Abstract
Objective
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is caused by cardiovascular developmental defects and has a global prevalence of ∼1%. The etiology of CHD is multifactorial and remains generally unknown, despite advances in analytical techniques based on next-generation sequencing (NGS). The aim of our study was to elucidate the multi-genetic origin and pathogenesis of an intriguing familial case with complex CHD.
Methods
We performed an original trio-based gene panel analysis using NGS of the family, including two siblings with CHD of single ventricular phenotype, and their unaffected parents. The pathogenicity of the detected rare variants was investigated in silico, and the functional effects of the variants were confirmed in vitro using luciferase assays. The combinatorial effect of gene alterations of the putative responsible genes was tested in vivo using genetically engineered mutant mice.
Results
NGS-based gene panel analyses revealed two heterozygous rare variants in NODAL and in TBX20 common to the siblings and to just one of parents. Both variants were suspected pathogenic in silico, and decreased transcriptional activities of downstream signaling pathways were observed in vitro. The analyses of Nodal and Tbx20 double mutant mice demonstrated that Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− embryos showed more severe defects than Nodal+/+Tbx20−/− embryos during early heart development. The expression of Pitx2, a known downstream target of Nodal, was downregulated in Tbx20−/− mutants.
Conclusions
Two rare variants on NODAL and TBX20 genes detected in this family were considered to be loss-of-function mutations. Our results suggest that NODAL and TBX20 may be complementary for the cardiac development, and a combinatorial loss-of-function of NODAL and TBX20 could be implicated in digenic inherence as the etiology of complex CHD associated with single ventricle defects in this family.
Keywords: trio gene analysis, nodal, tbx20, complex congenital heart disease, rare variants
1. Introduction
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is caused by defects in cardiovascular development during the first trimester of gestation and has an incidence of ∼2.5 to 13.8 per 1,000 births (1). The etiology of most CHDs remains generally unknown and is largely attributed to the so-called multifactorial, including genetic and environmental, factors. The genetic factors associated with CHD include chromosomal abnormalities in 12%, de novo copy number variants such as chromosomal microdeletion in 15%, de novo gene mutation affecting protein function in 10%, and inherited gene mutations in 1.3% of cases. About two to four hundred genes have been implicated in CHD, encompassing transcription factors, cell signaling and adhesion molecules, and structural proteins that are involved in heart development (1, 2). Scientific advances, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), help identify pathogenic variants associated with CHD with Mendelian patterns (3). However, the lack of experimental approaches fails to clarify the involvement of multiple genetic variants, especially oligogenic or polygenic inheritance and genetic modifiers, that lead to complex phenotypes.
NGS-based gene panel testing, which can be complemented with array comparative genomic hybridization and other methods, provides a comprehensive, timely, and efficient approach for the molecular diagnosis of heterogeneous disorders, such as CHD. Compared to single-gene test and whole exome sequencing analyses, NGS-based gene panel analysis increases analytical sensitivity for genetic diagnostic testing and can save time and money. It also simplifies the decision-making evidence for physicians, because the likelihood of discovering multiple confounding variants of unknown clinical significance is less than that when using whole-exome sequencing (4).
In this study, we performed genetic analyses of a family with complex CHD. Through NGS-based gene panel testing, in vitro functional analyses of the variants of interest, and in vivo function analyses using genetically engineered animal models, we attempted to provide evidence of digenic inheritance in complex CHD.
2. Methods
2.1. Clinical evaluation of patients and DNA collection
The patients were diagnosed as having congenital cardiac anomalies before birth. They were hospitalized in Keio University Hospital at birth and made a definitive diagnosis based on their clinical history, physical examination, echocardiogram, and heart catheterization by well-trained pediatric cardiologists. We checked that their parents do not have any cardiac diseases through oral interview and physical examination.
The parents provided written informed consent for this research on them and their children. Blood samples were obtained after receiving written informed consent.
Genomic DNA (gDNA) was extracted directly from whole blood using the Gentra Puregene Blood Kit (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands), according to the manufacturer's protocol.
2.2. NGS
Using NGS, the patients were screened for genomic variants in cardiac disease-specific genes. A total of 197 genes were selected and subjected to gene panel analysis using NGS conducted by the Center for Medical Genetics and the Department of Cardiology, Keio University School of Medicine (Supplementary Table S1).
2.3. Direct sequencing and variant analysis
Genetic variants detected using NGS were reconfirmed using Sanger sequencing. Arrays containing these variants in gDNA samples were amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and TaKaRa Ex Taq Hot Start Version (Takara Bio, Kusatsu, Japan). All reactions were performed using a DNA Engine Peltier Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The PCR products purified using NucleoSpin Extract II Kit (Takara Bio) were used for direct bidirectional sequencing to search for nucleotide changes, using the BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) and a 3130xl Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
2.4. In silico analyses of detected sequence variants
The detected sequence variants were validated using the UCSC genome browser (https://genome-asia.ucsc.edu, human assembly December 2013, GRch38/hg38), Ensembl (http://www.ensembl.org, Release 105), and ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/, updated in September 2021) database. SIFT (http://sift.jcvi.org, version 5.2.2) and PolyPhen-2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2, version 2.2.2) were used for analyzing the missense variants.
2.5. Plasmid construction and site-directed mutagenesis
A human cDNA clone of NODAL (ID; X01Y107A01) in pGEM-T Easy vector was purchased from DNAFORM (Yokohama, Japan), and a human cDNA clone of TBX20 (ID; FXC03772) in pF1K vector was purchased from Kazusa Genome Technologies (Kisarazu, Japan). To construct the variant cDNA, site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the PrimeSTAR Max Mutagenesis Basal Kit (Takara Bio), according to the manufacturer's instructions. All the PCR products were verified using sequencing.
