Abstract
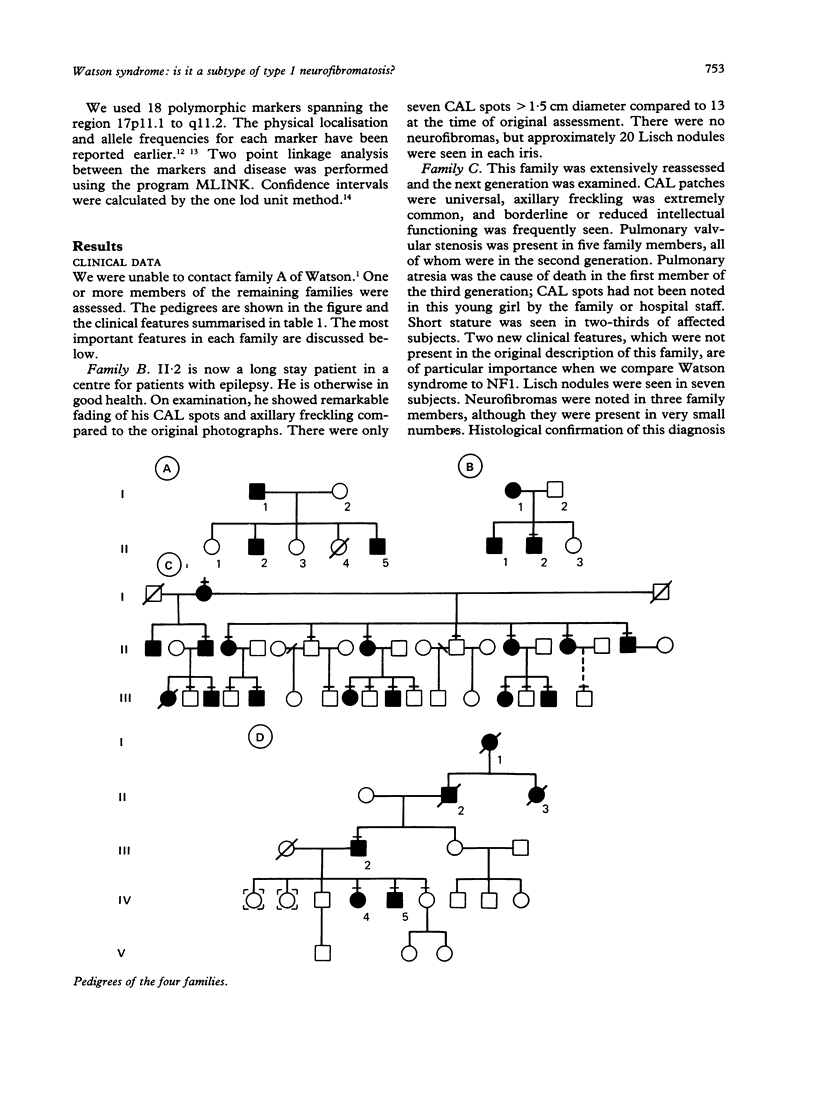
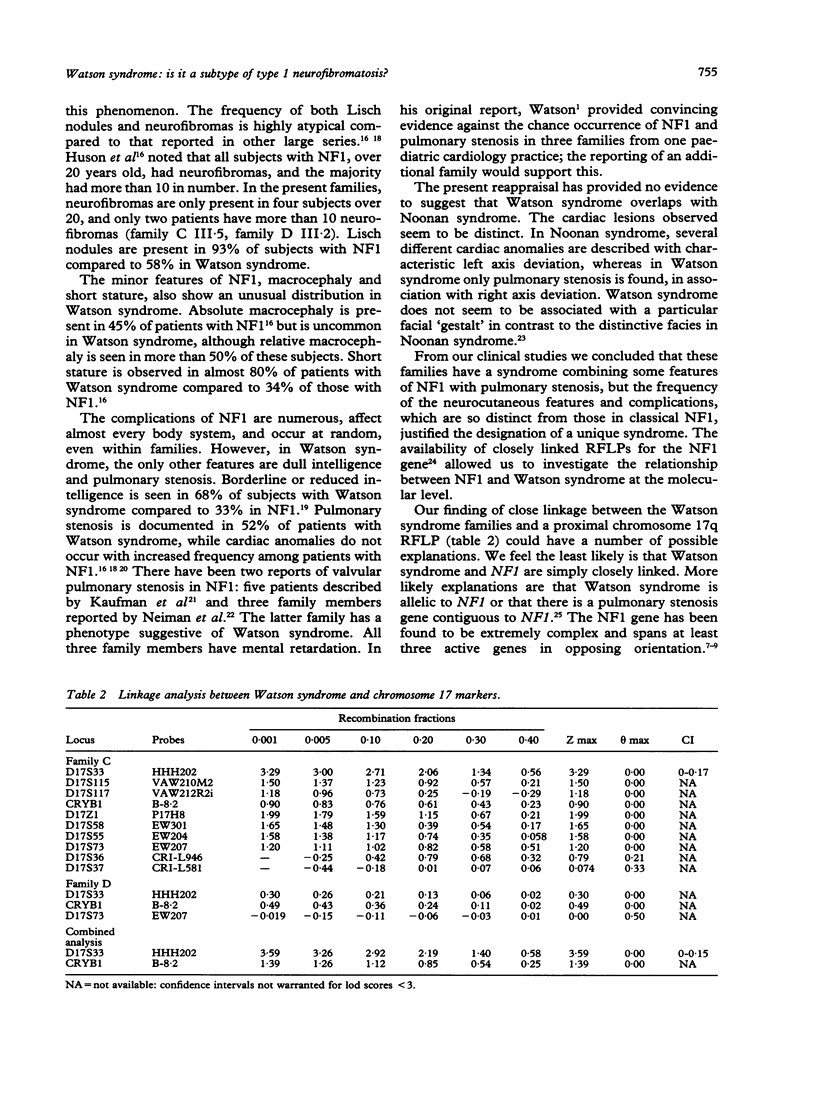
Over 20 years ago, Watson described three families with a condition characterised by pulmonary valvular stenosis, café au lait patches, and dull intelligence. Short stature is an additional feature of this autosomal dominant condition. A fourth family with Watson syndrome has since been reported. We have had the opportunity to review members of three of these four families. The clinical phenotype of Watson syndrome has been expanded to include relative macrocephaly and Lisch nodules in the majority of affected subjects, and neurofibromas in one-third of family members. Because the additional clinical findings enhance the similarity between Watson syndrome and neurofibromatosis 1, molecular linkage studies have been performed using probes flanking the NF1 gene on chromosome 17. Probe HHH202 showed the tightest linkage to Watson syndrome with a maximum lod score of 3.59 at phi = 0.0 (95% confidence limits of phi = 0.0-0.15). This suggests either that Watson syndrome and neurofibromatosis 1 are allelic, or that there is a series of contiguous genes for pulmonary stenosis, neurocutaneous anomalies, short stature, and mental retardation on 17q.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allanson J. E., Hall J. G., Hughes H. E., Preus M., Witt R. D. Noonan syndrome: the changing phenotype. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):507–514. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allanson J. E., Hall J. G., Van Allen M. I. Noonan phenotype associated with neurofibromatosis. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):457–462. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Wright E., Nguyen K., Cannon L., Fain P., Goldgar D., Bishop D. T., Carey J., Baty B., Kivlin J. Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.3107130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain P. R., Goldgar D. E., Wallace M. R., Collins F. S., Wright E., Nguyen K., Barker D. F. Refined physical and genetic mapping of the NF1 region on chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):721–728. