Full text
PDF
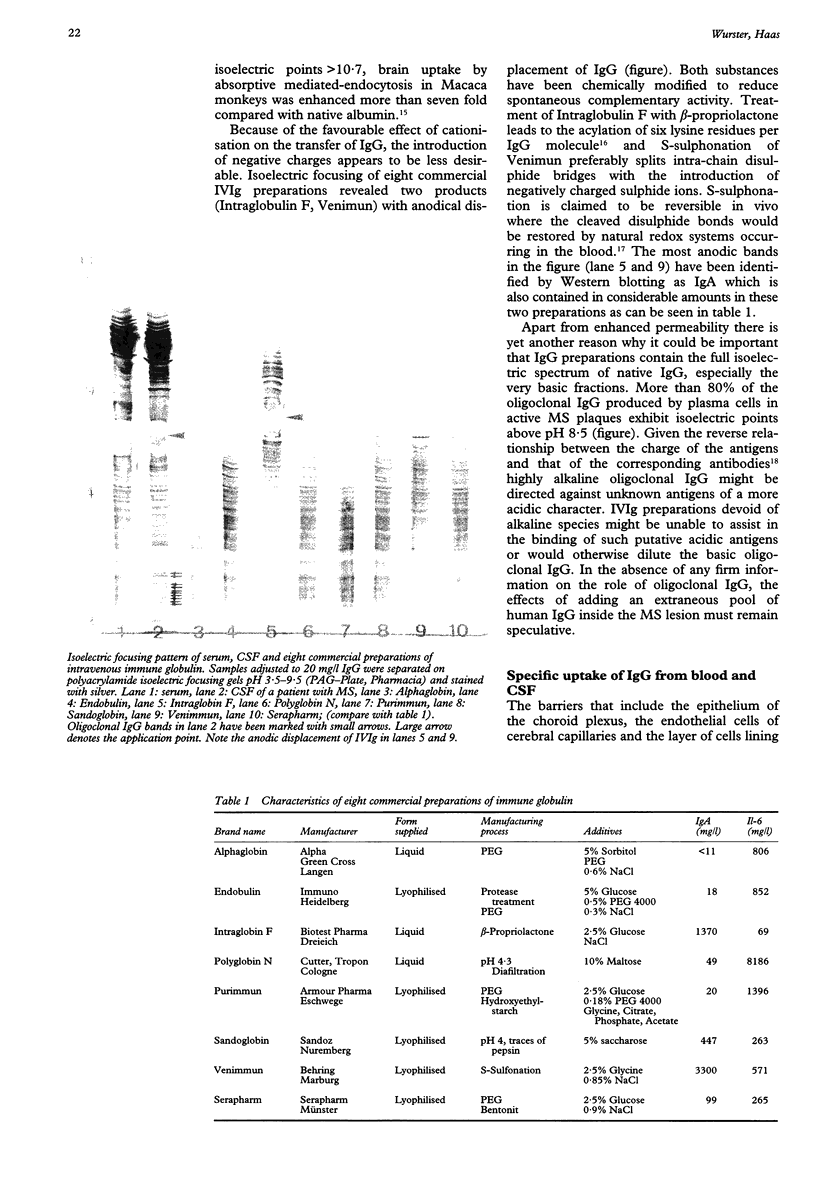



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Kawasugi K. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in various medical conditions. A Japanese experience. Cancer. 1991 Sep 15;68(6 Suppl):1454–1459. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910915)68:6+<1454::aid-cncr2820681409>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achiron A., Pras E., Gilad R., Ziv I., Mandel M., Gordon C. R., Noy S., Sarova-Pinhas I., Melamed E. Open controlled therapeutic trial of intravenous immune globulin in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1992 Dec;49(12):1233–1236. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530360031013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasczyk R., Westhoff U., Grosse-Wilde H. Soluble CD4, CD8, and HLA molecules in commercial immunoglobulin preparations. Lancet. 1993 Mar 27;341(8848):789–790. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90563-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges L. F., Elliott P. J., Gill R., Iversen S. D., Iversen L. L. Selective extraction of small and large molecules from the cerebrospinal fluid by Purkinje neurons. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):346–348. doi: 10.1126/science.2580350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosi V., Lombardi M., Piccolo G., Erbetta A. Treatment of myasthenia gravis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 Aug;84(2):81–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb04912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F., Knopf P. M. Cervical lymphatics, the blood-brain barrier and the immunoreactivity of the brain: a new view. Immunol Today. 1992 Dec;13(12):507–512. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlicek M., Liszka U., Jellinger K., Mohn-Staudner A., Lintner F., Grisold W. Circulating antineuronal antibodies reach neurons in vivo: an autopsy study. J Neurol. 1992 Aug;239(7):407–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00812161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M. Manipulating the immune system with immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 9;326(2):107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201093260206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlendsson K., Swartz T., Dwyer J. M. Successful reversal of echovirus encephalitis in X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia by intraventricular administration of immunoglobulin. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):351–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian R. H., Petroff G. Intraneuronal IgG in the central nervous system: uptake by retrograde axonal transport. Neurology. 1987 Nov;37(11):1780–1784. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.11.1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian R. H., Ritchie T. C. Intraneuronal IgG in the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1986 May;73(3):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K. Protein size and cerebrospinal fluid composition. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Dec 15;52(24):1158–1164. doi: 10.1007/BF01466734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graus F., Illa I., Agusti M., Ribalta T., Cruz-Sanchez F., Juarez C. Effect of intraventricular injection of an anti-Purkinje cell antibody (anti-Yo) in a guinea pig model. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Nov;106(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90198-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Giffels J. Study of protein characteristics that influence entry into the cerebrospinal fluid of normal mice and mice with encephalitis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):289–295. doi: 10.1172/JCI110616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronski P., Hofstaetter T., Kanzy E. J., Lüben G., Seiler F. R. S-sulfonation: a reversible chemical modification of human immunoglobulins permitting intravenous application. I. Physicochemical and binding properties of S-sulfonated and reconstituted IgG. Vox Sang. 1983;45(2):144–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Tsur V., Shalev R. S., Kazir E., Engelhard D., Amir N. Intravenous high-dose gammaglobulins for intractable childhood epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1993 Sep;88(3):204–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1993.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez E. G., Banks W. A., Kastin A. J. Murine tumor necrosis factor alpha is transported from blood to brain in the mouse. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Sep;47(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fallis R. J., Dawson D. M., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. Immunologic responses of progressive multiple sclerosis patients treated with an anti-T-cell monoclonal antibody, anti-T12. Neurology. 1986 Jun;36(6):777–784. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. MS: a CNS and systemic autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):104–107. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. P., Munro P. M., MacKenzie F., Kesselring J., Tofts P. S., du Boulay E. P., Landon D. N., McDonald W. I. Duration and selectivity of blood-brain barrier breakdown in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis studied by gadolinium-DTPA and protein markers. Brain. 