2.6. Western blot
The PCR products (both wildtype and mutated type) were subcloned into another mammalian cDNA expression vector (pCMV-Tag3; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The c-Myc tag was used for the detection of the recombinant fusion protein. Proteins were prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with the expression vectors using Lipofectamine 2000. c-Myc-tagged NODAL or TBX20 proteins were detected by western blotting using monoclonal anti-c-Myc antibodies, goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX), and SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA) after SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
2.7. Luciferase assays
For analysis of NODAL function, P19 cells, a cell line isolated from the embryo of a male mouse with teratocarcinoma, were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with 200 ng p(Smad binding element, SBE)4 luciferase reporter plasmid (Addgene, Cambridge, MA, USA) as a reporter vector, 125 ng of NODAL expression vector (Dnaform, Kanagawa, Japan), 42 ng each of CRIPTO, CRYPTIC and GDF1, expression vectors (5) as enhancers for NODAL, and 50 ng of pRL-SV40 Vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) as an internal control.
For analysis of TBX20 function, HeLa cells were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with 125 ng of NPPA promoter-luciferase plasmid as a reporter vector, 125 ng of TBX20 expression vector, 125 ng each of GATA4 and NKX2.5 expression vectors as enhancers for TBX20, and 50 ng of pRL-SV40 Vector (Promega) as an internal control.
Luciferase activity was measured 42 h after transient transfection using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega) and Synergy4 (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA) or Cytation5 (BioTek Instruments), according to the manufacturer's instructions. All experiments were repeated five times.
2.8. Mice, in situ hybridization, and quantitative Rt-PCR
Nodal+/− and Tbx20+/− mouse lines were used, as described previously (6, 7). Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− murine embryos were generated by intercrossing Nodal+/−Tbx20+/− and Tbx20+/− mice. Embryonic day (E) 8.75 to E9.5, mothers were euthanized using cervical dislocation, and their uteri were dissected to harvest embryos. PCR genotyping was performed using the following primers: forward, 5′-ataggcacgtgctctcccaa-3′ (for wildtype) or 5′-gagccatttggttctccctg-3′ (for mutant); reverse, 5′-ccccacacctcacataacct-3′ for the Nodal line, and forward, 5′-aataaatcggcccttgttct-3′; reverse, 5′-ggaggctttcgaaaagtgaa-3′ for the Tbx20 line. For Pitx2 expression analysis, whole-mount in situ hybridization using E9.5 embryos was performed as described previously (8, 9). Briefly, total RNA was extracted from E9.5 embryos, and cDNA was synthesized using High-Capacity RNA-to-cDNA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed with Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and a StepOnePlus system (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) was used as an internal control. Primer sequences used for Pitx2c and Gapdh are as follows: forward, 5′-ccctgaagtcgcagagaaaga-3′; reverse, 5′-agtgaaatgagtcctctgccg-3 ′, and forward, 5′-tgaaggtcggtgtgaacgg-3′; reverse, 5′-cgtgagtggagtcatactggaa-3′.
2.9. Statistical analyses
For luciferase assays, data are presented as normalized relative light units (fold activation). Data in luciferase assays and quantitative RT-PCRwere analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. R (version 4.2.2, https://www.r-project.org/) was used for statistical analysis.
2.10. Ethics approval
This study was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (1989). Clinical evaluations were approved by the Internal Ethics Committee of Keio University School of Medicine (approval number 20120042) and were conducted only after written informed consent had been obtained. All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Keio University [approval number 09122-(13), A2022-286] and of National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center (approval number 19026 and 19-6), and conformed to the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 0.75 mg/kg of medetomidine, 4.0 mg/kg of midazolam, and 5.0 mg/kg of butorphanol and then euthanized by cervical dislocation.
3. Results
3.1. A familial case with CHD suggests multifactorial inheritance
The pedigree chart of our patients is shown in Figure 1. Neither parent had heart disease or family history of heart disease. Their first child was a miscarriage without phenotype or genotype analysis. Their second child, a male, has severe tricuspid stenosis, atrial septal defect, and ventricular septal defect, manifesting a functional left-sided single ventricle. Their third child, a female, has right-sided single ventricle with asplenia-type heterotaxy.
Figure 1.
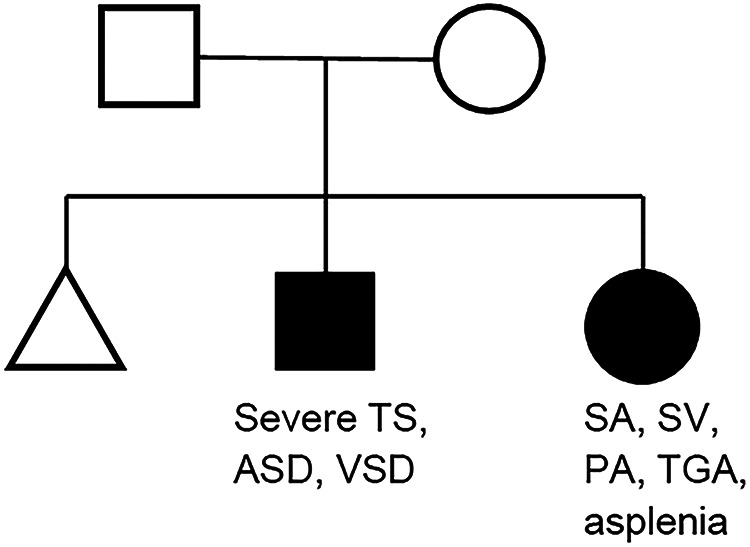
Pedigree chart of the family. TS, tricuspid valve stenosis; ASD, atrial septal defect; VSD, ventricular septal defect; SA, single atrium; SV, single ventricle; PA, pulmonary atresia; TGA, transposition of the great arteries.
From the pedigree, an autosomal recessive inheritance was assumed for siblings with CHD at first. Cardiac phenotype seemed common regarding as the single ventricular morphology between siblings; however, their detailed phenotypes were different (single left ventricle with severe tricuspid stenosis vs. single right ventricle with heterotaxy).
3.2. Four sequence variants identified in the family
NGS using gene panels for gDNA from the siblings identified four common missense variants in four genes that were candidates for the genetic cause of CHD in the siblings. All these variants were confirmed by direct sequencing (Table 1). In the analyses of gDNA from the parents, a heterozygous variant in NODAL (c.1021G > T, p.V341l) common to the siblings was found in the father, whereas three heterozygous variants in CASQ2 (c.1163A > G, p.E388G), SYNE1 (c.17867G > A, p.R5956H), and TBX20 (c.991A > G, p.T331A) common to the siblings were found in the mother.