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgar D. E., Green P., Parry D. M., Mulvihill J. J. Multipoint linkage analysis in neurofibromatosis type I: an international collaboration. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):6–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Allanson J. E. Neurofibromatosis I: predicting the relation of gene structure to gene function. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jan;38(1):135–135. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Compston D. A., Clark P., Harper P. S. A genetic study of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis in south east Wales. I. Prevalence, fitness, mutation rate, and effect of parental transmission on severity. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):704–711. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huson S. M., Harper P. S., Compston D. A. Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. A clinical and population study in south-east Wales. Brain. 1988 Dec;111(Pt 6):1355–1381. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.6.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. E., Garver K. L. Cardiac abnormalities in neurofibromatosis. Neurofibromatosis. 1988;1(3):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman H. L., Mena E., Holt J. F., Stern A. M., Perry B. L. Neurofibromatosis and congenital heart disease. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974 Sep;122(1):146–149. doi: 10.2214/ajr.122.1.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., Faryniarz A. G., Chao M. V., Huson S., Korf B. R., Parry D. M., Pericak-Vance M. A. Genetic linkage of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis to the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):589–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya M., Sarfarazi M., Huson S. M., Broadhead W., Fryer A., Harper P. S. Close flanking markers for neurofibromatosis type I (NF1). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):41–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson G. H. Pulmonary stenosis, café-au-lait spots, and dull intelligence. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Jun;42(223):303–307. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.223.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


