. Radioterapia da doença de Hodgkin. Acta Med Port. 1990 Jan-Feb;3(1):11–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B., Horn G. T., Merrill J. J., Klinger K. W. Characterization and rapid analysis of the highly polymorphic VNTR locus D4S125 (YNZ32), closely linked to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1991 Feb;9(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90247-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Nelson P. V., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. PCR of a KpnI RFLP in the alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5796–5796. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5796-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Nelson P. V., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. PCR of a VNTR linked to mucopolysaccharidosis type I and Huntington disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6348–6348. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6348-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skraastad M. I., Van de Vosse E., Belfroid R., Höld K., Vegter-van der Vlis M., Sandkuijl L. A., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J. Significant linkage disequilibrium between the Huntington disease gene and the loci D4S10 and D4S95 in the Dutch population. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):730–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Thompson L. M., Tagle D. A., Holloway T. L., Barnes G., Harley H. G., Sandkuijl L. A., MacDonald M. E., Collins F. S., Gusella J. F. A recombination event that redefines the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):357–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