Table 1.
Detected variants from the siblings with CHDs.
| gene | Nucleotide change | Amino acid change | Existence of the heterozygous variant | dbSNP | Allele frequencya (%) | SIFT | PolyPhen-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| brother | sister | father | mother | |||||||
| NODAL | 1021G > T | V341l | yes | yes | yes | no | No Data | No Data | Deleterious (0) | Probably damaging (1) |
| CASQ2 | 1163A > G | E388G | yes | yes | no | yes | No Data | No Data | Tolerated (0.65) | Unknown (0) |
| SYNE1 | 17867G > A | R5956H | yes | yes | no | yes | rs80265744 | 0.04137 | Deleterious (0.01) | Probably damaging (0.984) |
| TBX20 | 991A > G | T331A | yes | yes | no | yes | rs1420582400 | 0.0008023 | Tolerated (1) | Benign (0) |
Allele frequency were data from gnomAD exomes r2.1.1.
Because there was no result suggesting autosomal recessive inheritance of a certain gene, oligogenic or multifactorial inheritance was considered the genetic mechanism for CHD in the family. The siblings inherited heterozygous variants of different genes from their parents (one from father and another from mother), and the variants may not cause CHD alone, but they may cause CHD when combined. With reference to past reports (see Discussion), we hypothesized that the combination of the NODAL variant derived from the father and the TBX20 variants derived from the mother may be related to the onset of CHD, and we therefore focused on these two variants.
3.3. In silico analyses suggest NODAL and TBX20 to be candidate genes
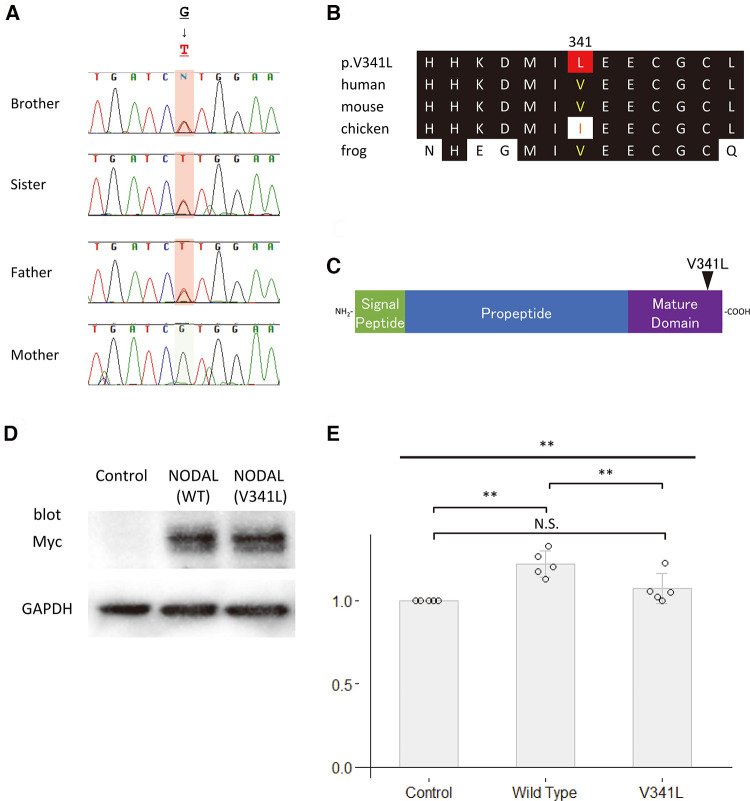
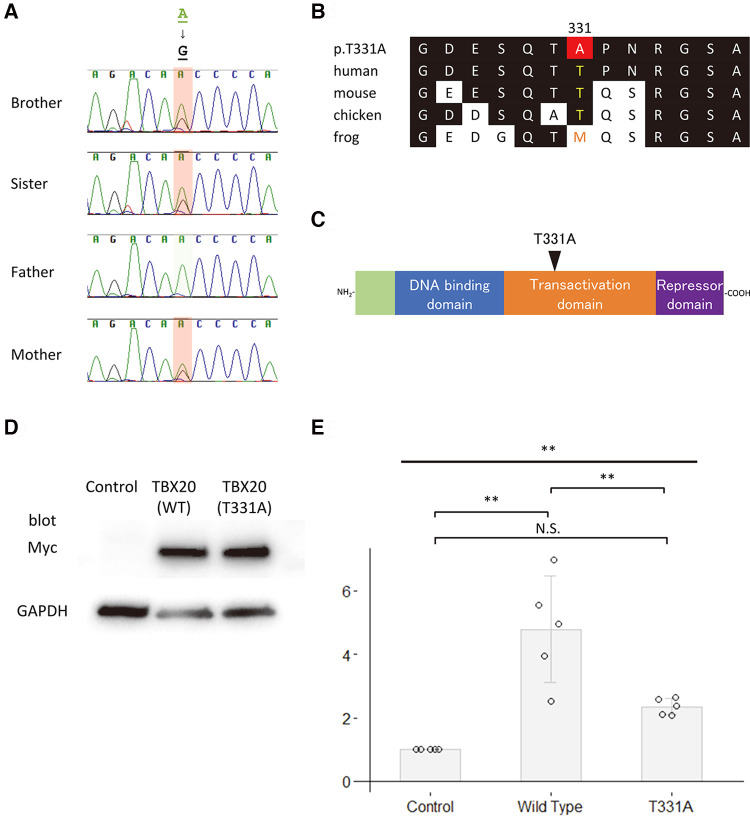
We performed in silico analyses of the variants (Figures 2A–C, 3A–C, and Table 1). The amino acid change p.V341l in NODAL was located in the mature domain, and variants near c.1021G have been reported in patients with various cardiovascular malformations (10). SIFT and PolyPhen-2 analyses predicted that p.V341l was implicated in change of function. The amino acid change p.T331A in TBX20 was located in the transactivation/repression domain (11). A previous study has reported the same variant in a Japanese patient with atrial septum defect (12), and variants near c.991A have been also reported in patients with CHD (13). Therefore, the variants of NODAL and TBX20 identified in this study were likely to be disease-causing.
