Abstract
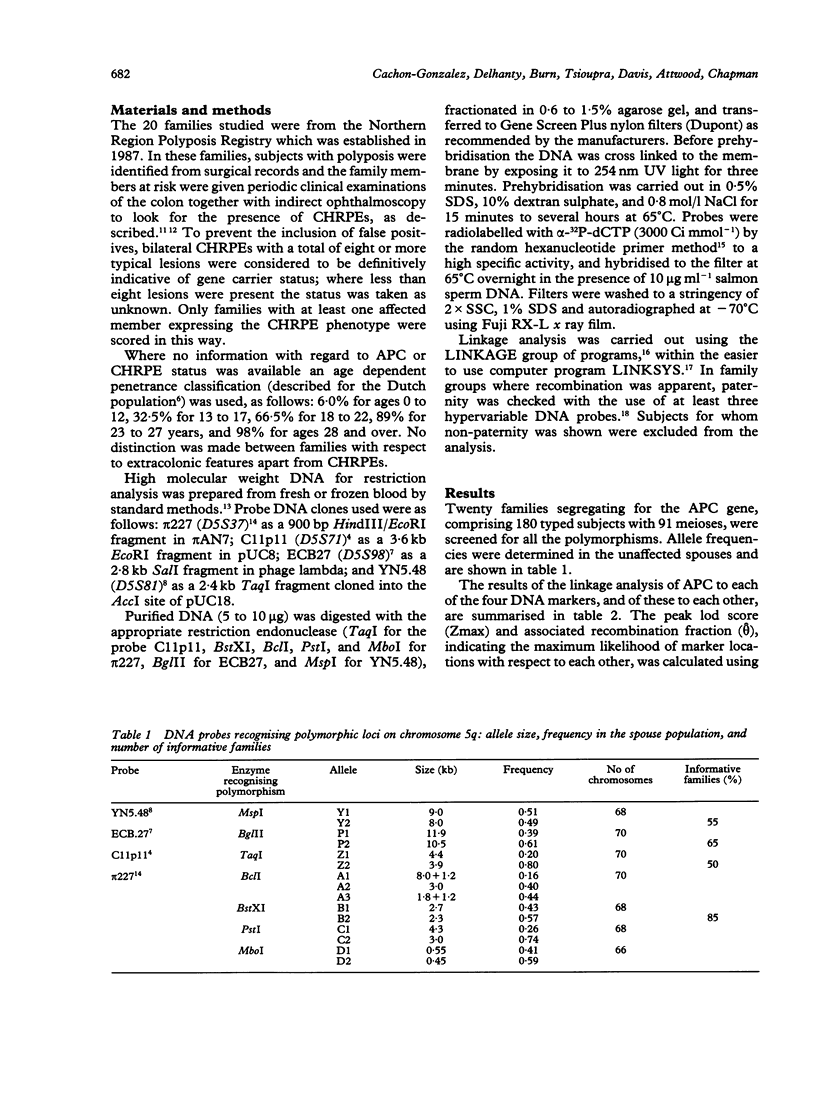
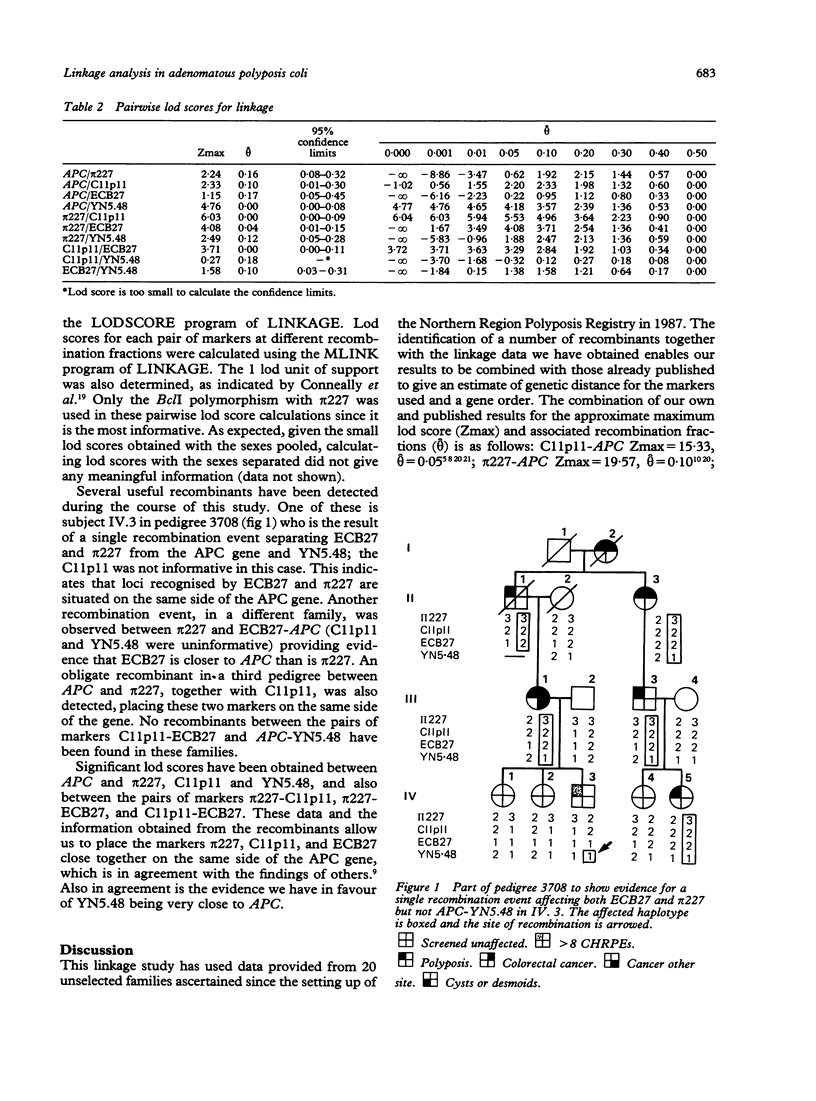
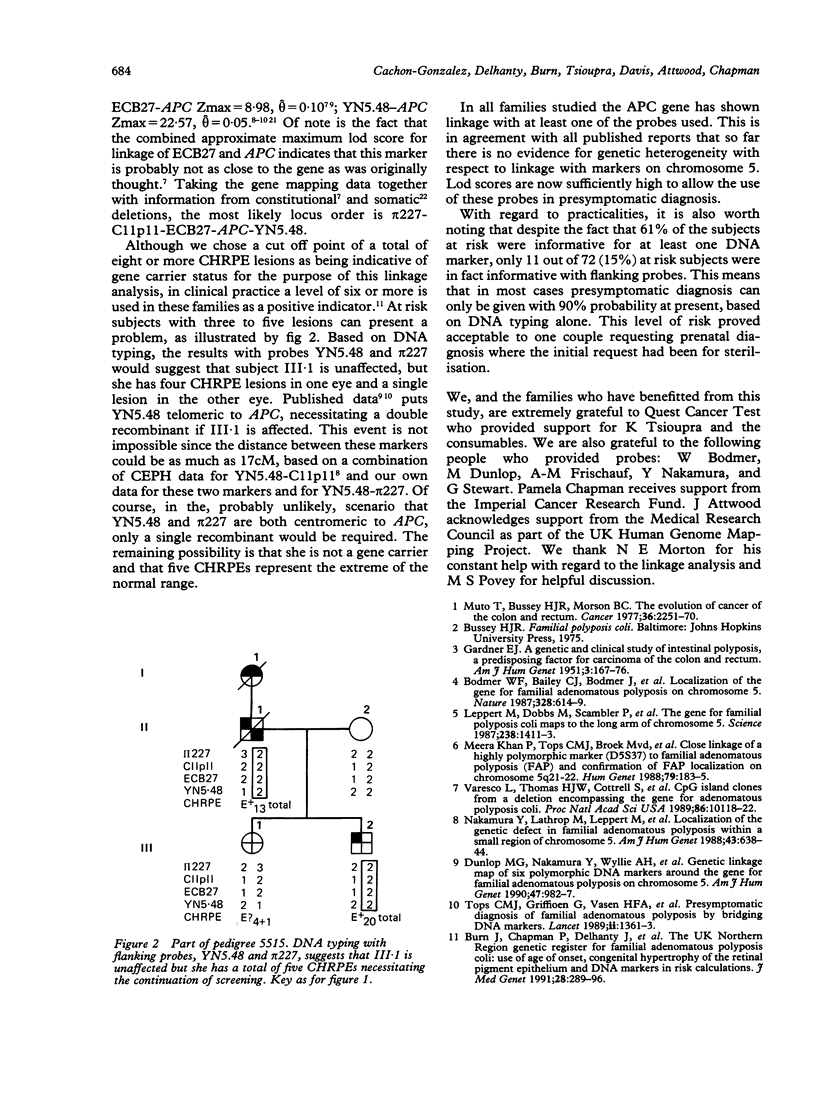
Linkage analysis was carried out on 20 unselected UK families segregating for adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) using four closely linked DNA probes. Significant lod scores were obtained between APC and three markers: pi 227 (D5S37) theta = 0.16; C11p11 (D5S71) theta = 0.10; and YN5.48 (D5S81) theta = 0.00. The fourth, ECB27 (D5S98), gave low lod scores. The APC gene showed linkage with at least one of the probes used in all families, which is in agreement with previous publications. Combined lod scores are now sufficiently high to allow the use of these probes in presymptomatic diagnosis. Despite the fact that 61% of persons at risk were informative for at least one DNA marker, only 15% were informative with flanking probes. One prenatal diagnosis was performed where the initial request had been for sterilisation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson P. H. Ozone and Acid rain. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):141–141. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4824.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Dunlop M. G., Nakamura Y., Morris R. G., Purdie C. A., Steel C. M., Evans H. J., Bird C. C., Wyllie A. H. High frequency of APC loss in sporadic colorectal carcinoma due to breaks clustered in 5q21-22. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood J., Bryant S. A computer program to make linkage analysis with LIPED and LINKAGE easier to perform and less prone to input errors. Ann Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;52(Pt 3):259–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1988.tb01103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J., Chapman