Abstract
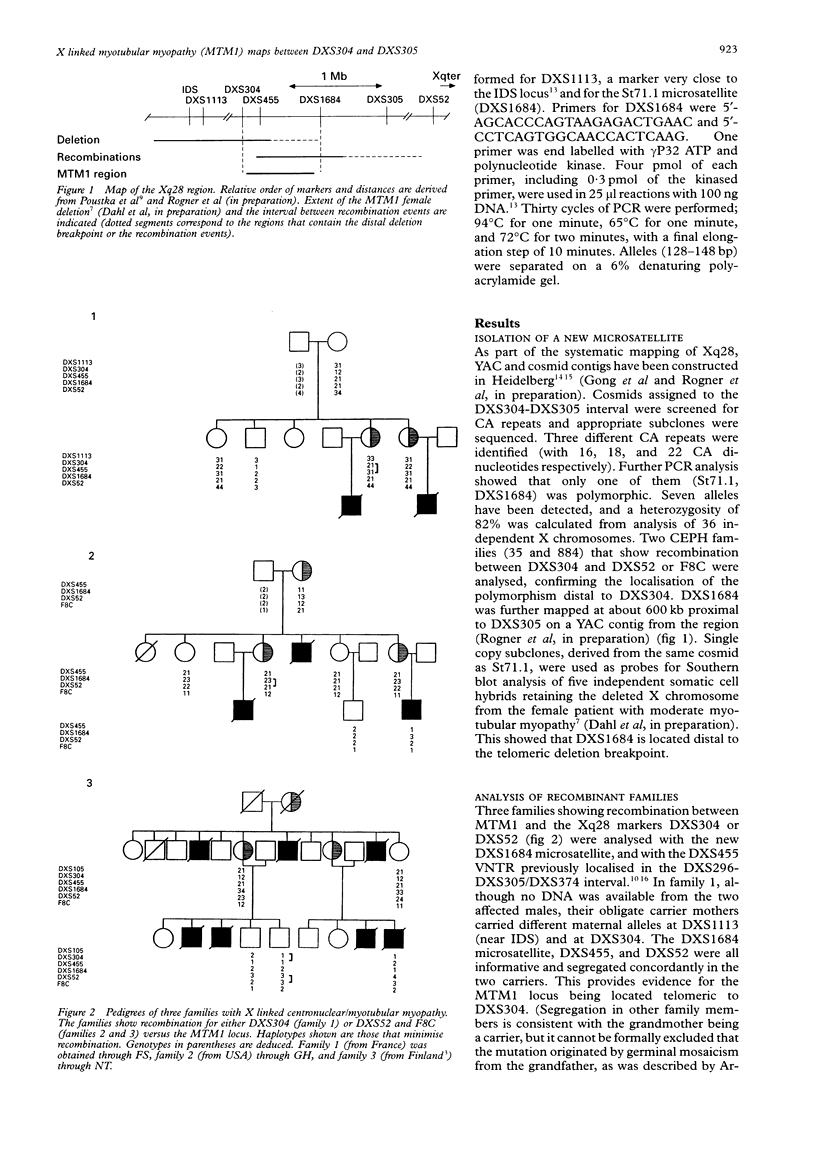
The locus for X linked recessive myotubular myopathy (MTM1) has previously been mapped to Xq28 by linkage analysis. We report two new families that show recombination between MTM1 and either DXS304 or DXS52. These families and a third previously described recombinant family were analysed with two highly polymorphic markers in the DXS304-DXS52 interval, the DXS455 VNTR and a newly characterised microsatellite, DXS1684 (82% heterozygosity). These markers did not recombine with MTM1 in the three families. Together with the recent mapping of an interstitial X chromosome deletion in a female patient with moderate signs of myotubular myopathy, our data suggest the following order of loci in Xq28: cen-DXS304-(DXS455, MTM1)-DXS1684-DXS305-DXS52-tel. This considerably refined localisation of the MTM1 locus should facilitate positional cloning of the gene. The availability of highly polymorphic and very closely linked markers will markedly improve carrier and prenatal diagnosis of MTM1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arveiler B., de Saint-Basile G., Fischer A., Griscelli C., Mandel J. L. Germ-line mosaicism simulates genetic heterogeneity in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):906–911. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consalez G. G., Stayton C. L., Freimer N. B., Goonewardena P., Brown W. T., Gilliam T. C., Warren S. T. Isolation and characterization of a highly polymorphic human locus (DXS455) in proximal Xq28. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnfors C., Larsson H. E., Oldfors A., Kyllerman M., Gustavson K. H., Bjursell G., Wahlström J. X-linked myotubular myopathy: a linkage study. Clin Genet. 1990 May;37(5):335–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Oberlé I., Arveiler B., Hanauer A., Vidaud M., Mandel J. L. Improved DNA markers for efficient analysis of fragile X families. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Sankila E. M., Miao J., Somer M., Salonen R., Rapola J., de la Chapelle A. X linked neonatal myotubular myopathy: one recombination detected with four polymorphic DNA markers from Xq28. J Med Genet. 1990 May;27(5):288–291. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.5.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liechti-Gallati S., Müller B., Grimm T., Kress W., Müller C., Boltshauser E., Moser H., Braga S. X-linked centronuclear myopathy: mapping the gene to Xq28. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(4):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90096-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Dietrich A., Langenstein G., Toniolo D., Warren S. T., Lehrach H. Physical map of human Xq27-qter: localizing the region of the fragile X mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8302–8306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Holman K., Kozman H., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S., Mulley J., Sutherland G. R. Fragile X syndrome: genetic localisation by linkage mapping of two microsatellite repeats FRAXAC1 and FRAXAC2 which immediately flank the fragile site. J Med Genet. 1991 Dec;28(12):818–823. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.12.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr J., Lamont M., Iselius L., Harvey J., Heckmatt J. A linkage study of a large pedigree with X linked centronuclear myopathy. J Med Genet. 1990 May;27(5):281–283. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.5.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Williams H., Cole G., Roberts K., Clarke A., Liechti-Gallati S., Braga S., Gerber A., Meier C., Moser H. X linked neonatal centronuclear/myotubular myopathy: evidence for linkage to Xq28 DNA marker loci. J Med Genet. 1990 May;27(5):284–287. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.5.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Dahl N., Oberlé I., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L., Malmgren H., Pettersson U. The polymorphic marker DXS304 is within 5 centimorgans of the fragile X locus. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):797–801. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. A new polymorphic marker very closely linked to DXS52 in the q28 region of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00288280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallgren-Pettersson C., Thomas N. S. Report on the 20th ENMC sponsored international workshop: myotubular/centronuclear myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 1994 Jan;4(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(94)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C., Oudet C., Johnson S., Pilia G., Schlessinger D., Hanauer A. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism close to IDS gene in Xq27.3-q28 (DXS1113). Hum Mol Genet. 1993 May;2(5):612–612. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.5.612-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