Figure 2.
Functional analyses of NODAL. (A) Sequence chromatograms of NODAL in the family. (B) The conservation of alignment of the variant in the coding regions between species. Changes in amino acids are highlighted in red. The position of V341 is well-conserved between species. (C) Structure of the human NODAL protein. The position of the variant is indicated by an arrowhead. (D) Western blot analysis of the c-Myc-tagged wildtype NODAL and the variant NODAL (p.V341l) proteins. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH, is used as an internal control. (E) Fold increase in relative luciferase activity in P19 cells transfected with green fluorescent protein (GFP) as control, wildtype NODAL or variant NODAL (p.V341l) expression construct, and p(SBE)4-Luc (N = 5). All values are expressed as the mean ± SD. Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. **, p < 0.01; N.S., not significant.
Figure 3.
Functional analyses of TBX20. (A) Sequence chromatograms of TBX20 in the family. (B) The conservation of alignment of the variant in the coding regions between species. Changes in amino acids are highlighted in red. The position of T331 is well-conserved between species. (C) Structure of the human TBX20 protein. The position of the variant is indicated by an arrowhead. (D) Western blot analysis of the c-Myc-tagged wildtype TBX20 and the variant TBX20 (p.T331A) proteins. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH, is used as an internal control. (E) Fold increase in relative luciferase activity in HeLa cells transfected with green fluorescent protein as control, wildtype TBX20 or variant TBX20 (p.T331A) expression construct, and NPPA-Luc (N = 5). All values are expressed as the mean ± SD. Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. **, p < 0.01; N.S., not significant.
3.4. Both NODAL p.V341l and TBX20 p.T331a fail their function
To assess the impact of the sequence variants p.V341l on the function of NODAL and p.T331A on the function of TBX20, site-directed mutagenesis was performed on human NODAL and TBX20 cDNAs cloned in c-Myc-tagged expression vectors, respectively. Western blot analyses showed that the sizes of both variant proteins of the NODAL p.V341l and the TBX20 p.T331A were same as those of the wildtype proteins (Figures 2D, 3D). Because NODAL, a member of TGF-ß superfamily, activates TGF-ß-regulated SMADs with the cofactors, CRIPTO, CRYPTIC and GDF1, and TBX20, one of the T-box transcription factors, interacts with NKX2.5, GATA4, and GATA5, collaborating to synergistically activate cardiac gene expression, we performed luciferase assay to investigate the transcription activities of the downstream signal signals, SMAD and NPPA. In the luciferase assay, neither NODAL p.V341l variant protein nor TBX20 p.T331A variant protein was able to activate their respective luciferase reporters, p(SBE)4 reporter (14) or NPPA promoter-luciferase plasmid (15) (Figures 2E, 3E). These results demonstrate that both sequence variants may lead to a functional disturbance of the proteins and may affect the regulation of their downstream target genes.
3.5. Nodal and TBX20 double mutant mice exhibit severe perturbation of cardiogenesis
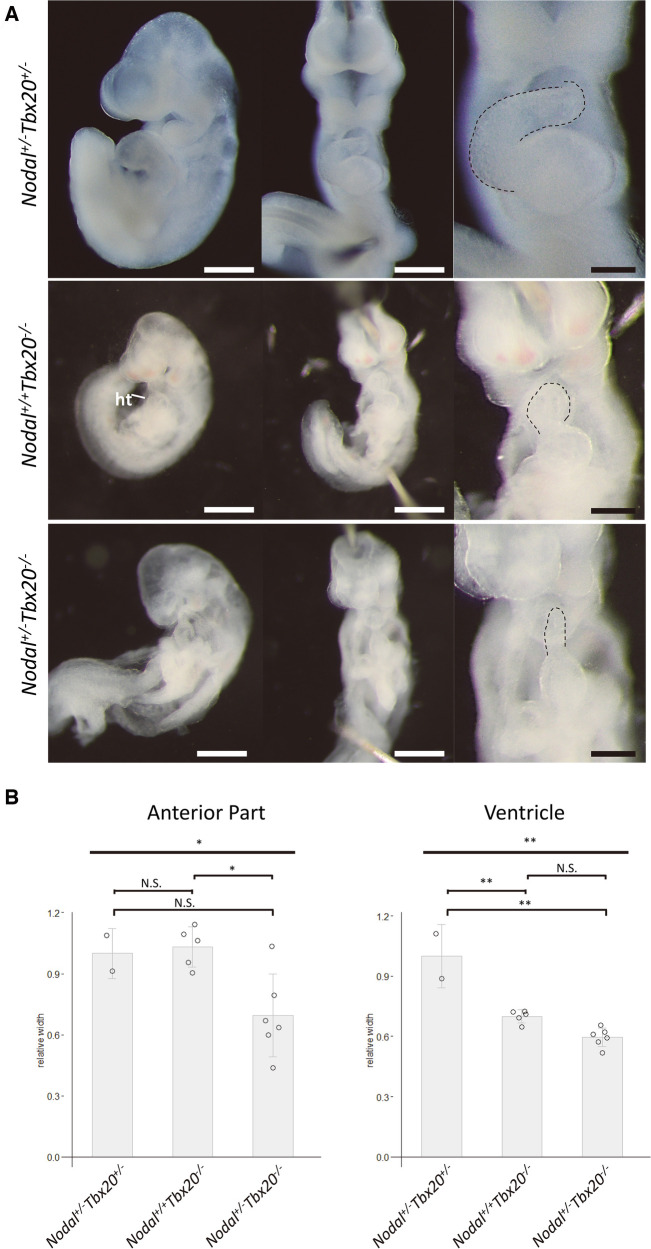
Because the development of CHD in the siblings was considered to be associated with the presence of both NODAL and TBX20 loss-of-function variants, we analyzed the knockout mice of these two genes to assess if any genetic interaction exists. Embryos homozygous null for Nodal die before heart formation is initiated (16), and Tbx20 homozygous null embryos have arrested development at E9.0 and died at E10.5 with failure of heart development (17–19). Therefore, at first, we generated Nodal and Tbx20 double-heterozygous knockout (Nodal+/−Tbx20+/−) mice. Most of the double-heterozygous mutants demonstrated normal cardiogenesis and could survive to adulthood. Although the frequency of double-heterozygous mice around postnatal day 10 was a little lower than that when single-heterozygous mutants of the two genes were bred with each other (data not shown), the cardiac phenotypes of the double-heterozygous mutants were normal and comparable to those of single-heterozygous mutants (Figure 4A). Next, we generated Nodal hetero- and Tbx20 homozygous knockout mice (Nodal+/−Tbx20−/−) and compared their cardiac phenotypes with those of Tbx20 homozygous knockout mice (Nodal+/+Tbx20−/−). Although both mutants exhibited delay of embryogenesis with disturbance of cardiac looping, Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− heart showed more severe hypoplasia of the developing heart tube, especially in the anterior part that gives rise to the outflow tract and right ventricular primordium at E9.5 (dotted line in Figure 4A), whereas the ventricle portions were comparable in both genotypes. The width of the anterior part of developing heart tube was significantly narrower than that in Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− (Figure 4B), suggesting a genetic interaction between Nodal and Tbx20 during early heart development.