P., Delhanty J., Wood C., Lalloo F., Cachon-Gonzalez M. B., Tsioupra K., Church W., Rhodes M., Gunn A. The UK Northern region genetic register for familial adenomatous polyposis coli: use of age of onset, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, and DNA markers in risk calculations. J Med Genet. 1991 May;28(5):289–296. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. D., Church W., Burn J., Gunn A. Congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium: a sign of familial adenomatous polyposis. BMJ. 1989 Feb 11;298(6670):353–354. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6670.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. G., Steel C. M., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C., Evans H. J. Linkage analysis in familial adenomatous polyposis: order of C11P11 (D5S71) and pi 227 (D5S37) loci at the apc gene. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):350–353. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. G., Wyllie A. H., Nakamura Y., Steel C. M., Evans H. J., White R. L., Bird C. C. Genetic linkage map of six polymorphic DNA markers around the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):982–987. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J. A genetic and clinical study of intestinal polyposis, a predisposing factor for carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Am J Hum Genet. 1951 Jun;3(2):167–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Burt R., Hughes J. P., Samowitz W., Nakamura Y., Woodward S., Gardner E., Lalouel J. M., White R. Genetic analysis of an inherited predisposition to colon cancer in a family with a variable number of adenomatous polyps. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):904–908. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Tops C. M., vd Broek M., Breukel C., Wijnen J. T., Oldenburg M., vd Bos J., van Leeuwen-Cornelisse I. S., Vasen H. F., Griffioen G. Close linkage of a highly polymorphic marker (D5S37) to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and confirmation of FAP localization on chromosome 5q21-q22. Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;79(2):183–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00280563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., Leppert M., Dobbs M., Wasmuth J., Wolff E., Carlson M., Fujimoto E., Krapcho K., Sears T. Localization of the genetic defect in familial adenomatous polyposis within a small region of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):638–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Bruns G. A., Wasmuth J. J., Kurnit D. M. An anonymous DNA segment (II227) maps to the long arm of human chromosome 5 and identifies a BstXI polymorphism (D5S26). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3939–3939. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tops C. M., Wijnen J. T., Griffioen G., von Leeuwen I. S., Vasen H. F., den Hartog Jager F. C., Breukel C., Nagengast F. M., van der Klift H. M., Lamers C. B. Presymptomatic diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis by bridging DNA markers. Lancet. 1989 Dec 9;2(8676):1361–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Thomas H. J., Cottrell S., Murday V., Fennell S. J., Williams S., Searle S., Sheer D., Bodmer W. F., Frischauf A. M. CpG island clones from a deletion encompassing the gene for adenomatous polyposis coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10118–10122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Patel I., Povey S., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;51(Pt 4):269–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