1990 Apr;113(Pt 2):365–378. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaveri S. V., Dietrich G., Hurez V., Kazatchkine M. D. Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Nov;86(2):192–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda Y., Takashima H., Ikeda A., Endo C., Neshige R., Kakigi R., Shibasaki H. Treatment of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy with high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin. J Neurol. 1991 Sep;238(6):309–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00315327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll J. W., Henzen-Logmans S. C., Van der Meché F. G., Vecht C. H. Early diagnosis and intravenous immune globulin therapy in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 Jan;56(1):112–112. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu I., Kreuter F., Prosiegel M., Pfaffenrath V., Autenrieth W., Bauer H. Liquorgängigkeit von therapeutischen Immunglobulinen der IgG-Klasse bei infektiös-entzündlichen Erkrankungen des ZNS. Fortschr Med. 1981 Nov 5;99(41):1719–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peress N. S., Roxburgh V. A., Gelfand M. C. Binding sites for immune components in human choroid plexus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Mar;24(3):520–526. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiber H., Felgenhauer K. Protein transfer at the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier and the quantitation of the humoral immune response within the central nervous system. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Mar 30;163(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman J., Fleit H. B., Peress N. S. Characterization of immunoglobulin G-Fc receptor activity in the outflow system of the cerebrospinal fluid. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Jun;248(3):599–605. doi: 10.1007/BF00216489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan W., Fasold H. Intravenöses Human-Immunglobulin durch chemische Modifizierung mit beta-Propiolacton. Radiochemische Untersuchungen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(12):2090–2093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton C. A., Ballow M. Safety of intravenous immunoglobulin. Arch Neurol. 1993 Feb;50(2):135–136. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540020013009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofts P. S., Kermode A. G. Blood brain barrier permeability in multiple sclerosis using labelled DTPA with PET, CT and MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Aug;52(8):1019–1020. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.8.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W., Potvin A. R., Fleming J. O., Murthy K. N., Levy J., Syndulko K., Potvin J. H. Multiple sclerosis: measurement and validation of central nervous system IgG synthesis rate. Neurology. 1980 Mar;30(3):240–244. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triguero D., Buciak J. L., Pardridge W. M. Cationization of immunoglobulin G results in enhanced organ uptake of the protein after intravenous administration in rats and primate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jul 1;258(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler C., Ulvestad E., Grundt I., Conti G., Nyland H., Matre R., Pleasure D. Fc receptor for IgG (FcR) on rat microglia. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jan;49(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler C., Ulvestad E., Grundt I., Conti G., Nyland H., Matre R., Pleasure D. Fc receptor for IgG (FcR) on rat microglia. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jan;49(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., Shapshak P., Graves M. C., Imagawa D. T., Tourtellotte W. W. Isoelectric point restriction of cerebrospinal fluid and serum IgG antibodies to measles virus polypeptides in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Apr;14(3):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Purification of autoantibodies to myelin basic protein by antigen specific affinity chromatography from cerebrospinal fluid IgG of multiple sclerosis patients. Immunoreactivity studies with human myelin basic protein. J Neurol Sci. 1991 May;103(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90289-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bois M. H., Arndt J. W., van der Velde E. A., van der Lubbe P. A., Westedt M. L., Pauwels E. K., Breedveld F. C. 99mTc human immunoglobulin scintigraphy--a reliable method to detect joint activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Sep;19(9):1371–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn P. A., Brand A., Strengers P. F., Meulstee J., Vermeulen M. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):209–212. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Engelen B. G., Hommes O. R., Pinckers A., Cruysberg J. R., Barkhof F., Rodriguez M. Improved vision after intravenous immunoglobulin in stable demyelinating optic neuritis. Ann Neurol. 1992 Dec;32(6):834–835. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meché F. G., Schmitz P. I. A randomized trial comparing intravenous immune globulin and plasma exchange in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Dutch Guillain-Barré Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1123–1129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]