Figure 4.
Hypoplasia of anterior part in NODAL heterozygous TBX20 homozygous heart. (A) Left lateral views and frontal views of Nodal+/+Tbx20−/− and Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− hearts at embryonic day 9.5. Dotted lines show the anterior parts of the heart tubes. ht, heart. Scale bars, 500 µm in left and middle panels and 200 µm in right panels. (B) Bar graphs showing the widths of the anterior or the ventricular part of the hearts. The significant decrease in the width of the anterior parts in Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− hearts. All values are expressed as the mean ± SD. Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; N.S., not significant.
To explore the molecular mechanism underlying the genetic interaction of Nodal and Tbx20, expression analyses of a candidate downstream molecule, PITX2, was performed using Tbx20 mutant embryos; PITX2 is a well-known downstream target of NODAL (20–23). Quantitative RT-PCR using primers for Pitx2c exhibited significant decrease of Pitx2c expression in Tbx20 homozygous null mutants compared to that in wildtype (Tbx20+/+) or Tbx20+/− embryos (Figure 5A). Whole-mount in situ hybridization showed a dramatic decrease in the expression of the developing hearts in Tbx20 null embryos (white arrows in Figure 5B), compared to that in wildtype embryos (black arrows in Figure 5B). These results suggest that PITX2 is a common downstream effector of both NODAL and TBX20.
Figure 5.
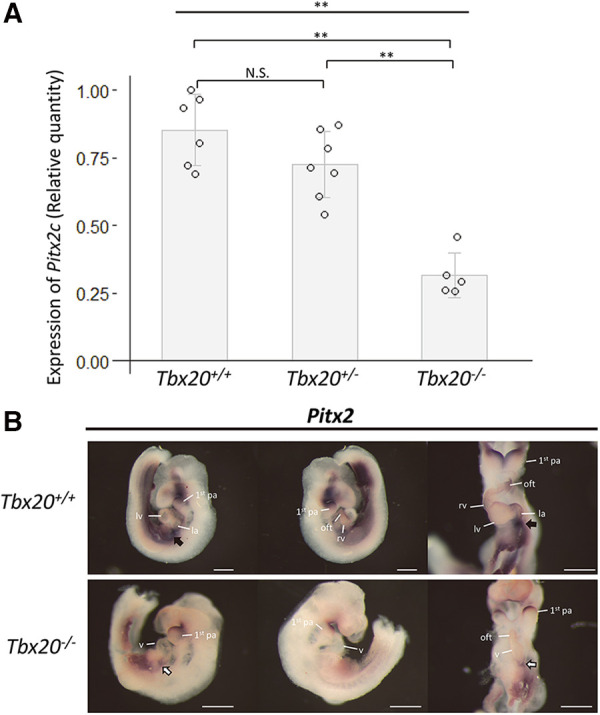
Decreased expression of Pitx2 in TBX20 homozygous embryos. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR results show the significant decrease in Pitx2c expression in Tbx20−/− embryos, compared with that in Tbx20+/+ or Tbx20+/− at embryonic day 9.5. Gapdh was used as internal control. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. **, p < 0.01; N.S., not significant. (B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with Pitx2 antisense riboprobe. Pitx2 expression dramatically decreases in the area of the cardiac inflows of Tbx20−/− embryos (white arrows in the lower panels), compared to that of Tbx20+/+ (black arrows in the upper panels) at embryonic day 9.5. 1st pa; first pharyngeal arch; la, left atrium; lv, left ventricle; oft, outflow tract; rv, right ventricle; v, ventricle. Scale bars, 500 µm.
4. Discussion
In this study, we were challenged to elucidate the genetic origin of an intriguing family with two affected siblings, one miscarriage fetus, and both healthy parents. Although we could not analyze the genome of the miscarried fetus, the genomes of the parents and both siblings were subjected to trio-based gene panel analysis by NGS, resulting in the identification of two heterozygous variants in NODAL (c.1021G > T, p.V341l) and TBX20 (c.991A > G, p.T331A) common to siblings and to just one of parents. These two variants had a very low allele frequency and were suggested to be pathogenic in silico; decreased transcription activities of downstream signaling pathways were observed in vitro. Our analyses of genetically engineered Nodal+/+Tbx20−/− and Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− mouse embryos demonstrated a genetic interaction between Nodal and Tbx20 in vivo where Nodal+/−Tbx20−/− embryos showed more severe defects than did Nodal+/+Tbx20−/− embryos during early heart development. These results suggest that NODAL and TBX20 are complementary for the cardiac development, and a combinatorial loss-of-function of NODAL and TBX20 could be implicated in the etiology of CHD.
