Abstract
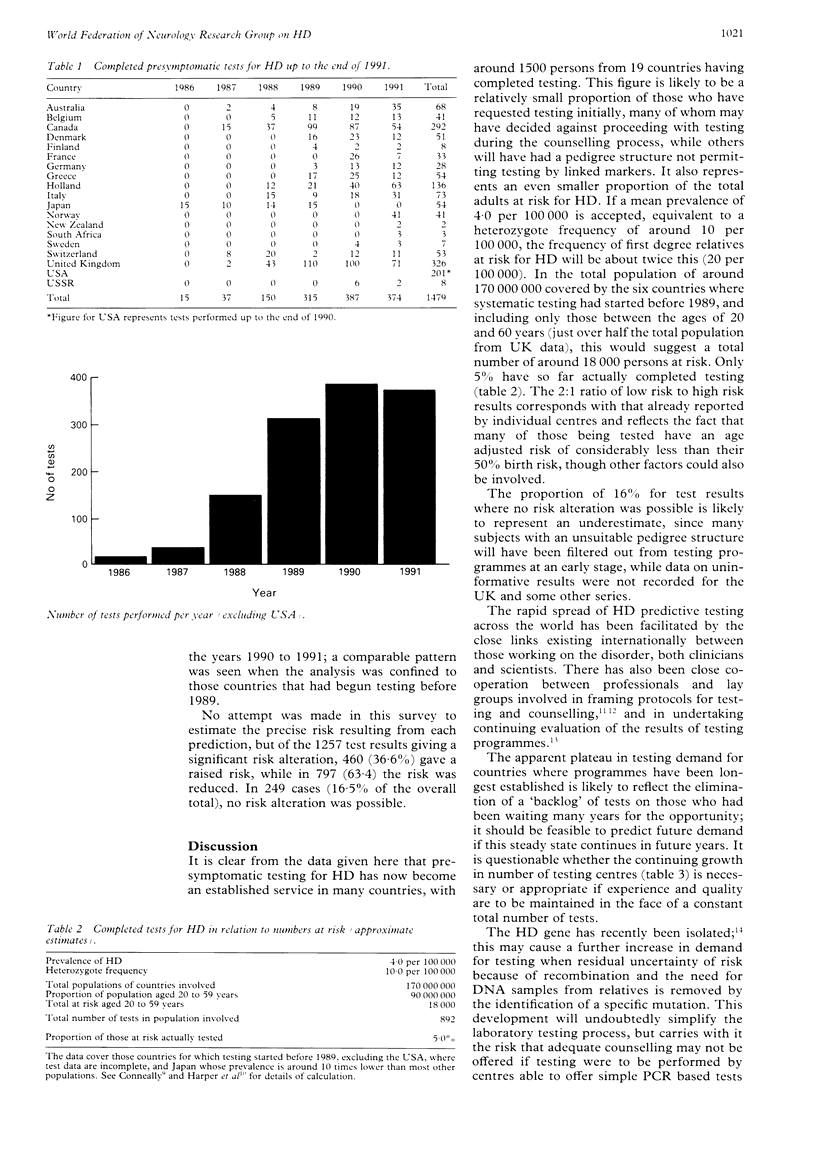
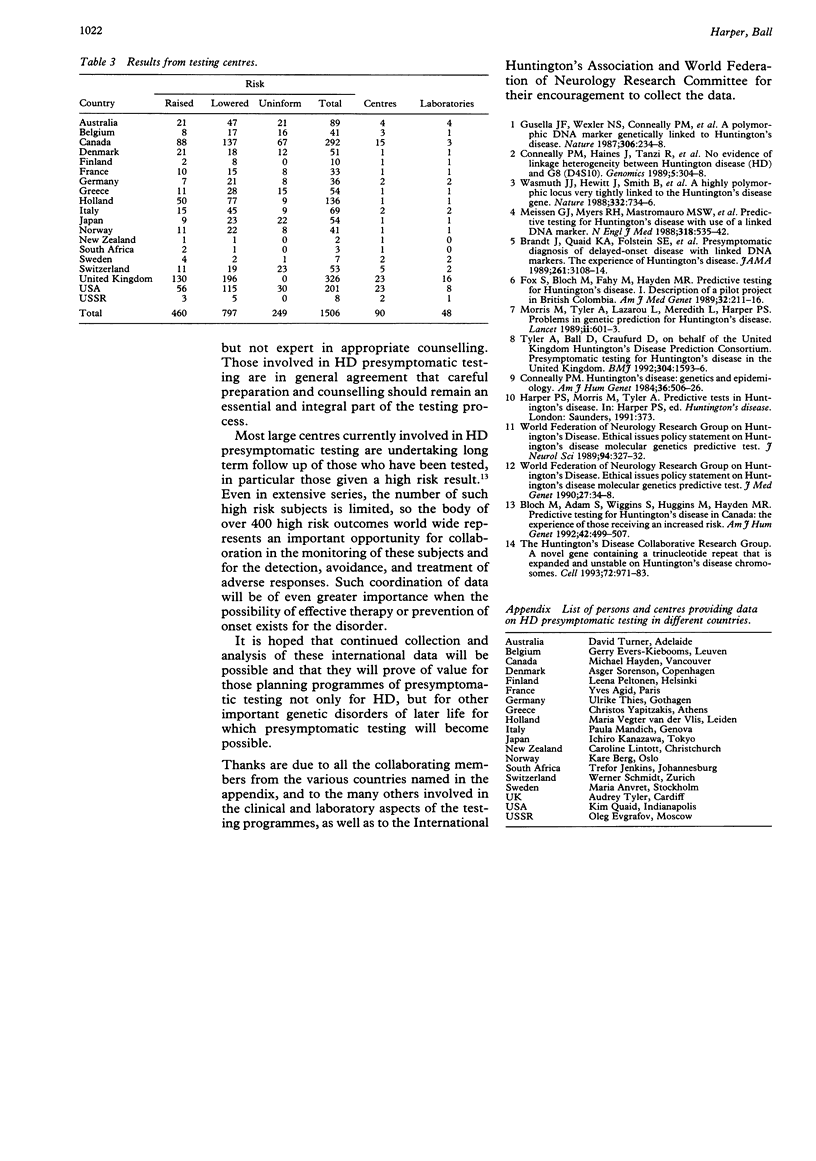
World wide data on presymptomatic testing for Huntington's disease using closely linked DNA markers show that 1479 persons at risk received completed test results up to the end of 1991. Testing has been carried out in 19 countries, with at least 88 centres involved, and numbers have levelled off after a peak in 1990. Only 5% of those at risk have been tested in six countries with the longest established programmes. Continued monitoring of international data will be of value in assessing the spread and impact of genetic testing, not only for Huntington's disease, but for other serious genetic disorders of later life.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch M., Adam S., Wiggins S., Huggins M., Hayden M. R. Predictive testing for Huntington disease in Canada: the experience of those receiving an increased risk. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Feb 15;42(4):499–507. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320420416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Quaid K. A., Folstein S. E., Garber P., Maestri N. E., Abbott M. H., Slavney P. R., Franz M. L., Kasch L., Kazazian H. H., Jr Presymptomatic diagnosis of delayed-onset disease with linked DNA markers. The experience in Huntington's disease. JAMA. 1989 Jun 2;261(21):3108–3114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Haines J. L., Tanzi R. E., Wexler N. S., Penchaszadeh G. K., Harper P. S., Folstein S. E., Cassiman J. J., Myers R. H., Young A. B. Huntington disease: no evidence for locus heterogeneity. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M. Huntington disease: genetics and epidemiology. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):506–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S., Bloch M., Fahy M., Hayden M. R. Predictive testing for Huntington disease: I. Description of a pilot project in British Columbia. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):211–216. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissen G. J., Myers R. H., Mastromauro C. A., Koroshetz W. J., Klinger K. W., Farrer L. A., Watkins P. A., Gusella J. F., Bird E. D., Martin J. B. Predictive testing for Huntington's disease with use of a linked DNA marker. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):535–542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. J., Tyler A., Lazarou L., Meredith L., Harper P. S. Problems in genetic prediction for Huntington's disease. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):601–603. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler A., Ball D., Craufurd D. Presymptomatic testing for Huntington's disease in the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom Huntington's Disease Prediction Consortium. BMJ. 1992 Jun 20;304(6842):1593–1596. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6842.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


