Abstract
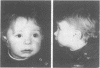
At least 16 cases of inversion tandem duplications of the short arm of chromosome 8 have been reported. Structural rearrangements of chromosome 8 have made it possible to localise the gene for glutathione reductase (GSR) to 8p21.1. We report here on a 16 month old boy with mental retardation with partial trisomy 8 owing to a de novo inv dup(8)(p12----p23.1).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dill F. J., Schertzer M., Sandercock J., Tischler B., Wood S. Inverted tandem duplication generates a duplication deficiency of chromosome 8p. Clin Genet. 1987 Aug;32(2):109–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Dereymaker A. M., Hoefnagels M., Heremans G., Marien J., van den Berghe H. Partial 8p trisomy due to interstitial duplication: karyotype: 46, XX, inv dup(8) (p21.1----p22). Clin Genet. 1985 Dec;28(6):546–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Francke U. Gene dose effect: regional mapping of human glutathione reductase on chromosome 8. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(5):282–286. doi: 10.1159/000130723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K., Junien C., Despoisse S., Bernsen A., Thelle T., Friedrich U., de la Chapelle A. Inverted tandem duplication of the short arm of chromosome 8: a non-random de novo structural aberration in man. Localization of the gene for glutathione reductase in subband 8p21.1. Ann Genet. 1982;25(4):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]