The way by which the combinatorial loss-of-function of NODAL and TBX20 can cause complex CHD associated with single ventricular morphology was not fully elucidated in this study. NODAL, a TGFβ-related signaling molecule, is regulated extracellularly by the epidermal growth factor-Cripto-1/FRL-1/Cryptic (EGF-CFC) cofactors and antagonists of the Lefty and Cerberus families of proteins, controlling mesoderm and endoderm formation, the positioning of the anterior-posterior axis, and left-right axis specification (24). Mice homozygous null for Nodal lack a primitive streak, displaying only sporadic formation of some posterior mesoderm (16, 25); the heterozygous mutant has no phenotype. Human genetic studies have shown that some variants of NODAL cause heterotaxy syndrome, which is often associated with single ventricular morphology, with incomplete penetrance (10, 26–28). A recent study demonstrated that Nodal regulates asymmetric morphogenesis of the embryonic heart tube by generating helical shape (29). By contrast, Tbx20, a T-box transcription factor, is expressed in cardiomyocytes throughout heart development, and mice homozygous null for Tbx20 experienced arrested development at E9.5 with hypoplastic unlooped hearts (Figure 4A; Nodal+/+Tbx20−/−), in part due to decreased cardiomyocyte proliferation (17–19). Numerous variants of TBX20 have been reported to be associated with various CHDs, including hypoplastic right heart syndrome, a type of single ventricular morphology, as well as cardiomyopathy (15, 30–34). Although we failed to show any complex CHD in Nodal+/−Tbx20+/− mutant mice, Nodal+/−Tbx20−/−mutants resulted in severe hypoplasia of ventricular primordium and probably defects of early heart looping (Figure 4). Taken together, we speculate that the combinatorial loss-of-function of NODAL and TBX20 could cause hypoplasia of one ventricle and the looping defect, resulting in single ventricular morphology with or without heterotaxy. Why the detailed phenotypes differ between siblings with single ventricle is still obscure, although we speculate other unidentified modifier gene(s), epigenetic factor(s), stochastic event(s), and/or environmental factor(s) might be involved.
In this study, Pitx2 expression was downregulated in Tbx20 null embryos. A previous report suggested that PITX2 might be a direct target of TBX20, using chromatin immunoprecipitation with high throughput sequencing data (35). PITX2 is a downstream target molecule of NODAL (36). Therefore, PITX2 is likely to be a common downstream target of NODAL and TBX20 during the cardiac development. Pitx2 generates three isoforms, Pitx2a, b, and c, and Pitx2c is mainly expressed in the heart, driving the asymmetrical cardiac morphogenesis (20, 22, 23). Pitx2 knockout mice die before birth and demonstrate right isomerism with double outlet right ventricle, reminiscent of our patient with heterotaxy, and atrial/ventricular septal defects. These findings molecularly suggest that downregulation of PITX2 expression caused by an additive or synergistic effect of the combinatorial loss-of-function of NODAL and TBX20 during early heart development, probably the looping stage, may result in single ventricular morphology and heterotaxy.
Other than the variants in NODAL and TBX20, we also detected variants in the two genes CASQ2 and SYNE1, common to the siblings. Calsequestrin 2 encoded by CASQ2 is localized in the sarcoplasmic reticulum in cardiomyocytes, functioning as a Ca2+ binding protein that stores Ca2+ for cardiomyocyte contraction (37). Mutations in CASQ2 cause fatal ventricular arrythmia, referred to as catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 2 (CPVT2) (38, 39), and the C-terminal end of this gene, where the variant (E388G) we found is located, is known to be functionally important (40). However, they have not been implicated in CHD. SYNE1 encodes a spectrin repeat-containing nuclear envelope, localized to the nuclear membrane in skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells (41, 42). Syne1-knockout mice exhibited decreased survival rates, growth retardation, and a significantly lower exercise capacity due to nuclear dysfunction in skeletal muscle, but no cardiac phenotype (43). Mutations in SYNE1 cause neuromuscular diseases, including spinocerebellar ataxia 8 (44, 45), Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 4 (46), and arthrogryposis multiplex congenita 3 (47), and there is a report that the variants on SYNE1 are involved in skeletal muscle disorder and cardiomyopathy (46). It may be possible that variants of SYNE1 can be associated with CHD as MYH7, a previously known to be a cardiomyopathy causing gene, is recently reported to be associated with CHD (48). Given these studies, it is a limitation of this study that we cannot completely rule out the effects of these CASQ2 and SYNE1 variants as well as the variants of genes that were not included in our gene analysis panel. They might be genetic modifiers for the phenotypes of siblings in our family, although their contributions are considered to be weak.
In conclusion, via a combination of NGS and in vitro and in vivo analyses, we show possible evidence of digenic inheritance in a family with complex CHD. Such an approach may provide insights into the pathogenesis of CHD with multifactorial nature.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients, their family members, and the referring physicians; Hiroshi Hamada for providing Nodal knockout mice and CRIPTO, CRYPTIC, and GDF1 expression vectors; Jun K. Takeuchi for providing cDNA of Pitx2 for digoxigenin-labeled riboprobe; and Ayami Kuramochi and Mayumi Suzuki for providing technical support. We are also grateful to the Collaborative Research Resources, School of Medicine, Keio University, for providing technical support. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under grant number JP20ek0109487. KU, JM, YW, ON, and HY were supported by JSPS KAKENHI [grant numbers JP17K10153 to KU, JP19K08352 to JM, JP19H03398 to YW, JP21H02890 to ON, and JP16H05359 to HY]. YW was supported by a grant from The Japan Foundation for Pediatric Research.
Data availability statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the main text or supplementary material. We submitted the novel NODAL and CASQ2 variant data in ClinVar and GenBank, respectively. Any remaining information is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Internal Ethics Committee of Keio University School of Medicine. Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardian/next of kin. The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Keio University and of the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)' legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YY, KK, RA, JM, KF, KK, HY, and KU designed the study. YY, RA, KK, YK, YS, and KU performed the experiments and analyzed the data. YW and ON generated and provided Tbx20 deletion mice. YY, KK, RA, and KU wrote the manuscript. HY revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
HY receives research grants from Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan Ltd. and Abbvie Japan Inc. The other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2023.1135141/full#supplementary-material.
