Abstract
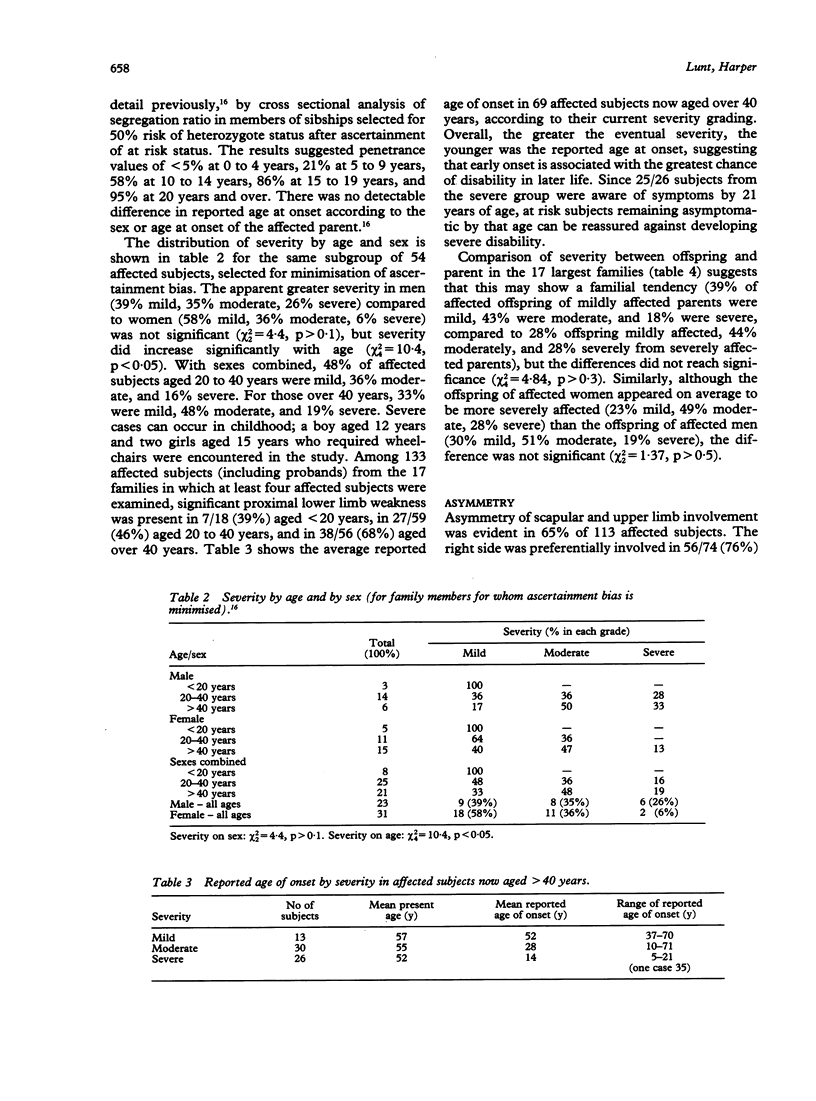
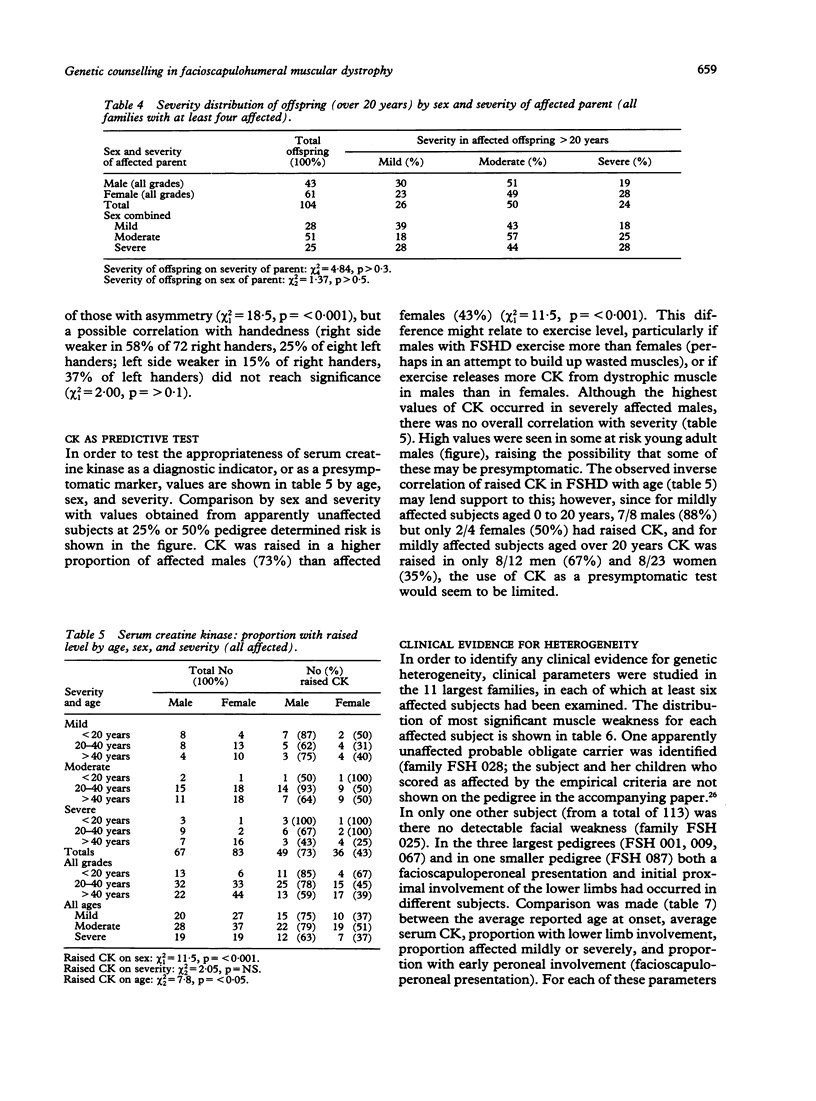
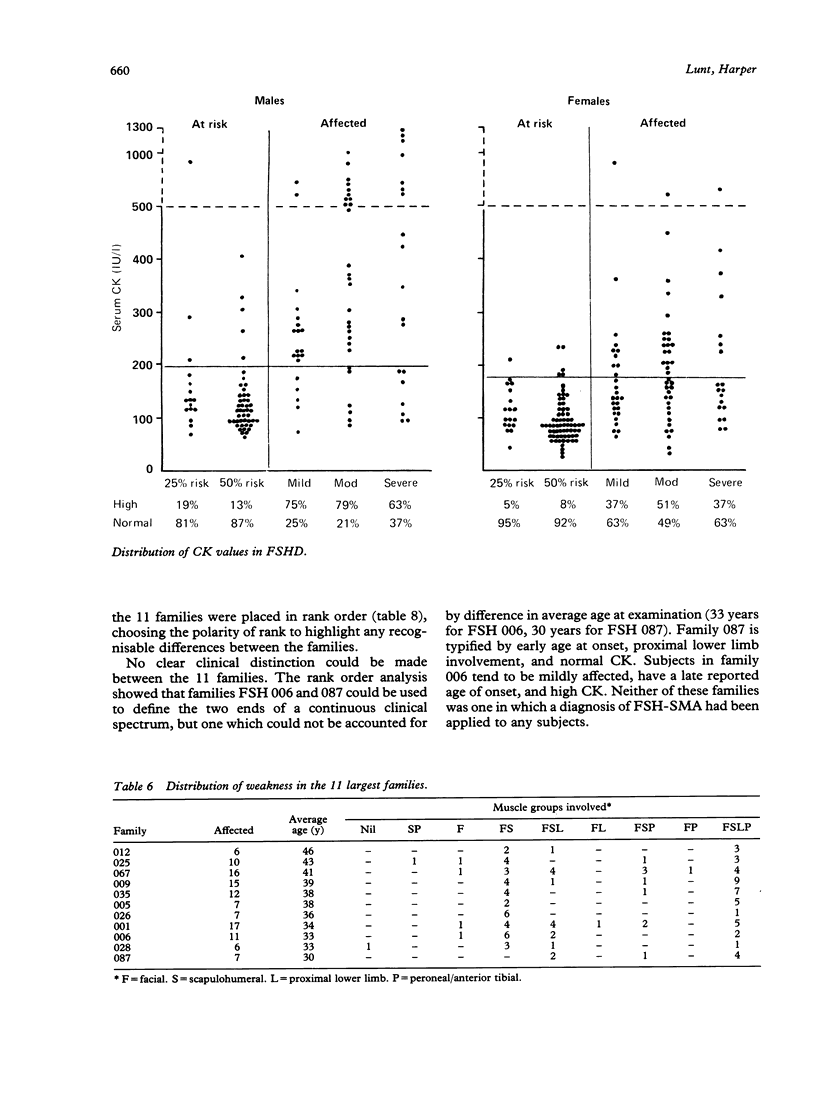
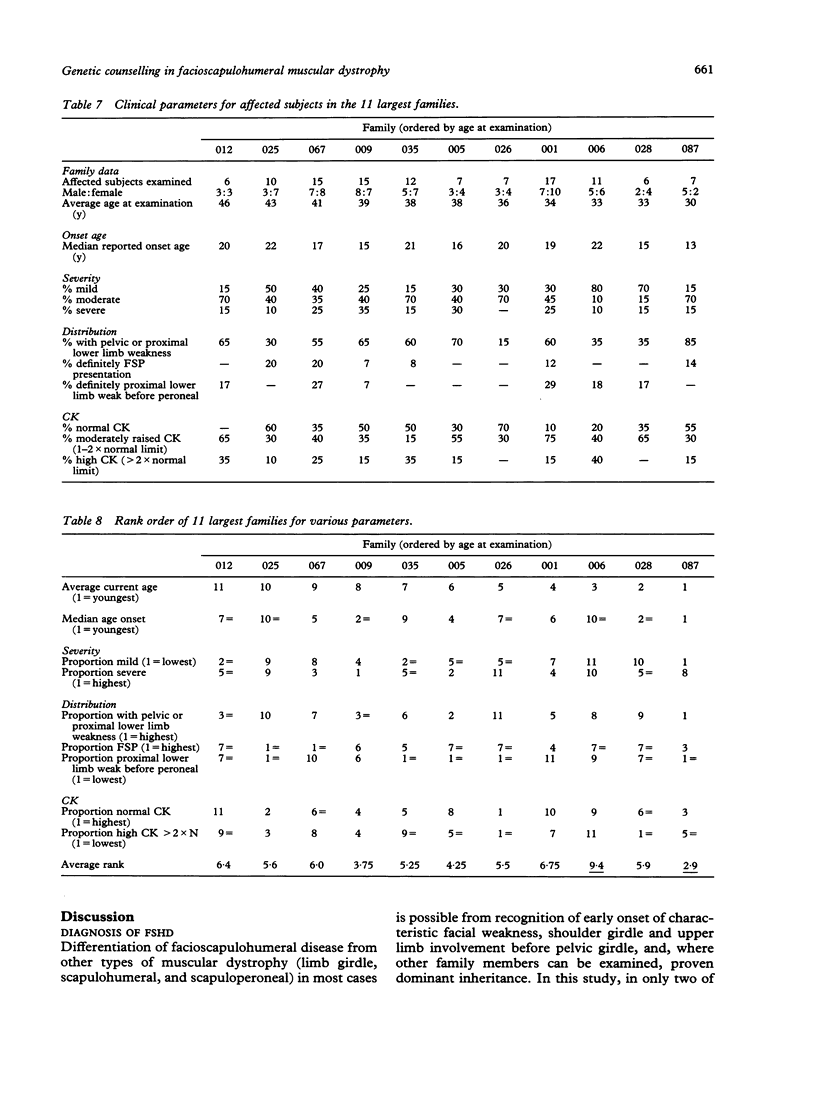
Clinical data are presented from a survey of 41 families with dominantly inherited facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) in which over 500 family members were examined, including 168 affected subjects. New mutation could account for six isolated cases. Results suggest that 33% of heterozygotes over 40 years are mildly affected and a majority develop significant lower limb weakness; 19% over 40 years require wheelchairs. Presymptomatic testing of serum creatine kinase level (CK) is limited as a raised level occurs in only 80% of affected males under 40 years and 48% of affected women. Distribution of weakness, severity, age at onset, and CK varied between subjects, but provided no clinical evidence for genetic heterogeneity in a comparison between the 11 largest families. The conclusion of genetic homogeneity in FSHD, including subjects previously diagnosed as FSH type spinal muscular atrophy, is strongly supported by recent genetic linkage data.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. O., Marzulo D. C., Hans M. B. Infantile facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: new observations. Acta Neurol Scand. 1986 Jul;74(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1986.tb04625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Davies K. E., Gardner-Medwin D., Burn J., Hudgson P. Xp21 DNA probe in diagnosis of muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet. 1989 Feb 25;1(8635):443–443. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland S. A., Howard R. C. Thoracoscapular fusion for facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978 Nov;60-B(4):547–551. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.60B4.711807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenichel G. M., Emery E. S., Hunt P. Neurogenic atrophy simulating facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. A dominant form. Arch Neurol. 1967 Sep;17(3):257–260. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470270035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons R. B., Gurwin E. B., Bird A. C. Retinal vascular abnormalities in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. A general association with genetic and therapeutic implications. Brain. 1987 Jun;110(Pt 3):631–648. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Toyokura Y. Chronic spinal muscular atrophy of facioscapulohumeral type. J Med Genet. 1976 Aug;13(4):285–289. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.4.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. P. Creatine phosphokinase in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Br Med J. 1971 Aug;3(5772):464–465. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5772.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov V. M., Bogorodinsky D. K., Skorometz A. A. The myogenic scapulo-peroneal syndrome. Muscular dystrophy in the K. kindred: clinical study and genetics. Clin Genet. 1976 Jul;10(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb00007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov V. M., Bogorodinsky D. K., Znoyko Z. V., Skorometz A. A. The facio-scapulo-limb (or the facioscapulohumeral) type of muscular dystrophy. Clinical and genetic study of 200 cases. Eur Neurol. 1974;11(4):236–260. doi: 10.1159/000114323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf B. R., Bresnan M. J., Shapiro F., Sotrel A., Abroms I. F. Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy presenting in infancy with facial diplegia and sensorineural deafness. Ann Neurol. 1985 May;17(5):513–516. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt P. W., Compston D. A., Harper P. S. Estimation of age dependent penetrance in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy by minimising ascertainment bias. J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;26(12):755–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.12.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt P. W., Cumming W. J., Kingston H., Read A. P., Mountford R. C., Mahon M., Harris R. DNA probes in differential diagnosis of Becker muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet. 1989 Jan 7;1(8628):46–47. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E., CHUNG C. S. Formal genetics of muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Dec;11:360–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J., Garg B., Silbert S. Death in childhood due to facio-scapulo-humeral dystrophy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1983 Jul;68(1):61–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb04817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prot J. Genetic-epidemiological studies in progressive muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1971 Mar;8(1):90–95. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Roper H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Shaw J., Warner K. L., Hung W. Y., Phillips K. L., Lunt P., Cumming W. J., Roses A. D. Linkage analysis in the spinal muscular atrophy type of facioscapulohumeral disease. J Med Genet. 1989 Aug;26(8):487–489. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.8.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. G. Coats' disease and muscular dystrophy. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar-Apr;72(2):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trosch R. M., Sze G., Brass L. M., Waxman S. G. Emotional facial paresis with striatocapsular infarction. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Sep;98(2-3):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90260-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Lunt P. W., Sarfarazi M., Broadhead W., Daniels J., Owen M., Harper P. S. A closely linked DNA marker for facioscapulohumeral disease on chromosome 4q. J Med Genet. 1991 Oct;28(10):665–671. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.10.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Lunt P. W., Sarfarazi M., Broadhead W., Daniels J., Owen M., Harper P. S. DNA marker applicable to presymptomatic and prenatal diagnosis of facioscapulohumeral disease. Lancet. 1990 Nov 24;336(8726):1320–1321. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93005-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit T., Lamprecht A., Lenard H. G., Goebel H. H. Hearing loss in facioscapulohumeral dystrophy. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;145(4):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00439401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Frants R. R., Brouwer O. F., Moerer P., Weber J. L., Padberg G. W. Location of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy gene on chromosome 4. Lancet. 1990 Sep 15;336(8716):651–653. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92148-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