References
- 1.Kodo K, Uchida K, Yamagishi H. Genetic and cellular interaction during cardiovascular development implicated in congenital heart diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:653244. 10.3389/fcvm.2021.653244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Williams K, Carson J, Lo C. Genetics of congenital heart disease. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:879. 10.3390/biom9120879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha KE, Banks E, Fennell T, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. (2016) 536:285–91. 10.1038/nature19057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Xue Y, Ankala A, Wilcox WR, Hegde MR. Solving the molecular diagnostic testing conundrum for Mendelian disorders in the era of next-generation sequencing: single-gene, gene panel, or exome/genome sequencing. Genet Med. (2015) 17:444–51. 10.1038/gim.2014.122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tanaka C, Sakuma R, Nakamura T, Hamada H, Saijoh Y. Long-range action of nodal requires interaction with GDF1. Genes Dev. (2007) 21:3272–82. 10.1101/gad.1623907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu Q, Kanata K, Saba R, Deng CX, Hamada H, Saga Y. Nodal/activin signaling promotes male germ cell fate and suppresses female programming in somatic cells. Development (Cambridge). (2013) 140:291–300. 10.1242/dev.087882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ihara D, Watanabe Y, Seya D, Arai Y, Isomoto Y, Nakano A, et al. Expression of Hey2 transcription factor in the early embryonic ventricles is controlled through a distal enhancer by Tbx20 and Gata transcription factors. Dev Biol. (2020) 461:124–31. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Uchida K, Aramaki M, Nakazawa M, Yamagishi C, Makino S, Fukuda K, et al. Gene knock-outs of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors types 1 and 2 result in perturbation of cardiogenesis. PLoS One. (2010) 5:e12500. 10.1371/journal.pone.0012500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Takeuchi JK, Mileikovskaia M, Koshiba-Takeuchi K, Heidt AB, Mori AD, Arruda EP, et al. Tbx20 dose-dependently regulates transcription factor networks required for mouse heart and motoneuron development. Development. (2005) 132:2463–74. 10.1242/dev.01827 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mohapatra B, Casey B, Li H, Ho-Dawson T, Smith L, Fernbach SD, et al. Identification and functional characterization of NODAL rare variants in heterotaxy and isolated cardiovascular malformations. Hum Mol Genet. (2009) 18:861–71. 10.1093/hmg/ddn411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stennard FA, Costa MW, Elliott DA, Rankin S, Haast SJP, Lai D, et al. Cardiac T-box factor Tbx20 directly interacts with Nkx2-5, GATA4, and GATA5 in regulation of gene expression in the developing heart. Dev Biol. (2003) 262:206–24. 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00385-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yoshida A, Morisaki H, Nakaji M, Kitano M, Kim K, Sagawa K, et al. Genetic mutation analysis in Japanese patients with non-syndromic congenital heart disease. J Hum Genet. (2016) 61:157–62. 10.1038/jhg.2015.126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Qian L, Mohapatra B, Akasaka T, Liu J, Ocorr K, Towbin JA, et al. Transcription factor neuromancer/TBX20 is required for cardiac function in Drosophila with implications for human heart disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2008) 105:19833–8. 10.1073/pnas.0808705105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kumar A, Novoselov V, Celeste AJ, Wolfman NM, ten Dijke P, Kuehn MR. Nodal signaling uses activin and transforming growth factor-β receptor-regulated smads. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:656–61. 10.1074/JBC.M004649200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kodo K, Ong S-G, Jahanbani F, Termglinchan V, Hirono K, InanlooRahatloo K, et al. iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes reveal abnormal TGF-β signalling in left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Nat Cell Biol. (2016) 18:1031–42. 10.1038/ncb3411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Conlon FL, Lyons KM, Takaesu N, Barth KS, Kispert A, Herrmann B, et al. A primary requirement for nodal in the formation and maintenance of the primitive streak in the mouse. Development. (1994) 120:1919–28. 10.1242/dev.120.7.1919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cai C-L, Zhou W, Yang L, Bu L, Qyang Y, Zhang X, et al. T-box genes coordinate regional rates of proliferation and regional specification during cardiogenesis. Development. (2005) 132:2475–87. 10.1242/dev.01832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Singh MK, Christoffels VM, Dias JM, Trowe M-O, Petry M, Schuster-Gossler K, et al. Tbx20 is essential for cardiac chamber differentiation and repression of Tbx2. Development. (2005) 132:2697–707. 10.1242/dev.01854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stennard FA, Costa MW, Lai D, Biben C, Furtado MB, Solloway MJ, et al. Murine T-box transcription factor Tbx20 acts as a repressor during heart development, and is essential for adult heart integrity, function and adaptation. Development. (2005) 132:2451–62. 10.1242/dev.01799 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Campione M, Steinbeisser H, Schweickert A, Deissler K, van Bebber F, Lowe LA, et al. The homeobox gene Pitx2: mediator of asymmetric left-right signaling in vertebrate heart and gut looping. Development. (1999) 126:1225–34. 10.1242/dev.126.6.1225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lin CR, Kioussi C, O’Connell S, Briata P, Szeto D, Liu F, et al. Pitx2 regulates lung asymmetry, cardiac positioning and pituitary and tooth morphogenesis. Nature. (1999) 401:279–82. 10.1038/45803 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Piedra ME, Icardo JM, Albajar M, Rodriguez-Rey JC, Ros MA. Pitx2 participates in the late phase of the pathway controlling left-right asymmetry. Cell. (1998) 94:319–24. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81475-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Logan M, Pagán-Westphal SM, Smith DM, Paganessi L, Tabin CJ. The transcription factor pitx2 mediates situs-specific morphogenesis in response to left-right asymmetric signals. Cell. (1998) 94:307–17. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81474-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schier AF, Shen MM. Nodal signalling in vertebrate development. Nature. (2000) 403:385–9. 10.1038/35000126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhou X, Sasaki H, Lowe L, Hogan BLM, Kuehn MR. Nodal is a novel TGF-β-like gene expressed in the mouse node during gastrulation. Nature. (1993) 361:543–7. 10.1038/361543a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yadav ML, Ranjan P, Das P, Jain D, Kumar A, Mohapatra B. Implication of rare genetic variants of NODAL and ACVR1B in congenital heart disease patients from Indian population. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 409:112869. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roessler E, Pei W, Ouspenskaia MV, Karkera JD, Veléz JI, Banerjee-Basu S, et al. Cumulative ligand activity of NODAL mutations and modifiers are linked to human heart defects and holoprosencephaly. Mol Genet Metab. (2009) 98:225–34. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.05.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barnes RM, Black BL. Nodal signaling and congenital heart defects. In: Nakanishi T, Markwald RR, Baldwin HS, Keller BB, Srivastava D, Yamagishi H, editors. Etiology and morphogenesis of congenital heart disease. Tokyo: Springer Japan; (2016). p. 183–92. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-54628-3_24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Desgrange A, le Garrec J-F, Bernheim S, Bønnelykke TH, Meilhac SM. Transient nodal signaling in left precursors coordinates opposed asymmetries shaping the heart loop. Dev Cell. (2020) 55:413–431.e6. 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.10.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang E, Nie Y, Fan X, Zheng Z, Gu H, Zhang H, et al. Minor alleles of genetic variants in second heart field increase the risk of hypoplastic right heart syndrome. J Genet. (2019) 98:45. 10.1007/s12041-019-1092-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhao C-M, Song H-M, Wang J, Xu W-J, Jiang J-F, Qiu X-B, et al. TBX20 loss-of-function mutation associated with familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM). (2016) 54:325–32. 10.1515/cclm-2015-0328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kirk EP, Sunde M, Costa MW, Rankin SA, Wolstein O, Castro ML, et al. Mutations in cardiac T-box factor gene TBX20 are associated with diverse cardiac pathologies, including defects of septation and valvulogenesis and cardiomyopathy. Am J Human Genet. (2007) 81:280–91. 10.1086/519530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vasilescu C, Ojala TH, Brilhante V, Ojanen S, Hinterding HM, Palin E, et al. Genetic basis of severe childhood-onset cardiomyopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 72:2324–38. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Packham EA. T-box genes in human disorders. Hum Mol Genet. (2003) 12:R37–44. 10.1093/hmg/ddg077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Boogerd CJ, Zhu X, Aneas I, Sakabe N, Zhang L, Sobreira DR, et al. Tbx20 is required in mid-gestation cardiomyocytes and plays a central role in atrial development. Circ Res. (2018) 123:428–42. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lowe LA, Yamada S, Kuehn MR. Genetic dissection of nodal function in patterning the mouse embryo. Development. (2001) 128:1831–43. 10.1242/dev.128.10.1831 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yano K, Zarain-Herzberg A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calsequestrins: structural and functional properties. Mol Cell Biochem. (1994) 135:61–70. 10.1007/BF00925961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lahat H, Pras E, Olender T, Avidan N, Ben-Asher E, Man O, et al. A missense mutation in a highly conserved region of CASQ2 is associated with autosomal recessive catecholamine-induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in Bedouin families from Israel. Am J Hum Genet. (2001) 69:1378–84. 10.1086/324565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kim CW, Aronow WS, Dutta T, Frenkel D, Frishman WH. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Cardiol Rev. (2020) 28:325–31. 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sanchez EJ, Munske GR, Criswell A, Milting H, Dunker AK, Kang C. Phosphorylation of human calsequestrin: implications for calcium regulation. Mol Cell Biochem. (2011) 353:195–204. 10.1007/s11010-011-0787-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Apel ED, Lewis RM, Grady RM, Sanes JR. Syne-1, A dystrophin- and klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:31986–95. 10.1074/jbc.M004775200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang Q, Skepper JN, Yang F, Davies JD, Hegyi L, Roberts RG, et al. Nesprins: a novel family of spectrin-repeat-containing proteins that localize to the nuclear membrane in multiple tissues. J Cell Sci. (2001) 114:4485–98. 10.1242/jcs.114.24.4485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang J, Felder A, Liu Y, Guo LT, Lange S, Dalton ND, et al. Nesprin 1 is critical for nuclear positioning and anchorage. Hum Mol Genet. (2010) 19:329–41. 10.1093/hmg/ddp499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gros-Louis F, Dupré N, Dion P, Fox MA, Laurent S, Verreault S, et al. Mutations in SYNE1 lead to a newly discovered form of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia. Nat Genet. (2007) 39:80–5. 10.1038/ng1927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dupré N, Gros-Louis F, Chrestian N, Verreault S, Brunet D, de Verteuil D, et al. Clinical and genetic study of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia type 1. Ann Neurol. (2007) 62:93–8. 10.1002/ana.21143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhang Q, Bethmann C, Worth NF, Davies JD, Wasner C, Feuer A, et al. Nesprin-1 and -2 are involved in the pathogenesis of emery–dreifuss muscular dystrophy and are critical for nuclear envelope integrity. Hum Mol Genet. (2007) 16:2816–33. 10.1093/hmg/ddm238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Laquerriere A, Maluenda J, Camus A, Fontenas L, Dieterich K, Nolent F, et al. Mutations in CNTNAP1 and ADCY6 are responsible for severe arthrogryposis multiplex congenita with axoglial defects. Hum Mol Genet. (2014) 23:2279–89. 10.1093/hmg/ddt618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ritter A, Leonard J, Gray C, Izumi K, Levinson K, Nair DR, et al. MYH7 Variants cause complex congenital heart disease. Am J Med Genet A. (2022) 188:2772–6. 10.1002/ajmg.a.62766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the main text or supplementary material. We submitted the novel NODAL and CASQ2 variant data in ClinVar and GenBank, respectively. Any remaining information is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.